Introduction Summary
-
Passwords fail every day—phishing, credential stuffing, and social engineering make them unreliable for modern security.
-
YubiKey solves this with hardware-backed, cryptographic authentication that attackers cannot phish, intercept, or replicate.
-
In this guide, you’ll learn:
-
What a YubiKey is and how a YubiKey works
-
What YubiKeys are used for across personal and enterprise environments
-
How to use a YubiKey and complete a full YubiKey setup
-
How YubiKey authentication supports MFA, passwordless login, Zero Trust, and CIAM strategies
-
The role of YubiKey biometric models in high-assurance identity flows
-
Whether you’re securing consumer accounts, building WebAuthn flows, or modernizing enterprise access, this guide shows how YubiKeys deliver strong, simple, and unphishable authentication at scale.
A YubiKey is a hardware security key that enables strong, phishing-resistant authentication using standards like FIDO2, WebAuthn, and OTP. Unlike passwords or SMS codes, a YubiKey stores private cryptographic keys on a secure chip and requires physical touch or presence—making it one of the safest and simplest authentication methods available.
YubiKey, a small, durable hardware token, replaces vulnerable passwords with strong, cryptographic authentication. When people ask “What is a YubiKey?”, the simplest explanation is that it’s a secure digital ID you physically carry with you—a key that proves who you are online.
Unlike passwords, which can be phished, guessed, reused, or stolen, a YubiKey relies on on-device cryptographic secrets that attackers can’t remotely access. This is why security teams, developers, governments, banks, and enterprises prefer hardware-backed identity verification.
They are hardware devices manufactured by Yubico that support multiple authentication standards, including FIDO2, WebAuthn, U2F, OTP, PIV smart card, and OpenPGP. This versatility means a YubiKey can secure everything from consumer Google accounts to enterprise VPNs, cloud infrastructure, SSH sessions, and internal dashboards. Because YubiKeys eliminate reliance on passwords, they dramatically reduce risks from phishing, MFA fatigue attacks, and credential stuffing.
YubiKeys harden login flows, power passwordless authentication, enforce high-assurance MFA, and protect privileged access. They also offer portability, no battery requirements, and support across macOS, Windows, Linux, Android, and iOS.
In short, a YubiKey is not just an authentication tool—it’s a foundation for zero-trust identity, modern CIAM architectures, and frictionless user experiences.
How Does a YubiKey Work?
A YubiKey works by storing private cryptographic keys inside a secure chip and using them to sign a login challenge from the website or app. Because the private key never leaves the device, only the physical YubiKey can complete authentication—making it phishing-resistant, uncloneable, and far stronger than passwords or SMS codes.
Every YubiKey contains a secure element, a tamper-resistant chip where private keys are generated and stored. These private keys never leave the YubiKey, which is the primary reason why YubiKey authentication is considered unphishable, interception-proof, and far more resilient than passwords or SMS-based MFA.
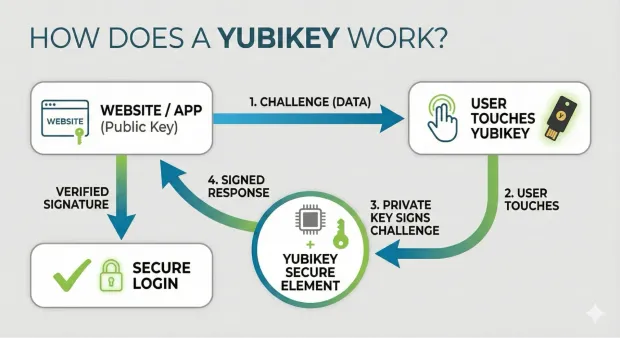
When you initiate a login, the service you’re accessing issues a cryptographic challenge—a piece of data that must be signed with the private key stored in your YubiKey. When you insert or tap the key and touch its sensor, the YubiKey signs the challenge and returns the response. Because the corresponding public key is stored with the service, it can verify the signature and confirm that the authentication came from the real YubiKey, not a fake or remote attacker.
This challenge–response mechanism powers several authentication standards.
