Introduction
Imagine walking into your office building. The security guard at the gate checks your ID. You swipe a keycard to access the elevator. Once at your floor, you enter a PIN to unlock your workstation. Behind each of these steps lies a powerful yet often invisible layer of protection: access control.
In the digital world, access control works in much the same way. Every time you log into a system, open a restricted file, or attempt to use a business app, a set of rules determines whether you’re allowed in. This process is called access control in security, which is a foundational pillar that governs who can access what, when, and how.
Today’s organizations deal with an overwhelming amount of sensitive data, cloud applications, remote employees, and third-party tools. Without access control systems in place, these assets are left exposed to misuse, accidental breaches, or even malicious attacks. That’s why access control isn’t just a technical feature, it's a business necessity.
We need to remember that access control cannot be a one-size-fits-all solution. There are different types of access control models, technologies, and policies depending on your security needs, workforce structure, and compliance goals. Whether you’re an enterprise managing millions of customers logins or a startup handling sensitive customer data, understanding how access control systems work can drastically improve your security posture.
In this blog, we’ll break down what access control in security really means, how it works, the types of systems available, and best practices to implement it effectively. Whether you're new to the concept or looking to refine your current setup, this guide will help you build smarter and more secure access environments.
Why Is Access Control Important?
Access control isn’t just a security protocol - it’s the frontline defense against unauthorized access, data breaches, and internal misuse. In today’s digital-first world, where employees work remotely, businesses adopt SaaS tools rapidly, and sensitive data lives across hybrid cloud environments, it’s more important than ever to control who gets access to what—and under what conditions.

At its core, access control ensures that only the right users, devices, or systems can interact with specific data, applications, or physical resources. This becomes essential not only for cybersecurity but also for operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. A weak or outdated access control system can lead to accidental data leaks, credential theft, and insider threats—all of which can cost organizations millions in lost trust and penalties.
Access control also plays a crucial role in managing partner organizations. For instance, when a new partner organization is onboarded, their users should automatically receive access only to the resources, apps, or APIs relevant to their assigned roles—nothing more. Similarly, if a partner ends their engagement or shifts scope, their access should be instantly updated or revoked. Without a centralized B2B IAM system, businesses risk over-permissioned external users and unintended exposure to sensitive systems.
Moreover, in industries governed by strict compliance standards like HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS, maintaining robust access control policies is not optional, it's mandatory. These regulations require companies to demonstrate that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized individuals and that all access is logged, monitored, and revocable.
Simply put, access control in security is no longer a technical checkbox. It’s the backbone of zero trust architecture, where every access request must be verified, regardless of where it originates.
With modern access control solutions and access management tools, organizations can not only strengthen their defense but also streamline how users interact with systems securely.
How Access Control Works
At a glance, access control may seem like a simple yes-or-no gate. But behind that decision lies a complex and intelligent process combining identity, context, policy, and permission.
To understand how access control in security works, let’s break it into two core components: authentication and access control.
-
Authentication answers the question: Are you really who you claim to be? This is typically done using something you know (like a password), something you have (a security token), or something you are (like a fingerprint).
-
Authorization, the next step, asks: Now that we know who you are, what are you allowed to do? This involves evaluating the user’s role, device trust, location, time of access, and other contextual factors.
Once both steps are satisfied, the system either grants or denies access based on predefined access control policies.
Let’s say you’re trying to access a cloud dashboard at 2 AM from an unknown device in another country. A well-configured security access control system would detect this anomaly and either block the attempt or require step-up authentication like a one-time passcode. That’s the power of context-aware access control.
Modern access control systems go far beyond hardcoded permission sets. Today’s solutions are dynamic, integrated, and API-driven. They plug into your existing IAM platforms, HR tools, and cloud infrastructure to enforce fine-grained access decisions in real time.
