Introduction
Healthcare today runs on data. From electronic health records and lab systems to telemedicine apps and wearable devices, every interaction generates new information. But here’s the challenge: when that data is incomplete, duplicated, or left unsecured, the risks aren’t just financial. They can directly affect patient safety and trust.
That’s why data governance in healthcare has become a defining priority. Put simply, it’s about creating the rules, processes, and responsibilities that make sure sensitive patient data is accurate, consistent, and protected.
If you’re wondering what data governance in healthcare is, think of it as the backbone of digital health. Without it, compliance breaks down, insights lose value, and decision-making becomes guesswork.
The importance of data governance in healthcare goes far beyond regulatory checklists like HIPAA or GDPR. Done right, it enables better outcomes: clinicians can make faster, safer decisions; patients gain confidence that their privacy is respected; and organizations unlock innovation through trustworthy analytics and AI.
In this blog, we’ll explore how to design a strong healthcare data governance framework, practical steps for implementation, and real-world examples of both successes and setbacks. We’ll also look ahead at the benefits of data governance in healthcare and the trends shaping its future, from AI governance to stricter regional privacy laws.
In an industry where every piece of information could mean the difference between right and wrong treatment, healthcare data governance isn’t optional. It’s essential.
What is Data Governance in Healthcare?
At its core, data governance in healthcare is about trust. It’s the framework that defines how healthcare organizations collect, manage, secure, and use patient information. Unlike general data practices, healthcare governance carries higher stakes because the quality of data directly influences diagnoses, treatments, and patient safety.
What is data governance in healthcare? It is the structured set of policies, processes, and roles that ensure patient data is accurate, consistent, secure, and compliant with regulations. A strong healthcare data governance framework enables better decision-making, regulatory compliance, and improved patient outcomes.
The importance of data governance in healthcare is also tied to accountability. It establishes clear ownership: who is responsible for data accuracy, who ensures compliance with HIPAA or GDPR, and who approves data use for secondary purposes like research. This prevents the “no one’s responsible” problem that often plagues complex healthcare systems.
In short, healthcare data governance transforms raw information into trusted intelligence. It’s not just an IT initiative; it’s a clinical, operational, and strategic necessity.

What are Key Compliance Mandates for Healthcare Data?
If there’s one thing every healthcare organization knows, it’s that regulations aren’t optional; they’re survival. The importance of data governance in healthcare is closely tied to compliance, because patient information is among the most tightly regulated types of data in the world.
Here are the key mandates that shape modern healthcare data governance:
1. HIPAA (United States)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act is the gold standard for protecting patient health information (PHI). It defines how data can be collected, stored, shared, and accessed and violations can mean multi-million-dollar fines.
Beyond rules, HIPAA is really about trust. Patients want assurance that their most sensitive details aren’t misused.
2. GDPR (European Union)
The General Data Protection Regulation extends its reach well beyond Europe. Any healthcare provider treating EU residents needs to comply, and that includes managing consent properly and giving patients the “right to be forgotten.”
GDPR has influenced global standards for data governance and healthcare practices, pushing organizations to take transparency seriously.
3. PIPEDA (Canada)
Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act governs how personal data, including medical records, is collected, used, and disclosed. Healthcare providers must align their governance frameworks to ensure accountability and security across provinces.
4. State-Level and Emerging Regulations
Laws like the Washington My Health My Data Act (US) and similar regional frameworks are raising the bar even higher. These rules cover everything from mobile health apps to third-party data sharing, expanding the scope of data management healthcare strategies.
What’s clear across all these regulations is that compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about embedding patient rights and privacy into the heart of a healthcare data governance framework. Organizations that succeed don’t just avoid penalties; they earn patient trust, improve collaboration across care systems, and set themselves up for future innovations like AI-driven diagnostics.
Why is Data Governance in Healthcare Important?
The importance of data governance in healthcare goes far beyond meeting compliance checklists. At its heart, it’s about ensuring that the data guiding medical decisions is accurate, consistent, and trusted. In an industry where one wrong detail could change the course of treatment, governance directly impacts patient safety and care quality.
Here are some of the biggest reasons why healthcare data governance is critical today:
1. Patient Safety and Better Outcomes
If a patient’s allergy information or lab result is incorrect, duplicated, or missing, the risk of misdiagnosis or harmful treatment skyrockets. Proper governance reduces these risks by maintaining data quality across systems.
