Introduction
As SaaS applications grow in complexity and scale, managing user identities and securing access across multiple organizations, roles, and environments becomes a critical business priority.
However, traditional identity and access management (IAM) solutions, often designed for internal workforce or consumer use cases, fall short when applied to the unique requirements of modern SaaS platforms.
SaaS identity and access management (IAM) involves far more than just login functionality. It demands multi-tenant support, role-based access control, federated identity integration, delegated administration, and real-time provisioning. Without these capabilities, SaaS companies face increased operational overhead, inconsistent access policies, slower customer onboarding, and elevated security risks.
Many organizations attempt to bridge these gaps through custom development or by adapting legacy IAM solutions, leading to long-term scalability challenges and rising maintenance costs.
This blog outlines:
-
What defines SaaS identity and access management, and how it differs from traditional IAM
-
The common pain points SaaS platforms encounter in managing user identities
-
A framework of best practices for addressing these challenges
-
A practical approach to implementing scalable SaaS IAM using LoginRadius
Whether you're evaluating IAM for a new SaaS product or modernizing your current identity stack, understanding the specific needs of SaaS environments is essential to securing your platform and enabling long-term growth.

What is Identity and Access Management (IAM) for SaaS?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) for SaaS refers to the frameworks, technologies, and policies used to authenticate users, authorize access, and manage identities across a multi-tenant software environment. Unlike traditional IAM, which is primarily built for internal employee use (Workforce IAM) or individual consumers (CIAM), SaaS IAM must address the complexities of external organizations, partner ecosystems, and scalable user hierarchies.
In a typical SaaS model, each customer or tenant requires isolated identity spaces, delegated administrative controls, and flexible access management based on roles, attributes, or organizational context. These requirements introduce additional layers of complexity that legacy IAM solutions aren’t equipped to handle out of the box.
Effective SaaS IAM enables:
-
Centralized user and access management across multiple organizations
-
Support for federated identity through standards like SAML and OIDC
-
Role- and attribute-based access control (RBAC/ABAC) for granular policy enforcement
-
Real-time provisioning and deprovisioning of users across tenant boundaries
-
Governance and visibility for compliance, audit, and saas identity risk management
In short, SaaS IAM is not a subset of identity management; it’s a distinct and strategic requirement that enables secure, scalable service delivery across distributed and dynamic user ecosystems.
IAM Challenges with SaaS Apps
SaaS platforms operate in inherently complex environments, where identity and access requirements extend far beyond those of internal workforce systems. As these platforms scale, the challenges associated with managing identities, enforcing access policies, and maintaining security multiply, often outpacing the capabilities of legacy IAM tools.
1. Lack of Native Multi-Tenant Support
Most traditional IAM solutions are built around a single-tenant or flat user model. In a SaaS context, each customer (or partner) functions as an independent tenant with its own users, roles, and data. Without native support for multi-tenancy, organizations are forced to implement costly workarounds that increase technical debt and compromise security boundaries.
2. Fragmented Access Control Across Organizations
Managing access becomes increasingly difficult when policies must be applied across multiple tenants with varying needs. Inconsistent role structures, hardcoded logic, and manual overrides can lead to privilege escalation, unauthorized access, and policy drift.
3. Manual Provisioning and Deprovisioning Workflows
Onboarding and offboarding users manually, especially across dozens or hundreds of customer organizations, is inefficient and error-prone. This increases the risk of stale accounts, missed revocations, and delayed partner onboarding.
4. Limited Support for Delegated Administration
SaaS customers expect autonomy in managing their own users, roles, and access permissions. However, many IAM systems do not provide secure mechanisms for delegated administration, forcing platform teams to build and maintain custom access layers that are difficult to scale or audit.
5. Inadequate Audit and Compliance Visibility
Without centralized logging and identity activity tracking, it becomes difficult to generate reliable audit trails or prove compliance with data protection regulations. This lack of visibility into saas identity risk management introduces operational and regulatory risks.
6. Increased Maintenance and Slower Product Velocity
Custom IAM implementations often result in brittle, non-reusable configurations that slow down development cycles. Engineering teams are diverted from core product innovation to maintain access rules, integrations, and exceptions.
Addressing these challenges requires a purpose-built IAM architecture that is flexible enough to support tenant isolation, extensible enough to handle complex access scenarios, and scalable enough to grow with your SaaS business.
SaaS Identity and Access Management Best Practices
To operate securely and efficiently in a modern B2B SaaS environment, identity and access management must be treated as a strategic capability, not just a feature. A robust SaaS IAM strategy supports product scalability, accelerates time-to-market, and reduces identity-related risk across the partner ecosystem. Below are best practices that leading SaaS platforms are implementing to build a secure and scalable identity foundation.