Here’s what typically happens behind the scenes in an enterprise-grade access control solution:
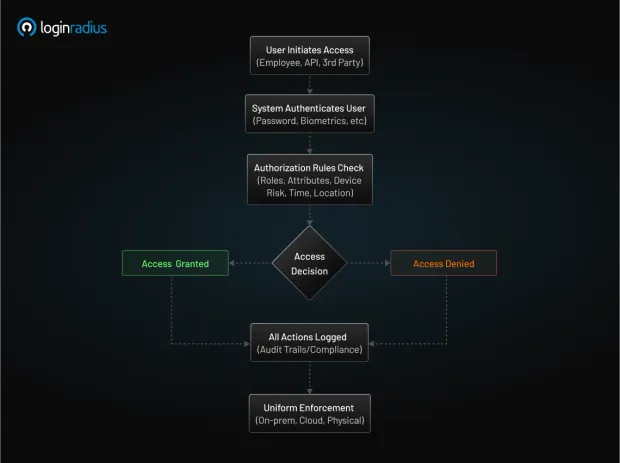
-
The user initiates access – This could be an employee logging in, an API requesting data, or a third-party vendor accessing a shared resource.
-
The system authenticates the identity – Through username/password, biometrics, or tokens.
-
Authorization rules are checked – The request is matched against your defined access control techniques and policies.
-
The system grants or denies access – Based on roles, attributes, device risk, time, location, and more.
-
All actions are logged – For audit trails and compliance.
This process happens within milliseconds but determines the safety of your entire ecosystem. With integrated access control systems, you can apply these checks uniformly across on-prem apps, cloud platforms, and even physical environments.
How to Implement Access Control
Implementing access control in security isn’t just about plugging in a tool—it’s about designing a strategic framework that aligns with your organization's structure, risk profile, and regulatory environment. Done right, access control enhances both security and usability. Done wrong, it leads to over-restriction, security gaps, or a frustrating user experience.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to implementing effective access control:
1. Define Access Control Policies Based on Business Needs
Start by identifying:
-
Who needs access (e.g., employees, vendors, customers)?
-
What do they need access to (apps, files, APIs, environments)?
-
When, where, and how they should access it (time, location, device type)?
These considerations form the basis of your access control policies. For example, your finance team may need access to accounting software only during business hours from company-issued devices, while your developers may require broader access to cloud environments.
This step is critical—without clear policies, security access control systems can’t enforce appropriate rules. Here’s how you can quickly define access control policies in the LoginRadius console:
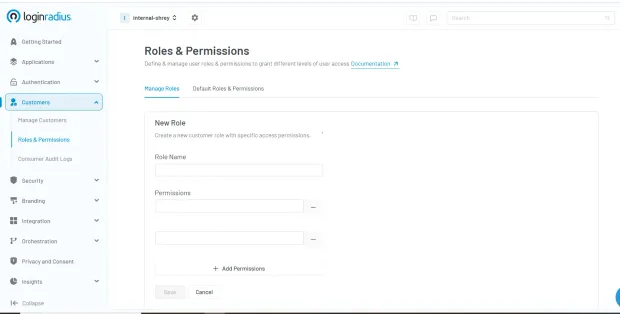
2. Choose the Right Access Control Model
There are several access control techniques you can choose from based on your organization's size and complexity:
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC grants permissions based on job roles. It's easy to scale and common in enterprise environments.
-
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Makes decisions based on attributes like department, project, location, or device trust.
-
Discretionary or Mandatory Access Control (DAC/MAC): Typically used in military or high-security environments.
Some businesses benefit from a hybrid model that blends multiple techniques for more precise control.
3. Leverage Access Management Tools
Now that your policy and model are clear, the next step is implementation through reliable access management tools. These platforms allow you to:
-
Centralize access decisions
-
Automate user provisioning and de-provisioning
-
Integrate with identity providers (IdPs)
-
Set rules for employee access control, external users, or APIs
Modern access control solutions offer RESTful APIs, SAML, OAuth, and SCIM integrations—ideal for cloud-native and enterprise applications alike.
4. Use Integrated Access Control Systems
Rather than managing access in silos, aim for integrated access control systems that tie together physical access (e.g., office entry badges) with digital access (e.g., system logins). This holistic approach enhances visibility and makes compliance reporting easier.