2. Building Patient Trust
Patients want assurance that their information won’t be misused or exposed. Strong governance, backed by encryption, consent management, and clear accountability, builds confidence and strengthens provider–patient relationships.
3. Regulatory Compliance Made Practical
With HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA, and state laws setting strict requirements, governance provides a structured way to stay compliant. Instead of scrambling at audit time, organizations that follow a healthcare data governance framework are already prepared.
4. Operational Efficiency
Data silos, duplicates, and mismatched records cost time and money. Governance reduces these inefficiencies, helping teams work with consistent, accurate data. For healthcare providers, that means more focus on patients, not paperwork.
5. Unlocking Innovation
Reliable, governed data is the foundation for advanced analytics and AI in healthcare. From predictive diagnostics to population health studies, the benefits of data governance in healthcare extend into research and innovation that shape the future of medicine.
In short, the importance of data governance in healthcare lies in its ability to transform data from a liability into an asset. When done right, it protects patients, empowers providers, and prepares organizations for the next wave of digital transformation.
Best Practices for Data Governance in Healthcare

Understanding the importance of data governance in healthcare is one thing, but turning that understanding into action requires a clear strategy. Healthcare organizations are complex, juggling EHRs, billing systems, telehealth platforms, and even wearable device integrations. Without a roadmap, governance can feel overwhelming. That’s why best practices are so critical: they translate broad principles into practical, everyday actions.
Here are some proven best practices for data governance in healthcare:
1. Define Clear Ownership and Accountability
Assign data stewards or custodians who are responsible for maintaining accuracy, security, and compliance. This avoids the all-too-common “not my responsibility” problem and ensures accountability at every stage.
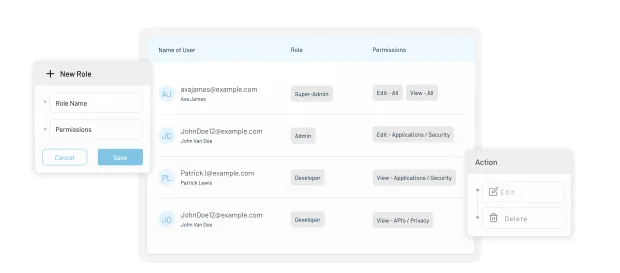
2. Establish Role-Based and Attribute-Based Access Controls (RBAC & ABAC)
Not every staff member in a healthcare system needs the same level of access to patient data. A receptionist may need to verify insurance details, while a physician requires full access to clinical records. That’s where Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) come into play.
-
RBAC assigns permissions based on a person’s role (doctor, nurse, admin, billing).
-
ABAC adds more granularity by using attributes like department, location, or patient consent preferences to determine access.
Together, these models reduce the risk of unauthorized access, strengthen compliance with HIPAA/GDPR, and ensure sensitive information is only shared with the right people at the right time.
How LoginRadius Helps:
LoginRadius makes implementing RBAC and ABAC straightforward within a healthcare data governance framework:
-
Centralized Identity Management: Define user roles (clinician, nurse, staff, vendor) and enforce permissions consistently across all systems, including EHRs, patient portals, and mobile apps.
-
Granular Access Policies: With LoginRadius’ fine-grained authorization APIs, you can build ABAC rules that factor in attributes like department, job function, location, device, or even patient consent status.
-
Adaptive MFA Integration: For higher-risk actions (e.g., accessing lab results outside normal hours), LoginRadius can automatically trigger an additional authentication mechanism through its cutting-edge adaptive MFA.
-
Audit & Compliance Ready: Every access attempt is logged, making HIPAA and GDPR audits easier by showing who accessed what, when, and under what conditions.
For healthcare staff, this means less friction — they get the right access when they need it. For patients, it means confidence that their personal health information isn’t floating around unchecked. And for administrators, it means easier compliance and fewer sleepless nights worrying about breaches.
3. Ensure Data Quality and Standardization
Duplicate records, inconsistent formats, and incomplete entries undermine trust in data. Implement rules for validation, regular audits, and interoperability standards (HL7, FHIR) to improve consistency.
4. Embed Consent Management into Workflows
Patients increasingly expect transparency about how their data is used. Integrating consent collection, preference tracking, and audit trails directly into systems ensures both compliance and trust.