1. Adopt a Multi-Tenant Identity Model from the Ground Up
SaaS applications naturally serve multiple organizations or business units under a single platform. Without a purpose-built multi-tenant architecture, identity sprawl becomes inevitable.
Your IAM solution should support logical tenant separation, ensure access isolation, and allow centralized visibility across all organizations. This is essential for implementing saas user account management and ensures you can scale across customer segments without duplicating identity infrastructure or compromising security.
2. Support Federated SSO Through Open Standards
Enterprise customers expect seamless and secure login experiences, especially when working with external SaaS vendors. Implementing standards-based federated SSO (such as SAML and OIDC) allows your partners and customers to use their existing identity providers to log in to your platform.
This minimizes friction for onboarding, reduces reliance on password-based authentication, and improves authentication saas posture while maintaining full auditability on your side.
3. Enforce Fine-Grained Access Control with RBAC and ABAC
Controlling who can access what and under what conditions is critical in SaaS. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) assigns permissions based on organizational roles, while Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) enables even more flexibility by evaluating contextual attributes such as department, region, or time.
By combining RBAC and ABAC, you create layered access control saas policies that adapt to changing needs without requiring hardcoded logic in your application.
4. Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) Provisioning and Automated Deprovisioning
Manual user onboarding is time-consuming, error-prone, and a security risk, especially when users are spread across dozens or hundreds of tenant organizations.
With JIT provisioning, user accounts are created on the fly during the first login using federated identity or identity brokering. Paired with automated deprovisioning mechanisms (based on inactivity, revocation, or role changes), this ensures real-time saas user access management with minimal administrative overhead.
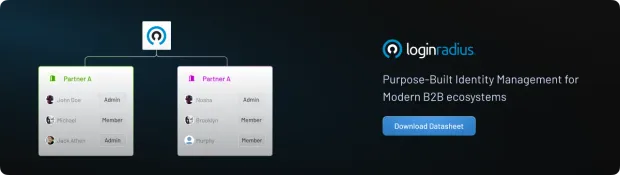
5. Enable Delegated Administration for Organizational Autonomy
SaaS customers don’t want to depend on your support team every time they need to create users or assign roles. A mature IAM solution should support delegated administration, allowing each partner organization to manage its own users, groups, and policies within the limits you define.
This decentralizes operational burden, accelerates onboarding, and creates a more flexible SaaS delivery model while still maintaining centralized governance.
Example: “A fast-growing SaaS CRM provider used LoginRadius Partner IAM to onboard 300+ customer organizations, enabling delegated administration and reducing manual provisioning efforts by 70% within two months.”
6. Incorporate Risk-Based Adaptive Authentication
Static authentication is no longer enough. Modern SaaS security requires saas identity risk management that adapts to context.
Use signals like geolocation, IP risk score, device fingerprinting, and login velocity to detect anomalies. Trigger step-up authentication or block suspicious logins in real time—without disrupting normal users. This proactive defense model is key to mitigating credential abuse and session hijacking.
7. Centralized Visibility with Comprehensive Logging and Auditing
As your partner and customer base grows, visibility into identity activity becomes a compliance and operational imperative.
Your IAM platform should offer real-time logs and immutable audit trails covering login activity, permission changes, session durations, and admin actions. These logs are essential not only for internal security teams but also for compliance with regulations like SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA, ensuring security saas standards are consistently met.
Adopting these best practices ensures your identity system matures alongside your product, supporting secure scale, partner flexibility, and regulatory alignment. More importantly, it shifts IAM from a patchwork of custom logic into a core product capability that drives long-term SaaS success.
![]()
What to Consider When Choosing an IAM Solution for SaaS
Selecting the right IAM solution isn’t just a security decision—it’s a product decision. For SaaS platforms, especially those operating in multi-tenant, partner-driven, or enterprise environments, identity infrastructure directly impacts how fast you scale, how easily you onboard partners, and how securely you manage user access across ecosystems.
Here are the key factors to evaluate when choosing an IAM platform tailored for SaaS:
1. Native Multi-Tenant Architecture
Ensure the IAM platform is purpose-built for multi-tenant applications, not just retrofitted with basic grouping or tagging. A native multi-tenant identity model provides clear boundaries between tenants (organizations), supports isolated roles and data, and allows you to apply policies independently across your customer base.
This is fundamental for saas identity management, it enables centralized control while supporting tenant-specific customization and autonomy.
2. Support for Delegated Administration
Can customers or partners manage their own users without going through your support or engineering team? Delegated admin is non-negotiable in modern SaaS. Your IAM solution should empower each organization to assign roles, manage groups, and configure access within their own scope, without risking platform-wide exposure. This drastically reduces operational overhead and improves customer satisfaction.
