Introduction
The convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and cybersecurity marks a critical evolution in the digital landscape. As organizations digitize more of their operations, the attack surface expands, creating fertile ground for sophisticated cyber threats.
AI in cybersecurity has emerged as a formidable solution to combat these risks by providing real-time threat intelligence, predictive analytics, and enhanced response mechanisms.
Notably, the global AI in cybersecurity market was valued at $25.40 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $31.38 billion in 2025, reflecting the increasing reliance on AI-driven security solutions.
Undoubtedly, AI empowers security systems with learning capabilities, enabling them to detect anomalies and respond faster than traditional tools.
By integrating AI and cybersecurity, businesses can not only defend against existing threats but also adapt to emerging attack vectors.
This synergy not only streamlines security operations but also strengthens resilience against data breaches and cyber fraud, particularly relevant in today’s zero-trust and data-driven ecosystems. Let’s dig deeper into this.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
The role of AI in cybersecurity is transformative. By applying machine learning, natural language processing, and behavioral analytics, AI can process massive datasets and identify patterns indicative of malicious activities. This makes the cybersecurity ecosystem more agile and proactive.

Professionals benefit from AI in cybersecurity through automation of repetitive tasks such as log analysis, threat detection, and compliance monitoring. AI-driven tools can filter out noise and focus on genuine threats, thus improving decision-making.
Furthermore, AI in information security enables predictive defense mechanisms that anticipate future threats based on historical trends.
For instance, financial institutions use AI algorithms to detect fraudulent transactions in real time. In healthcare, AI secures sensitive patient data by monitoring network activity for unauthorized access. These use cases highlight the extensive impact of AI on cybersecurity and demonstrate how it augments human intelligence.
Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
The advantages of using AI in cybersecurity are both tactical and strategic. On a tactical level, AI enables rapid identification and neutralization of threats. Strategically, it fosters a security-first culture by enabling continuous monitoring and adaptive defenses.
Reduction of false positives
Traditional systems often overwhelm security teams with alerts, many of which are not genuine threats. AI reduces this burden by applying context-aware analysis.
Scalability
AI systems handle growing volumes of data without a proportional increase in resources, making them ideal for expanding enterprises.
Low response times
AI impact on cybersecurity is also evident in response times. Where manual intervention might take hours or days, AI can act within milliseconds to isolate affected systems. Overall, AI in information security not only mitigates risks but also optimizes security investments.
How Does AI Work in Cybersecurity?
AI in cybersecurity operates through a synergy of data collection, pattern recognition, and machine learning. Initially, AI systems ingest vast datasets from network logs, user activities, and threat intelligence feeds. These inputs are then analyzed using machine learning algorithms that identify unusual patterns or behaviors.
Pattern recognition is at the heart of how AI can help in cybersecurity. For example, a sudden spike in login attempts from a single IP address could indicate a brute-force attack. AI systems detect such anomalies and trigger alerts or automatic countermeasures.
Moreover, predictive analysis helps organizations forecast potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited. For instance, AI may predict that a software component is susceptible to a known exploit based on usage patterns and historical incidents. This proactive capability is a cornerstone of using AI in cybersecurity effectively.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence for the Cybersecurity Industry
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape, offering advanced capabilities that enhance threat prevention, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance across industries. Below are the key ways AI is benefiting cybersecurity:
1. Enhanced Threat Intelligence and Real-Time Detection
AI accelerates the process of threat analysis by quickly scanning and correlating data from multiple sources. This enables security systems to detect and respond to complex cyberattacks in real time. Sectors like the government sector and defense, where protecting sensitive data is critical, benefit significantly from AI-driven threat intelligence that delivers faster, more accurate insights.
2. Optimized Resource Allocation and Incident Response
By automating repetitive security tasks such as monitoring, alerting, and low-level incident response, AI allows human experts to focus on high-impact decision-making. This is especially valuable in industries like retail and eCommerce, where security teams face constant pressure to detect fraud without compromising user experience. It also helps reduce alert fatigue and burnout among cybersecurity professionals.
3. Adaptive Learning for Evolving Threat Landscapes
Unlike static rule-based systems, AI models continuously learn from new data to adapt to emerging threats. This dynamic learning approach is crucial in highly regulated sectors like healthcare, where cybersecurity must not only protect patient data but also comply with strict legal standards. AI also enhances identity verification, offering more secure and seamless user authentication across industries.