5. Secure Data Across Its Lifecycle
From collection to archiving, patient information should always be encrypted, monitored, and backed up. Strong security controls reduce the risk of breaches and align with HIPAA, GDPR, and other mandates.
6. Train Staff Continuously
Governance isn’t just an IT function. Clinicians, admin staff, and even external vendors need awareness of governance rules. Regular training helps reduce accidental misuses and builds a culture of accountability.
7. Monitor, Measure, and Improve
Governance is not “set and forget.” Establish KPIs such as data accuracy rates, time to resolve discrepancies, or audit pass rates. Use dashboards to monitor progress and refine policies as the organization grows.
By following these best practices, healthcare organizations can move from reactive fixes to proactive, sustainable strategies. More importantly, they can unlock the benefits of data governance in healthcare, safer patients, happier staff, and a stronger reputation for trust.
Implementing Data Governance in Healthcare Organizations
Knowing the theory is one thing, but making data governance in healthcare work inside a real hospital or clinic is where the challenge begins. Healthcare systems are complex: multiple EHRs, third-party labs, insurance partners, and growing volumes of telehealth and IoMT data. Without a structured approach, governance efforts can stall before they even begin.
Here’s a practical roadmap to help healthcare organizations put data management healthcare principles into action:
1. Assess the Current State
-
Start by mapping your data ecosystem: EHRs, billing, lab systems, patient portals, and mobile apps.
-
Identify silos, duplication, and areas where compliance or consent tracking may already be weak.
-
This baseline assessment sets the stage for improvement.
2. Define Governance Goals and Policies
-
Are you aiming for stronger HIPAA compliance? Better interoperability? AI-readiness?
-
Document policies for data collection, storage, sharing, and disposal.
-
Build accountability by assigning ownership at every step of the healthcare data governance framework.
3. Appoint Data Stewards and Champions
-
Data governance isn’t just an IT problem. Create cross-functional teams with clinicians, compliance officers, and IT leaders.
-
Appoint “data stewards” who own quality and “data champions” who advocate governance across departments.
4. Embed Consent and Privacy Controls
-
Bake patient consent management into workflows.
-
Use dashboards to track how data is being used, stored, and shared. This adds transparency and builds trust.
5. Pilot Governance Programs
-
Choose one department or system to test your framework. For example, roll out RBAC/ABAC access controls in the oncology department.
-
Monitor progress, refine processes, and gather staff feedback before scaling across the organization.
6. Train Staff at All Levels
-
Nurses, front desk staff, and even temporary contractors interact with patient data daily.
-
Short, ongoing training sessions ensure that everyone understands policies, from password hygiene to reporting a suspected breach.
7. Measure and Continuously Improve
-
Track KPIs such as data accuracy rates, audit readiness, and breach incidents.
-
Use dashboards to monitor improvements and identify new risks. Governance is not a “project” — it’s a continuous cycle.
Implementing healthcare data governance may feel overwhelming at first, but the key is to start small, gain buy-in, and show quick wins. Over time, the program will expand naturally, creating a culture where everyone from clinicians to IT admins sees governance not as red tape, but as a way to protect patients and improve care.
Overcoming Common Healthcare Data Governance Challenges
Even with a strong healthcare data governance framework in place, organizations often run into practical hurdles. These aren’t minor speed bumps — they’re recurring roadblocks that can derail even the most well-intentioned initiatives. Understanding these data governance challenges in healthcare upfront can help leaders prepare strategies to address them.
Here are some of the most common obstacles, along with practical solutions:
1. Data Silos Across Systems
The challenge: Patient data lives in multiple places — EHRs, lab systems, insurance portals, and even mobile health apps. These silos prevent providers from seeing the full patient picture.
The fix: Invest in interoperability standards like HL7/FHIR and establish governance processes that unify data across systems.
Example of data governance in healthcare: A hospital merging lab and EHR records under a governance program reduced duplicated test orders, saving costs and improving patient safety.
2. Legacy Infrastructure
The challenge: Many healthcare organizations still run on outdated systems that weren’t built with modern compliance, interoperability, or security in mind.
The fix: Gradual modernization, starting with middleware or cloud-based governance tools, ensures a smoother transition without disrupting critical workflows.
3. Privacy and Consent Management
The challenge: With rising regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and state-level acts (like Washington’s My Health My Data law), healthcare providers struggle to keep consent records consistent across platforms.