Platforms like LoginRadius offer the ability to connect authentication and access control flows, enforce risk-based policies, and maintain consistent access logic across user types.
5. Monitor, Audit, and Evolve
Access control isn’t a “set it and forget it” task. It requires:
-
Regular audits to identify dormant accounts or over-permissioned users
-
Access reviews to verify compliance with evolving access control policies
-
Continuous improvement based on changes in your workforce, applications, or threat landscape
Investing in access logs, analytics, and alerts helps security teams proactively respond to unauthorized access attempts and policy violations.
By thoughtfully implementing access control, you're not just locking digital doors—you’re building a responsive, intelligent security access control system that evolves with your organization.
Challenges of Access Control
While access control in security is essential for protecting sensitive systems and data, its implementation and ongoing management come with a unique set of challenges. Many organizations struggle to strike the right balance between strong security enforcement and seamless user experience and that’s just the beginning.
Let’s explore some of the most common obstacles security and IT teams face when implementing and managing access control systems:
1. Over-Permissioning and Access Creep
As employees move between roles, get promoted, or switch departments, they often accumulate access privileges they no longer need. This phenomenon known as access creep is a serious risk. Without regular reviews, these over-permissioned accounts can become backdoors for insider threats or external attackers.
Robust access control policies and automated employee access control tools can help, but only if organizations enforce regular audits and cleanups.
2. Fragmented Access Across Environments
In today’s hybrid IT ecosystems, access needs to be managed across cloud platforms, SaaS tools, legacy on-prem systems, mobile apps, APIs, and even IoT devices. Without integrated access control systems, visibility and consistency become difficult to maintain.
Many organizations use separate tools for physical access, identity management, and application-level control, leading to silos that undermine security.
3. Usability vs Security
A common challenge is finding the right equilibrium: tight enough security to prevent unauthorized access, but not so rigid that it slows down legitimate users. If access controls are too complex or intrusive, employees may start circumventing them—using shadow IT tools, weak passwords, or shared logins.

User-friendly access control solutions that incorporate contextual awareness and risk-based authentication are key to solving this tension.
4. Lack of Policy Standardization
Without well-documented and consistently applied access control techniques, different teams may set up their own rules, leading to conflicting policies and unexpected behaviors. This inconsistency not only creates confusion but can also open up security loopholes.
Having centralized access management tools ensures uniform enforcement, auditability, and compliance across departments and systems.
5. Complexity in Role and Attribute Management
While models like RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) and ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control) offer powerful ways to define permissions, they also require deep understanding of user roles, business logic, and system dependencies. Poorly defined roles or overused attributes can quickly spiral into unmanageable complexity.
That’s why scalable security access control systems must offer intuitive role definitions, templates, and analytics to manage complexity over time.
Access control is not a one-time project—it’s a continuous journey. From shifting employee responsibilities to evolving compliance mandates and growing threat vectors, your access strategy needs to adapt. Recognizing these challenges is the first step to building a smarter, more resilient access control framework.
Different Types of Access Control
When it comes to securing digital or physical environments, no single approach fits all. Depending on your organization's needs, size, risk profile, and level of regulatory oversight, you’ll choose different access control techniques to govern user access. Understanding these models is essential to designing an efficient and secure access control system.
Let’s explore the most commonly used types of security access control models:
1. Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
In DAC, access decisions are made by the resource owner—usually the person who created the file or system. For example, a team lead might give read or write access to their project folder.
-
Pros: Flexible and easy to set up.
-
Cons: Can lead to inconsistent permissions and accidental exposure.
-
Use Case: Small teams or startups where users manage their own resources.
2. Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
MAC is the opposite of DAC. Here, access rules are enforced by a central authority based on classification levels (like Top Secret, Confidential, Public). Users can’t override these rules—even if they own the data.
-
Pros: Very secure, used in high-security environments.
-
Cons: Rigid and harder to manage at scale.
-
Use Case: Government agencies, defense, or heavily regulated industries.
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC grants access based on a user’s role within the organization. Roles (like HR Manager, Developer, Finance Analyst) come with pre-defined permissions, which makes scaling and auditing easier.