4. AI-Powered Phishing Detection
AI algorithms are highly effective at detecting phishing attempts. They analyze email content for suspicious language patterns, unusual sender behavior, and potentially harmful attachments. This proactive scanning helps prevent employees from falling prey to social engineering attacks—a leading cause of data breaches.

5. Advanced Malware and Zero-Day Threat Detection
Traditional antivirus solutions often rely on known signatures, making them ineffective against new or unknown malware. AI, however, can evaluate file behavior and characteristics to identify malicious software—even when no signature exists. This capability makes AI essential in defending against zero-day threats and evolving attack vectors.
6. Behavioral Analytics for Insider Threats
AI enhances security through behavioral analytics by establishing a profile of normal user activity. When deviations occur—such as unusual access times, data transfers, or login locations—AI can flag these as potential insider threats or signs of a compromised account. This early warning system enables faster response and mitigation.
Additionally, AI is revolutionizing how user authentication works, by enabling smarter, context-aware verification methods that enhance both security and user experience. Explore how AI is transforming user authentication to learn more about its application beyond threat detection.
What Are the Challenges of AI in Cybersecurity?
While AI in cybersecurity offers many advantages, it also comes with challenges. One significant issue is data privacy. AI systems require access to large volumes of data to function effectively, raising concerns about compliance and ethical data usage.
Another challenge is adversarial attacks. Cybercriminals can exploit AI systems by feeding them manipulated data, causing misclassifications or evading detection. These adversarial techniques can undermine the integrity of AI models if not adequately guarded against.
Additionally, implementing AI is resource-intensive. It requires substantial investment in hardware, software, and skilled personnel. Organizations must weigh these costs against the potential benefits when deploying AI in security infrastructures.
How to Safeguard Yourself
To safeguard against the risks associated with AI in cybersecurity, organizations should adopt a multi-layered approach. Regular audits are essential to ensure that AI systems function correctly and are not biased or outdated.
One essential step in this layered defense strategy is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA), which adds a robust additional layer of security.
To understand how MFA complements AI in creating a stronger cybersecurity posture, read this guide on the benefits of MFA. This is how MFA works:
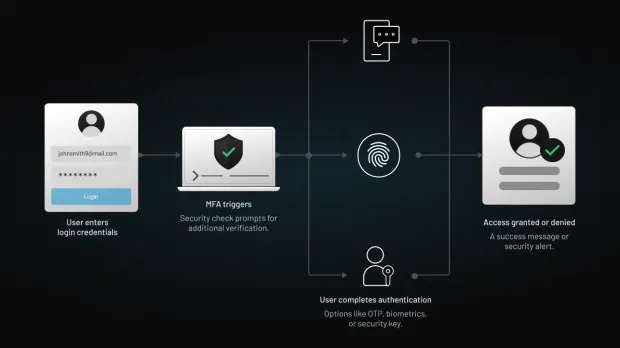
Data governance plays a crucial role. Establishing clear policies on data collection, usage, and storage ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Transparency in AI decision-making also enhances trust among stakeholders.
Continuous monitoring of AI systems allows for real-time adjustments. By identifying and addressing anomalies early, organizations can prevent AI from becoming a liability rather than an asset in cybersecurity.
Why is AI in Cybersecurity Important?
AI in cybersecurity is vital because it provides the speed, accuracy, and adaptability needed to combat modern threats. Unlike traditional systems, AI adapts to new attack methods and learns from each encounter, enhancing long-term resilience.
Speed is a critical factor. In cybersecurity, delayed responses can lead to growing risk of data breaches and financial loss. AI mitigates this by automating detection and response, often resolving issues before human analysts are even aware.
Moreover, AI improves accuracy by reducing human error and contextualizing alerts. This ensures that security teams focus on genuine threats, improving overall efficiency. In essence, AI in cybersecurity is not just important—it is indispensable.
How Does AI Improve Managed Detection and Response (MDR)?
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) services benefit significantly from AI integration. AI automates the detection of threats, reducing the time it takes to identify and respond to incidents.
