CIAM Strategy and Business Value
Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) is no longer just an authentication layer. It is a strategic system that directly impacts customer experience, security posture, compliance readiness, and digital growth.
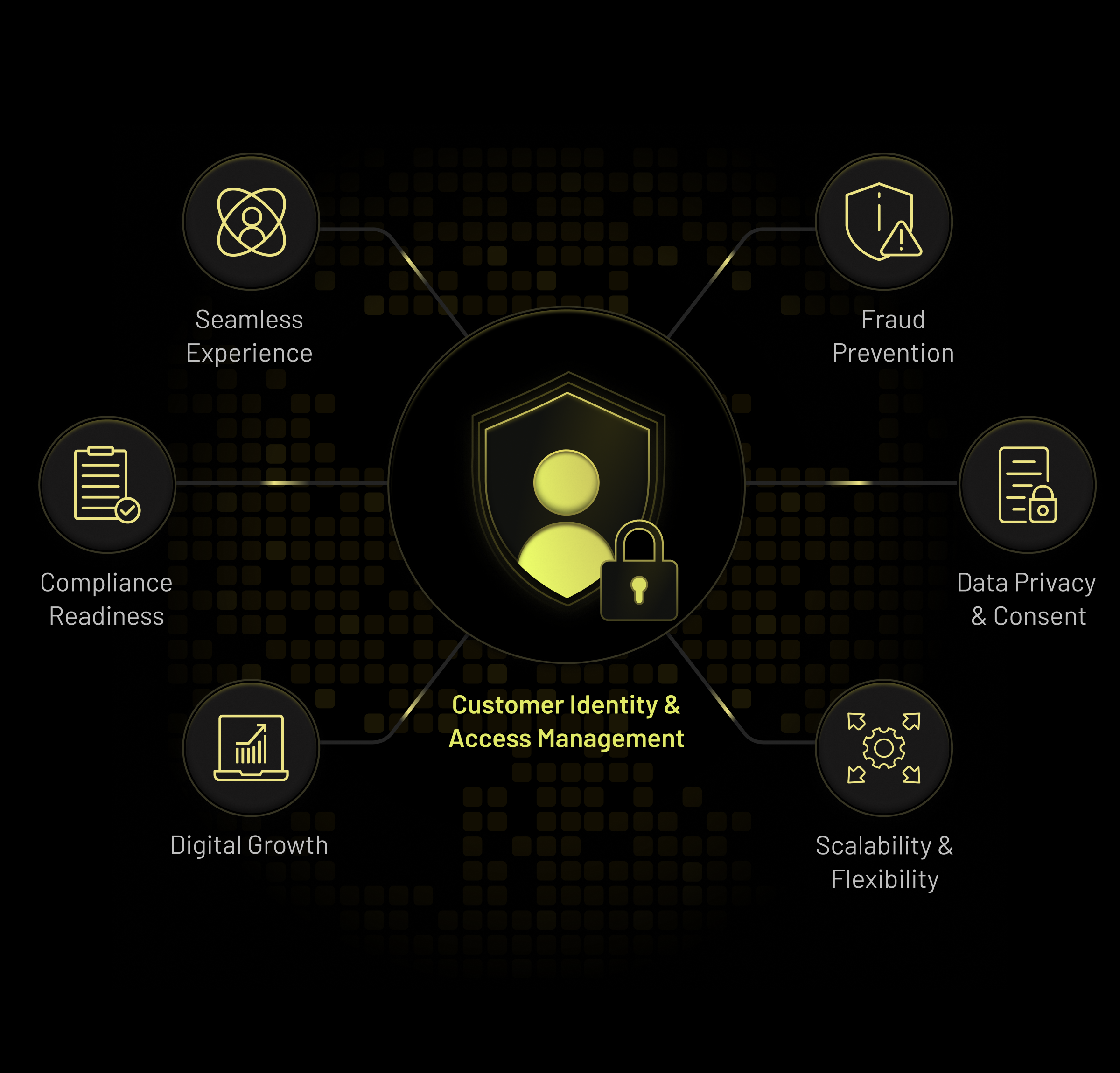
What Is a CIAM Strategy?