-
FIDO2 and WebAuthn enable true passwordless login - just insert or tap your YubiKey and confirm with a touch.
-
U2F provides strong second-factor protection, stopping phishing even if passwords are compromised.
-
For older or specialized systems, the YubiKey can generate dynamic OTP codes, act as a PIV smart card, or store OpenPGP certificates for signing, encryption, or SSH authentication.
Instead of typing OTPs, checking SMS messages, or relying on mobile apps, you simply connect your YubiKey via USB or tap it with NFC and authenticate with a touch. This pairs something you have (the physical key) with cryptographic proof—a combination that dramatically boosts login assurance.
In short, YubiKey authentication works by binding identity verification to a physical device and cryptographic operations that cannot be duplicated or intercepted. This makes every login fast, seamless, and extremely secure.
What Is a YubiKey Used For?
A YubiKey protects online accounts from unauthorized access and enables strong MFA, phishing-resistant login, and passwordless authentication. YubiKeys are used because they provide a security guarantee that SMS OTPs, authenticator apps, and passwords cannot.
For personal use, YubiKeys secure accounts like Google, Microsoft, Facebook, GitHub, Reddit, Dropbox, X (Twitter), and password managers such as 1Password and Bitwarden. They also protect financial accounts, cryptocurrency wallets, email clients, and mobile devices. Anyone who has ever been phished, password-hacked, or SIM-swapped benefits massively from hardware-backed security.
In the enterprise world, YubiKey authentication plays a critical role in Zero Trust architectures. Organizations use YubiKeys for SSO portals, internal dashboards, DevOps pipelines, SSH authentication, VPN access, code signing, PIV smart card login, and compliance-driven controls for ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI, or SOC 2. Because YubiKeys reduce human error and eliminate weak MFA mechanisms, they lower breach risk and support long-term compliance.
Developers use YubiKeys for Git signing, package publishing, SSH key storage, and securing cloud infrastructure such as AWS IAM, Azure AD, and GCP. This ensures that only verified developers can push code or access sensitive resources.
To summarize, YubiKeys are used for ensuring attackers cannot log in, even if passwords are compromised.
Types of YubiKeys
When exploring what YubiKeys are, it helps to look at the available models. Each YubiKey model serves a slightly different purpose, and knowing the differences helps you choose the right fit based on device compatibility, security requirements, and authentication use cases.
1. YubiKey 5 Series
This is the most complete and versatile lineup. The 5 Series supports FIDO2, WebAuthn, U2F, OTP, PIV smart card, and OpenPGP, making it ideal for enterprise and developer environments. Variants include USB-A, USB-C, USB-C with NFC, and USB-A with NFC. These keys handle passwordless authentication, SSH login, encrypted email, code signing, and more.
2. Security Key Series
The Security Key line is designed for consumers or small teams needing strong two-factor authentication at a lower price point. These keys support FIDO2, WebAuthn, U2F, and NFC on some models. If your primary goal is phishing-resistant login for personal accounts, these keys offer exceptional value.
3. YubiKey Bio (YubiKey Biometric)
The YubiKey Biometric series adds a fingerprint sensor for local biometric verification. This means that even if someone steals your key, they can’t use it without your fingerprint. These keys still support FIDO2 and WebAuthn, making them highly suitable for organizations needing both strong possession and biometric factors in one device.
4. Niche and Legacy Models
Older YubiKeys support legacy OTP or specific enterprise smart card configurations. Though still powerful, the industry is steadily shifting toward FIDO2/WebAuthn.
Whether you need flexible enterprise-grade security or simpler passwordless login, the different YubiKey models ensure compatibility with virtually any device and environment.
How to Use a YubiKey
If you've wondered how to use a YubiKey, the process is remarkably simple—regardless of your technical skill level. Once the key is registered with an account, authentication becomes a seamless flow requiring only a physical touch or tap. This simplicity is one of the biggest reasons why YubiKey authentication has widespread adoption across both personal and enterprise scenarios.

The basic usage pattern for a YubiKey is always the same:
-
Go to the login page of the service you want to access.
-
Enter your username or email.
-
When prompted, insert your YubiKey into a USB port or tap it via NFC on your smartphone.