The fix: Embed consent management directly into workflows and use dashboards to track patient choices in real time. This reduces compliance risk and builds patient trust.
4. Cultural Resistance and Lack of Training
The challenge: Clinicians and staff may view governance as “extra red tape” rather than something that helps them.
The fix: Provide short, role-based training sessions and show how governance reduces their workload (e.g., fewer duplicate forms, fewer audit headaches).
5. Vendor and Third-Party Risks
The challenge: Healthcare providers often rely on external vendors (billing, analytics, cloud hosting), but each vendor introduces a new risk layer.
The fix: Extend governance policies to vendors, requiring business associate agreements (BAAs) and regular compliance checks.
6. Data Quality and Accuracy Issues
The challenge: Incomplete or incorrect records reduce trust in the system and can directly affect patient care.
The fix: Assign data stewards who run regular audits, enforce validation rules, and oversee corrections.
Example of data governance in healthcare: A clinic reduced readmission rates by ensuring allergy information was standardized and governed across all systems.
7. Keeping Up with Evolving Regulations
The challenge: Laws evolve constantly — what was compliant yesterday may not be tomorrow.
The fix: Build flexibility into governance frameworks. Use monitoring tools and assign compliance officers to track changes and adjust policies quickly.
Challenges are inevitable, but they’re not insurmountable. When approached with a mix of technology, training, and accountability, data governance in healthcare shifts from being a burden to a trusted safety net, one that protects patients, supports clinicians, and prepares organizations for what’s next.
Conclusion
In today’s digital-first healthcare environment, data is more than just numbers and records it is the foundation of patient trust, clinical decision-making, and medical innovation. Yet without proper governance, even the most advanced systems can turn fragile. Errors multiply, privacy is compromised, and compliance risks grow. That’s why the importance of data governance in healthcare can’t be overstated: it is the glue that holds together compliance, security, and patient care.
A well-structured healthcare data governance framework ensures that data is accurate, secure, and available when needed most. From establishing clear roles and policies to adopting modern tools like consent management, adaptive access controls, and data quality checks, governance empowers organizations to do more than simply “manage” data; it helps them transform it into actionable intelligence.
The benefits of data governance in healthcare ripple across every level of the system:
-
Patients feel reassured that their information is protected and respected.
-
Clinicians work with reliable, complete records that lead to safer, faster decisions.
-
Administrators meet compliance requirements without last-minute fire drills.
-
Researchers and innovators gain access to trustworthy datasets for groundbreaking insights.
Yes, the journey comes with obstacles. From data silos to cultural resistance and evolving laws, the data governance challenges in healthcare are real. But as we’ve seen, each challenge has a practical solution, and many organizations are already proving what’s possible when governance becomes a strategic priority.
Looking ahead, the future of data governance in healthcare is not just about rules and restrictions. It’s about enabling AI, unlocking new research opportunities, and putting patients at the center of their health journeys. Whether it’s blockchain-powered audit trails, cloud-native platforms, or privacy-preserving analytics, governance is evolving into a driver of progress rather than a roadblock.
In short, strong governance transforms healthcare data from a liability into one of the industry’s greatest assets. It builds resilience, fosters innovation, and most importantly, saves lives. For healthcare leaders and practitioners alike, the question isn’t whether governance is necessary. It’s how quickly you can make it a reality in your own organization.
FAQs
1. Why is data governance important in healthcare?
A: Data governance in healthcare is important because it ensures that patient information is accurate, consistent, and secure. It helps organizations stay compliant with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR while building patient trust by protecting sensitive health data.
2. How does data governance improve patient care?
A: Strong healthcare data governance gives clinicians access to complete and reliable patient records. This reduces errors, prevents duplicate tests, and supports faster, more accurate diagnoses, ultimately improving the quality and safety of patient care.
3. What are the key components of healthcare data governance?
A: A healthcare data governance framework typically includes principles, policies, defined roles (like data stewards), secure processes, lifecycle management, and performance metrics. Together, these elements create accountability and ensure data is used responsibly across the organization.
4. How does data governance reduce security risks in healthcare?
A: By enforcing access controls, consent management, and continuous monitoring, data governance in healthcare minimizes the risk of breaches and unauthorized use of patient information. It adds structured safeguards that protect both organizations and patients from data misuse.