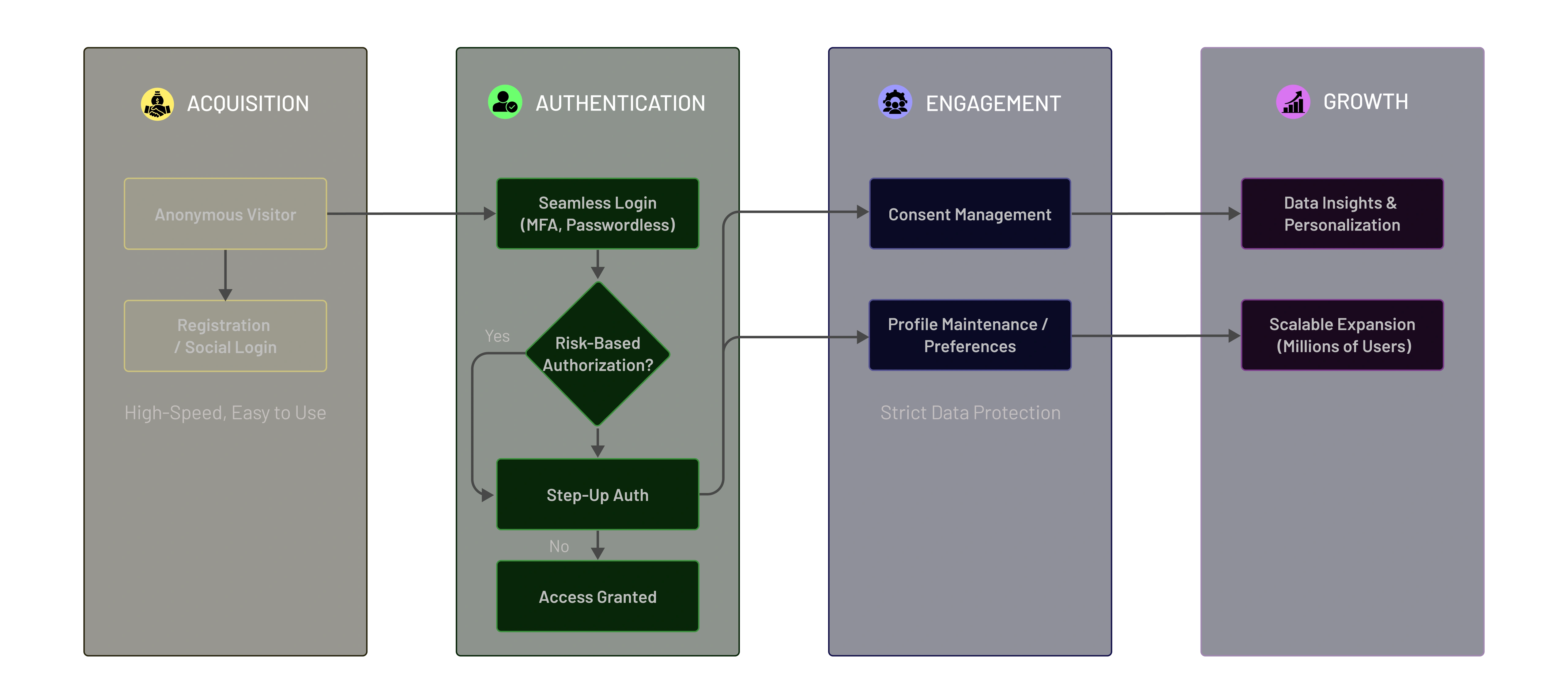
A CIAM strategy defines how an organization manages customer identities across their entire digital ecosystem. It covers how users register, authenticate, authorize access, and maintain their profiles - while ensuring security, privacy, and scalability. A strong CIAM strategy helps organizations manage millions of customer identities securely while enabling frictionless access across applications, channels, and devices.
Core Pillars of a Strong CIAM Strategy
CIAM Pillar
What It Covers
Why It Matters
What It Covers
Registration, login, single sign-on, social login, and passwordless access.
Why It Matters
Reduces drop-offs during onboarding, improves conversion rates and customer retention.
Registration, login, single sign-on, social login, and passwordless access.
Reduces drop-offs during onboarding, improves conversion rates and customer retention.
What It Covers
Multi-factor authentication, adaptive authentication, token-based access, and protection against account takeover and fraud.
Why It Matters
Protects customer trust, reduces breach-related costs, and strengthens overall security posture.
Multi-factor authentication, adaptive authentication, token-based access, and protection against account takeover and fraud.
Protects customer trust, reduces breach-related costs, and strengthens overall security posture.
What It Covers
Ability to handle large, unpredictable user volumes with low latency and high availability.
Why It Matters
Ensures consistent user experiences during traffic spikes, launches, and global expansion.
Ability to handle large, unpredictable user volumes with low latency and high availability.
Ensures consistent user experiences during traffic spikes, launches, and global expansion.
What It Covers
Customer profile management, consent capture, preference tracking, and privacy controls.
Why It Matters
Supports regulatory compliance and builds long-term trust through responsible data handling.
Customer profile management, consent capture, preference tracking, and privacy controls.
Supports regulatory compliance and builds long-term trust through responsible data handling.
What It Covers
APIs, SDKs, and standards-based integrations across applications, platforms, and ecosystems.
Why It Matters
Enables faster time to market and reduces engineering overhead as digital systems evolve.
APIs, SDKs, and standards-based integrations across applications, platforms, and ecosystems.
Enables faster time to market and reduces engineering overhead as digital systems evolve.
CIAM Strategic Frameworks
As digital products mature, identity choices evolve—from building internally, to migrating platforms, to optimizing identity for measurable business impact. The following approaches represent the most common paths teams take when shaping their CIAM strategy.
Build and Maintain In-House : Teams design, host, and operate identity systems internally, retaining full control but taking on long-term security, scalability, and maintenance responsibility.

Migrate to a Dedicated CIAM Platform : Organizations move from custom or legacy systems to a purpose-built CIAM solution to reduce operational burden and accelerate secure identity delivery.

Optimize for Business Value and Scale : Teams optimize identity choices to align with business objectives: CIAM is treated as a strategic platform, with decisions driven by measurable outcomes like conversion, risk reduction, compliance readiness, and development velocity.