-
Pros: Scalable, auditable, and widely adopted.
-
Cons: Needs frequent updates when roles evolve.
-
Use Case: Medium to large organizations with well-defined job functions.
4. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
ABAC takes it a step further by making decisions based on user attributes, resource attributes, and environmental context. For example, a user in the “Sales” department accessing from Canada between 9–5 may be granted access.
-
Pros: Highly flexible and granular.
-
Cons: Complex to configure and maintain without a strong identity foundation.
-
Use Case: Enterprises with dynamic environments and diverse user needs.
5. Rule-Based or Policy-Based Access Control
In this approach, access is governed by defined rules or policies rather than user roles. For example, a policy might deny access to sensitive data outside business hours or trigger multi-factor authentication for high-risk actions.
-
Pros: Dynamic and responsive to context.
-
Cons: Requires a mature access management system.
-
Use Case: Organizations looking for context-aware access control or implementing Zero Trust architectures.
Each of these access control techniques has its advantages and trade-offs. Many modern access management tools and security access control systems combine multiple models (e.g., RBAC + ABAC) to deliver fine-grained, adaptive access control that meets business, user, and compliance needs.
Benefits of Access Control Systems
Whether you're protecting cloud applications, sensitive databases, or physical entry points, implementing a well-designed access control system delivers far more than just gatekeeping. It enhances security, streamlines operations, and builds digital trust across your organization.
Let’s break down the key benefits of using modern security access control systems:
1. Prevent Unauthorized Access
The most obvious benefit is also the most critical—keeping intruders out. With robust access control policies, you ensure that only authenticated and authorized users can access protected systems, files, or environments. This drastically reduces the risk of data breaches caused by stolen credentials, insider misuse, or brute-force attacks.
2. Enable Role and Attribute-Based Efficiency
With models like RBAC and ABAC, you can assign permissions based on user roles or attributes, eliminating the need to manually manage access for each individual. This simplifies employee access control and reduces the chance of human error.
- Example: When someone joins the sales team, they’re automatically given access to the CRM, sales dashboards, and email tools—without needing IT intervention.
3. Automate Provisioning and De-Provisioning
Using advanced access management tools, organizations can automate the entire access lifecycle—from onboarding to role changes to offboarding. This ensures that users don’t keep access they no longer need, which is one of the leading causes of security gaps.
- Automation also reduces IT workload and accelerates user productivity.
4. Strengthen Compliance and Auditability
Industries like finance, healthcare, and SaaS often operate under strict regulatory mandates (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001). Access control solutions help maintain compliance by:
-
Enforcing least privilege access
-
Maintaining access logs for auditing
-
Generating reports for security assessments
5. Improve User Experience Without Compromising Security
Modern integrated access control systems use contextual signals (like device trust, geolocation, or access time) to adapt authentication requirements dynamically. This means users only face friction when needed, keeping the experience smooth without sacrificing protection.
6. Support Scalable Security for Hybrid and Cloud Environments
Today’s IT landscape spans on-prem apps, cloud services, and remote users. With the right access control in security architecture, you can unify access policies across platforms, ensuring consistent protection regardless of where the user or resource resides.
7. Respond Quickly to Security Incidents
Real-time monitoring and analytics provided by modern security access control systems help you detect suspicious behavior and respond before it escalates. For example, if an access attempt is made from a blocked location or an inactive account, the system can flag or block it instantly.
8. Support Zero Trust and Emerging Security Models
Modern access control systems form the foundation of Zero Trust architecture, where no user or device is inherently trusted. Advanced solutions are also beginning to incorporate AI-driven access decisions and Just-in-Time (JIT) access granting temporary permissions only when needed, and revoking them automatically after use. These trends enhance security without adding administrative burden.
By investing in the right access control solutions, organizations don’t just protect their assets—they gain operational agility, audit readiness, and peace of mind. In an era of identity-based threats and compliance pressure, access control is no longer a backend function—it’s a business-critical enabler.