-
Touch the sensor to confirm presence.
That’s it—no OTP codes, no scanning an app, no waiting for SMS messages. This makes YubiKeys especially valuable in environments where speed and reliability matter.
They simply replace or supplement passwords with hardware cryptography. If your goal is simplicity, a YubiKey removes nearly all friction from login flows.
For developers and technical teams, using a YubiKey extends beyond basic sign-in. You can sign Git commits, authenticate SSH sessions, unlock password managers, and verify PGP signatures—using the same physical key. In this sense, using a YubiKey depends on whether you’re securing consumer apps or high-stakes infrastructure.
Because YubiKeys work offline and do not rely on Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, they remain functional even in secure or low-connectivity environments.
YubiKey Setup: How to Set Up a YubiKey
One of the most common questions is how to set up a YubiKey. The setup process varies slightly across platforms, but it almost always follows the same logical flow. Proper YubiKey setup is essential for smooth adoption, whether you're securing personal accounts or rolling out hardware-backed MFA at an enterprise level.
Step 1: Register the YubiKey
Go to your account’s security settings and choose Add Security Key. Services like Google, Microsoft, GitHub, AWS, Okta, and Dropbox have built-in support.
Step 2: Insert or tap the YubiKey
Depending on your model, insert it via USB-A/USB-C or tap via NFC on your phone.
Step 3: Touch the sensor
This proves human intent and prevents malware from triggering authentication.
Step 4: Create fallback methods
Set up a backup YubiKey, passkeys, or recovery codes. This ensures you never get locked out.
Step 5: Test authentication
Log out and log back in to confirm whether your YubiKey authentication works as expected.
Additional Setup Tools
Yubico also offers configuration apps for advanced features:
-
YubiKey Manager for personalization
-
Yubico Authenticator to store TOTP secrets securely on the key
-
CLI tools for developers
Because the YubiKey supports so many standards, knowing how to set up a YubiKey for different platforms can dramatically expand its utility—from passwordless login to enterprise smart card flows.
In every scenario, setup is quick, repeatable, and user-friendly.
YubiKey Biometric
The YubiKey Biometric series, also known as YubiKey Bio, introduces fingerprint-based verification to the YubiKey ecosystem. It’s a hardware key that combines possession (the key itself) with inherent traits (your fingerprint). This adds an additional layer of security that strengthens both personal and enterprise authentication workflows.
Unlike biometric authentication built into phones or laptops—where biometrics unlock the device rather than authenticate you to a service—the YubiKey Biometric validates your fingerprint on the key itself. This means your biometric data never touches cloud servers or operating systems. The entire match happens inside the secure chip on the YubiKey.
If you're researching “how does a YubiKey work?”, the biometric version follows the same cryptographic challenge-response model as non-biometric YubiKeys but adds a fingerprint match as a prerequisite to signing the authentication request. This ensures that even if someone steals your physical key, they cannot complete a login without your fingerprint.
The YubiKey Biometric is ideal for industries such as healthcare, finance, law enforcement, and government—where both identity assurance and physical control are essential. It also fits consumer scenarios where users want the convenience of touch-based authentication without sacrificing strong cryptographic controls.
From an administrative perspective, biometric keys can streamline onboarding while supporting strict MFA, PIV-style authentication, and FIDO2 passwordless flows. They’re compact, easy to carry, and built to withstand years of daily use.
In short, YubiKey Biometric models bring together two of the strongest authentication factors—biometrics and hardware keys—in one seamless experience.
Benefits of YubiKeys
YubiKeys aren’t popular by accident—organizations and individuals use them because they deliver tangible improvements in security, usability, compliance, and operational efficiency. If you’re evaluating what a YubiKey is used for, the benefits paint a very clear picture of why hardware-backed authentication is one of the most trusted defenses available.
1. Phishing-Resistant Authentication
Unlike passwords or SMS codes, YubiKeys use domain-bound cryptographic signatures. This means you can’t be tricked into typing credentials on a fake website—the YubiKey simply refuses to authenticate the wrong domain.