3. Scalable Role and Access Management
Look for flexible and composable support for Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), and policy definitions that can evolve with your product. Whether you're managing internal teams, external users, or partners, saas user access management must scale with your business and support fine-grained control.
4. Standards-Based Authentication and Federation
Support for OAuth 2.0, OIDC, and SAML is essential. Your enterprise customers likely have their own identity providers, and they expect seamless SSO via federated login. A robust authentication saas setup not only improves security but also reduces support requests related to account access and password resets.
5. Automation-Ready Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Manual user management doesn’t scale. Look for capabilities like Just-in-Time (JIT) provisioning, SCIM-based user sync, and webhook triggers for lifecycle events. Automated identity workflows are key to saas user account management and help enforce compliance across your platform without creating bottlenecks.
6. Built-In Security and Risk Intelligence
The IAM solution should offer risk-aware access controls, whether through geo-aware MFA, device fingerprinting, or anomaly detection. If the platform cannot handle saas identity risk management natively, you’re likely to invest significant time and cost in building those layers yourself.
7. Developer-Friendly APIs and SDKs
Your IAM system must plug directly into your CI/CD pipeline, not slow it down. Look for well-documented APIs, SDKs in multiple languages, and native support for common frameworks. This ensures your developers can build, iterate, and scale identity logic without being blocked by IAM complexity.
8. Compliance-Ready Logging and Auditing
From SOC 2 to GDPR, identity logs are a critical compliance requirement. The right IAM solution will offer structured logging, real-time audit trails, and secure storage of identity events, enabling security saas readiness without building from scratch.
Ensure the IAM platform supports industry compliance requirements, including SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, and regional data residency controls, especially if your SaaS handles sensitive customer or partner data.
Choosing the wrong IAM system can lock you into costly workarounds, hinder partner growth, and expose your platform to avoidable risk. The right IAM system, on the other hand, becomes a strategic asset, enabling faster delivery, stronger compliance, and differentiated user experiences across your SaaS ecosystem.
How to Implement IAM for SaaS with LoginRadius
Implementing IAM for a SaaS platform doesn’t have to mean stitching together generic solutions or writing custom logic for every new partner, tenant, or access rule. With LoginRadius Partner IAM, you get a purpose-built framework designed to handle SaaS-specific identity needs out of the box, without sacrificing flexibility or developer control.
Here’s how you can structure and implement identity and access management using LoginRadius for your SaaS product.
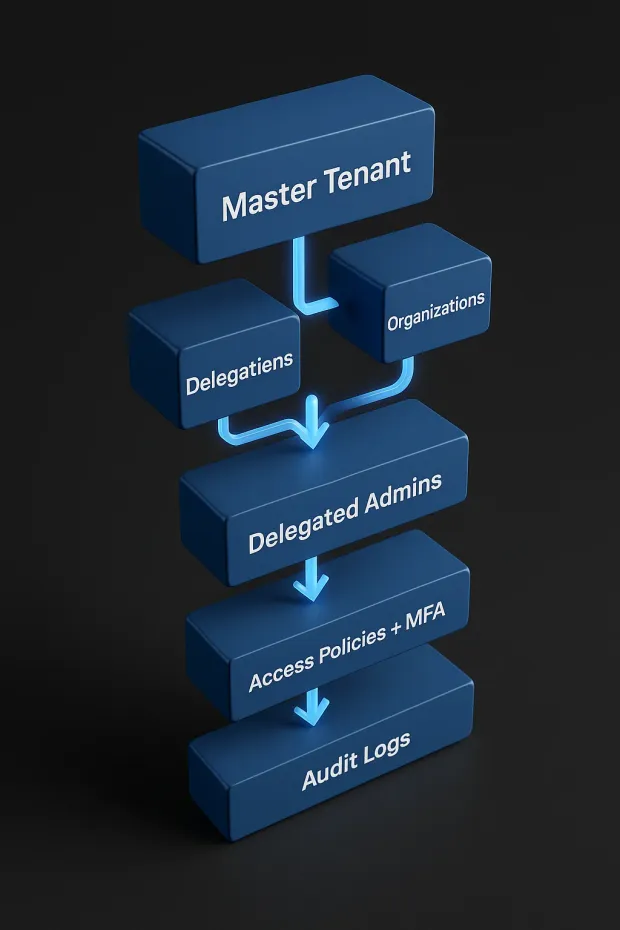
1. Start with the Master Tenant Model
In LoginRadius, everything begins with the Master Tenant your primary SaaS instance that acts as the root authority. From here, you can provision multiple Organizations, each representing a distinct customer, partner, or business unit. This structure enforces tenant isolation and gives you centralized governance over user identities across all orgs.
Each Organization gets:
-
Its own user base
-
Custom branding options
-
Role-based admin access
-
Independent login and access policies
This approach aligns perfectly with modern saas identity and access management where you need to isolate access per org while maintaining shared infrastructure.