Access Control Security Best Practices
Implementing access control in security is just the beginning. To keep your systems truly secure over time, it’s essential to follow best practices that align with evolving threats, organizational changes, and compliance demands. These practices ensure your access control systems remain effective, scalable, and audit-ready.
Below are some key best practices every organization should adopt:
1. Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Always give users the minimum level of access required to perform their job nothing more, nothing less. This minimizes the potential damage if an account is compromised.
-
Regularly review user permissions to ensure no one has unnecessary access.
-
Use role-based or attribute-based access control techniques to simplify PoLP implementation across departments.
2. Conduct Regular Access Reviews and Audits
Access that made sense last year might not make sense today. Schedule periodic reviews of:
-
Employee access control lists
-
Role assignments
-
Third-party and contractor access
-
Admin privileges
This helps identify dormant accounts, privilege creep, or misconfigured access control policies.
3. Use Centralized Access Management Tools
Instead of relying on manual updates or siloed systems, use modern access management tools that centralize user permissions, automate provisioning, and integrate with your HR or identity systems.
- These tools allow consistent authentication and access control enforcement across cloud and on-prem resources.
4. Enable Context-Aware and Risk-Based Access Control
A user logging in from an unknown location or an unmanaged device should not be treated the same as someone using a trusted company laptop at headquarters.
-
Leverage integrated access control systems that adapt based on user behavior, location, device, and time of day.
-
Use adaptive MFA for high-risk scenarios without making access overly complicated. Learn more about adaptive MFA by downloading this insightful resource:
5. Log Everything and Monitor Continuously
Visibility is key. Ensure your security access control systems log every access request—successful or failed. These logs are invaluable for:
-
Detecting anomalies
-
Investigating incidents
-
Proving compliance
-
Strengthening your threat response
Bonus: Pair access logs with real-time alerting and SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools for proactive defense.
6. Make MFA Non-Negotiable
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a critical second layer of verification that drastically reduces the chances of unauthorized access—especially when credentials are stolen.
-
Enforce MFA for all users accessing sensitive resources or admin dashboards.
-
Combine it with your access control solutions for seamless policy enforcement.
7. Test and Simulate Access Scenarios
Regularly test how your access control system behaves under different conditions:
-
What happens if an employee changes roles?
-
Can a terminated account still access email?
-
Are sensitive files accidentally exposed to all staff?
Simulations can uncover hidden gaps and improve both system logic and user training.
By following these best practices, organizations can build a resilient and adaptive security access control system one that evolves with business needs, regulatory standards, and cyber threats.
Conclusion
Access control is no longer just a backend IT task it’s the cornerstone of modern security strategy. Whether you’re protecting sensitive customer data, preventing internal misuse, or meeting compliance requirements, a robust and flexible access control system is critical to safeguarding your digital ecosystem.
As organizations grow more distributed and digital-first, the need for context-aware, user-friendly, and policy-driven access control solutions will only increase. The good news? With the right combination of strategy, tools, and governance, implementing effective access control policies doesn’t have to be complicated.
If you’re looking to streamline employee access control, enforce compliance, and build trust across your organization, now is the time to invest in a next-gen access management tool that supports your long-term vision for security and scalability.
Ready to take control of access? Explore how LoginRadius can help you implement secure, scalable access control tailored to your business needs. Get Started Today.
FAQs
Q. What is access control in cybersecurity?
A: Access control in cybersecurity is the process of regulating who can access digital systems, data, or resources. It ensures that only authorized users perform permitted actions based on defined security policies.
Q. Why is access control important?
A: Access control prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats. It also helps organizations enforce compliance, protect sensitive data, and reduce operational risk.
Q. What are the main types of access control?
A: The main types include Discretionary (DAC), Mandatory (MAC), Role-Based (RBAC), Attribute-Based (ABAC), and Rule-Based access control—each varying by how permissions are assigned and enforced.
Q. What’s the difference between physical and logical access control?
A: Physical access control secures entry to buildings or rooms using locks, keycards, or biometrics. Logical access control governs access to digital systems, applications, and data using authentication and authorization protocols.