2. Passwordless Login
With WebAuthn and FIDO2, a YubiKey supports full passwordless flows. Users authenticate by inserting or tapping the key and confirming with a touch, eliminating password fatigue and improving user experience.
3. Zero Batteries, Zero Network Requirements
A YubiKey doesn’t need charging, pairing, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi. It works anywhere, anytime, on any supported device. This reliability makes YubiKeys ideal for both remote and on-site workforces.
4. Enterprise-Level Security
YubiKeys support PIV smart cards, TOTP, OpenPGP, SSH authentication, and identity federation through SSO platforms. This gives security teams granular control over access policies, monitoring, and compliance requirements.
5. Cross-Platform Flexibility
Because YubiKeys support multiple authentication protocols, they can integrate with thousands of services. Whether you’re using Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, or iOS, your YubiKey works seamlessly.
6. Reduced IT Support Costs
Replacing passwords with hardware keys dramatically reduces support tickets around password resets, account lockouts, OTP delays, and MFA issues—saving organizations time and budget.
In short, the strengths of YubiKeys span security, efficiency, usability, and compliance.
Challenges and Limitations of YubiKeys
Even though YubiKeys are incredibly powerful, they’re not without limitations. Understanding these challenges helps organizations design better fallback strategies and more resilient authentication policies.
1. Physical Device Dependency
A YubiKey must be physically available to authenticate. If it’s lost, misplaced, or damaged, access interruption is possible—unless backup keys or recovery methods are in place. This makes redundancy essential during deployment.
2. User Adoption Friction
For users accustomed to passwords or app-based MFA, switching to hardware security keys may feel unfamiliar. Education, onboarding guides, and internal training can help ease the transition.
3. Limited Compatibility With Legacy Systems
Some older applications and on-prem environments don’t support FIDO2 or WebAuthn. In such cases, OTP or smart card modes may be necessary—but not all systems support them natively.
4. Biometric Model Cost
YubiKey Biometric keys offer strong protection but are priced higher due to the embedded fingerprint sensor. Organizations must balance enhanced security against budget constraints.
5. Initial Setup Effort
Even though setting up a YubiKey is straightforward, enterprise deployments require planning around device management, backup keys, user education, and integration with identity platforms.
6. Limited Support for Some Mobile Devices
While NFC and USB-C models work with most smartphones, some older devices may require adapters or alternate MFA methods.
Despite these challenges, the advantages overwhelmingly outweigh the limitations—especially when hardware-backed authentication is part of a broader Zero Trust and CIAM strategy.
Conclusion
The shift toward passwordless experiences, Zero Trust security, and modern identity management has made hardware-backed authentication essential—and the YubiKey stands at the center of that evolution. Understanding what a YubiKey is, what YubiKeys are used for, how a YubiKey works, and how to use a YubiKey empowers you to deploy unphishable, high-assurance authentication across consumers, employees, or developers.
Whether you’re setting up a YubiKey for personal accounts, using YubiKey authentication for enterprise SSO, exploring YubiKey setup for developers, or evaluating YubiKey biometric models for high-assurance workflows, the YubiKey offers a simple and secure path forward.
In a world where cyber threats grow more sophisticated each year, YubiKeys offer what passwords never could: physical control, cryptographic strength, and effortless user experience. If you want authentication that is reliable, scalable, and future-proof, a YubiKey is one of the strongest choices available today.
FAQs
1. What is a YubiKey?
A YubiKey is a hardware security key used for phishing-resistant authentication, MFA, and passwordless login using FIDO2, WebAuthn, and OTP.
2. How does a YubiKey work?
A YubiKey works by storing private keys on a secure chip and signing cryptographic challenges during login, ensuring the authentication is unphishable.
3. What is a YubiKey used for?
YubiKeys are used for securing online accounts, enterprise SSO, SSH authentication, passwordless login, and protecting against phishing and credential theft.
4. How to set up a YubiKey?
Register it in your account’s security settings, insert or tap the key, touch the sensor, and add a backup key for redundancy.
5. What is YubiKey Biometric?
YubiKey Biometric models use fingerprint verification combined with hardware-backed authentication for higher identity assurance.