2. Create and Configure Partner Organizations
Organizations can be created using the Partner IAM APIs, either manually via the dashboard or programmatically. Below is an example API call to create an Organization:
POST https://api.loginradius.com/identity/v2/manage/account/organization
Payload Example:
1{
2"Name": "Acme Corporation",
3"Description": "B2B Partner for Logistics",
4"IsActive": true,
5"CustomFields": {
6"industry": "Logistics",
7
8"region": "North America"
9
10}
11}You can associate each organization with unique metadata, login experiences, and admin permissions.
3. Implement Delegated Administration
Once an org is created, you can assign delegated administrators. These admins can manage users within their own organization create new users, assign roles, reset passwords, and configure security policies without needing access to the global tenant.
Use the following endpoint to assign an admin to an org:
POST /identity/v2/manage/account/organization/userrole
This structure empowers customers to self-manage their environments and reduces your operational overhead while still giving you full audit visibility and overriding access from the master tenant.
4. Configure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Each Organization can define its own roles and permission hierarchies, mapped to the functions needed within that context—be it end users, team leads, analysts, or system admins.
Here’s an example configuration pattern for a role:
1{
2"OrganizationId": "ORG_ID",
3"RoleName": "Analyst",
4"Permissions": [
5"read_reports",
6
7"export_data",
8
9"view_user_activity"
10
11]
12}This allows for tenant-specific access control models while still maintaining consistency in how permissions are enforced across the platform, supporting true saas user access management.
5. Enable Just-in-Time (JIT) Provisioning for Seamless Onboarding
Using LoginRadius' Identity Brokering and Federated Login capabilities, you can automatically create users the first time they log in, without requiring pre-registration. This is ideal for partner ecosystems where user identities originate outside your platform (e.g., through an external IdP).
You can configure identity mapping and provisioning rules using:
POST /identity/v2/auth/login
...combined with SSO integrations and access token processing to dynamically assign org-level roles upon first login.
6. Apply Adaptive Security and MFA Across Tenants
Every login request can be evaluated in real time using contextual signals (IP, device, geolocation, etc.), and you can configure tenant-specific MFA policies.
Example options include:
-
TOTP (Time-Based One-Time Passwords)
-
Email/phone OTPs
-
Passkeys (FIDO2/WebAuthn)
-
Security Questions
All of which are configurable per organization, using the LoginRadius dashboard or via the API layer. This supports advanced saas identity risk management with step-up authentication when anomalies are detected.
7. Monitor and Audit Access Activity
LoginRadius provides detailed logging and event tracking for every authentication and authorization event. You can use this to:
-
Track login activity across organizations
-
View user-specific access logs
-
Export data for compliance reporting (SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR)
This real-time observability supports security saas requirements and keeps your audit posture strong, without bolting on third-party tooling.
Conclusion
Identity and access management is no longer a background function for SaaS platforms; it is a core architectural consideration that directly impacts product scalability, partner enablement, and overall security posture. Yet, most traditional IAM solutions fall short when applied to the unique demands of SaaS environments, where multi-tenancy, delegated administration, and external user governance are the norm.
By adopting a modern, SaaS-specific IAM approach, organizations can streamline user onboarding, enforce consistent access policies across tenants, reduce identity-related risk, and accelerate time to market. More importantly, they can shift IAM from a reactive, maintenance-heavy burden into a strategic enabler for growth.
LoginRadius Partner IAM is designed specifically to meet these requirements. With native multi-tenant support, flexible role management, real-time provisioning, and granular access control APIs, it empowers SaaS teams to manage complex identity scenarios with clarity and confidence, without the overhead of custom development.
As SaaS ecosystems become more distributed and identity-centric, investing in the right IAM foundation is no longer optional; it’s a competitive imperative.
Ready to Modernize Your SaaS IAM?
Explore how LoginRadius Partner IAM can help you secure user access, accelerate partner onboarding, and scale your identity architecture with ease. → Talk to an Identity Specialist
FAQs
1. What are the common IAM challenges in SaaS environments?
A: SaaS platforms often face fragmented user management, a lack of tenant isolation, manual provisioning, and poor visibility into access activity. These gaps increase security risk and slow down onboarding and product innovation.
2. What are the benefits of centralized IAM in SaaS?
A: Centralized IAM enables unified user access control, automated provisioning, delegated administration, and consistent policy enforcement across all tenants. It reduces operational overhead and strengthens security and compliance.
3. What is the role of CIAM in SaaS platforms?
A: CIAM in SaaS supports secure customer onboarding, authentication, and identity governance across multi-tenant environments. It helps manage users, partners, and roles while enhancing user experience and protecting sensitive data.