By leveraging AI, MDR providers can offer more accurate and timely alerts, freeing up human analysts for high-level tasks. AI also helps in correlating data across multiple sources, providing a unified view of the threat landscape.
Furthermore, AI enhances the scalability of MDR solutions. As organizations grow, their security needs become more complex. AI ensures that MDR services can scale without compromising performance or reliability.
LoginRadius and Adaptive Authentication: AI-Powered Security
LoginRadius leverages AI in cybersecurity through its adaptive/ risk-based authentication mechanisms. This intelligent system evaluates login attempts using parameters such as IP location, device fingerprint, and login behavior.
Suspicious attempts trigger additional verification steps, ensuring that only legitimate users gain access.
For example, if a user logs in from an unusual location or device, the system may prompt for multi-factor authentication. This proactive approach minimizes login fraud and enhances user trust.
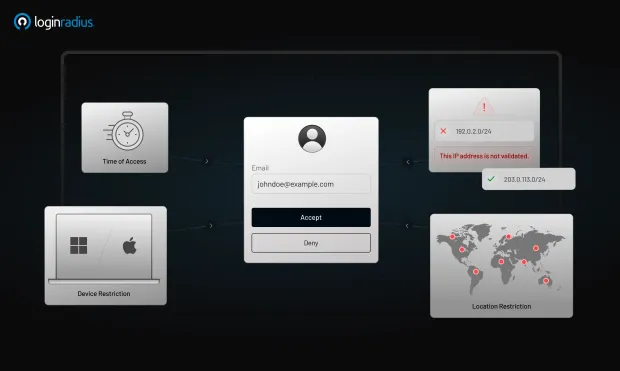
By using AI in information security, LoginRadius delivers a seamless yet secure user experience. This not only improves security but also supports business goals by reducing friction in the authentication process.
Want to experience intelligent authentication in action? Explore our risk-based authentication solution.
The Future Of Cybersecurity: How AI Is Shaping The Industry
The future of cybersecurity is undeniably tied to AI. As threats evolve, AI will become more integral to defensive strategies. Predictive analytics, autonomous response systems, and AI-driven governance frameworks will redefine how we approach information security.
We can expect AI to be integrated with technologies like blockchain and quantum computing, creating robust and tamper-proof security ecosystems. Additionally, AI’s role in regulatory compliance will expand, helping organizations stay ahead of legal and ethical challenges.
Ultimately, the convergence of cyber security and artificial intelligence promises a future where security is proactive, intelligent, and deeply integrated into business processes.
Summary
AI in cybersecurity is not a trend—it’s a necessity. From real-time threat detection to intelligent fraud prevention, AI enhances every facet of security operations. Despite its challenges, the benefits far outweigh the risks, particularly when AI is deployed thoughtfully and ethically.
LoginRadius exemplifies how organizations can harness AI to deliver both security and user satisfaction. As cyber threats grow in sophistication, integrating AI and cybersecurity will remain the cornerstone of a secure digital future.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of AI in cybersecurity?
A. Artificial intelligence (AI) offers several significant benefits in enhancing cybersecurity. Here are the top three advantages:
-
Real-Time Threat Detection AI can analyze vast amounts of data at high speed to identify unusual patterns and detect threats as they happen, helping to prevent breaches before damage is done.
-
Automated Response AI can automate routine security tasks like responding to low-level threats, allowing security teams to focus on more complex issues and reducing response time drastically.
-
Advanced Threat Prediction With machine learning, AI systems can predict potential threats based on historical data, helping organizations proactively strengthen defenses against future attacks.
2. Will AI take over cybersecurity?
A. No, AI will augment cybersecurity efforts, enhancing human capabilities rather than replacing them.
3. Can AI predict cyber attacks?
A. Yes, predictive analytics in AI can foresee potential threats based on historical and contextual data.
4. What is an example of AI in cybersecurity?
A. AI-based phishing detection that scans email content and behavior patterns is a practical example.
5. How can generative AI be used in cybersecurity?
A. It can simulate threat scenarios, helping teams to prepare and fortify defenses against evolving attacks.
6. What are the latest advancements in AI-driven cybersecurity solutions?
A. Innovations include AI-powered SOAR platforms, autonomous threat hunting, and adaptive authentication systems like those from LoginRadius.



