A Complete Guide to Adaptive MFA for Modern CIAM
Adaptive MFA strengthens security by analyzing real-time risk signals and stepping up authentication only when something looks suspicious.

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Adaptive MFA?
- How Adaptive Authentication Works?
- Risk Signals Used in Adaptive MFA
- Adaptive MFA Benefits
- Adaptive MFA vs Traditional MFA vs 2FA
- Adaptive MFA in CIAM
- Real-World Use Cases & Industry Scenarios
- The Future of Adaptive Authentication
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction

Learn How to Master Digital Trust

The State of Consumer Digital ID 2024

Top CIAM Platform 2024
Introduction
Authentication has come a long way from simple passwords and one-size-fits-all security checks. As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated and user expectations shift toward fast, frictionless experiences, organizations can no longer rely on static authentication methods especially when protecting millions of customer identities.
This is where Adaptive MFA (Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication) steps in as one of the most strategic advancements in modern identity security.
Unlike traditional 2FA or static MFA, adaptive authentication doesn’t treat every login attempt the same. Instead, it evaluates context, behavior, and real-time risk signals to decide whether a user should be allowed in seamlessly, prompted for additional verification, or denied entirely. The result is stronger security and a smoother user experience, two outcomes that rarely coexist in traditional authentication models.
For developers, product leaders, and security architects, adaptive MFA represents a practical way to reduce account takeover risk, eliminate unnecessary friction, and align with a zero-trust, identity-first security approach. For everyday users, it feels effortless: no OTPs when the system knows the login is legitimate, and additional checks only when something seems off.
At its core, adaptive MFA represents a shift from static authentication toward intelligent, context-aware identity security. If you’re asking what is adaptive MFA or what is adaptive multi-factor authentication, the simplest answer is this: it dynamically adjusts authentication requirements based on real-time risk instead of forcing the same MFA challenge on every login.
As customer identity becomes central to business growth, trust, and compliance, adaptive MFA is quickly becoming the standard for modern CIAM environments. In this guide, we’ll break down what adaptive MFA is, how it works behind the scenes, and why it’s one of the most important upgrades organizations can make to their authentication strategy today.
What Is Adaptive MFA?
Often referred to as adaptive multi factor authentication, this approach is also closely tied to adaptive authentication, a broader security model where identity verification adapts continuously to user behavior, device trust, and environmental signals. In fact, when people ask what is adaptive authentication, they are usually referring to this same risk-based, context-driven decision-making applied across login and session activity.
Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication (Adaptive MFA) is an intelligent, context-aware approach to authentication that adjusts security requirements based on real-time risk. Instead of challenging every user with the same static factors like OTPs or push notifications, adaptive MFA analyzes the situation around each login attempt and decides whether additional verification is needed.
In simple terms, adaptive authentication asks: “Does this login look safe, or does something feel unusual?” Then it tailors the authentication process accordingly.
At a deeper level, adaptive MFA evaluates a wide range of contextual and behavioral indicators: user location, device reputation, IP risk level, login time patterns, behavioral deviations, and dozens of additional signals.
Based on these inputs, it assigns a risk score.
-
Low-risk users pass through seamlessly.
-
Medium-risk users may face a silent check or subtle challenge.
-
High-risk users are prompted to enter a step-up factor or are blocked entirely.
This dynamic approach not only improves security but also dramatically reduces unnecessary friction. Users no longer face OTP fatigue, slow SMS codes, or repetitive verification steps when everything about their login is normal.
What makes adaptive MFA powerful is its ability to blend risk-based authentication, contextual intelligence, and modern CIAM principles into a single workflow. It shifts authentication from something rigid and predictable into something smart, flexible, and user-aware—providing protection precisely when it’s needed, and staying invisible when it’s not.
Understanding what is adaptive multi-factor authentication requires looking beyond OTPs and static rules and focusing on how adaptive authentication engines assess trust dynamically before deciding whether additional verification is even necessary.
Also read: Adaptive Authentication- Is it the Next Breakthrough in Customer Authentication?
How Adaptive Authentication Works?
Adaptive MFA works by analyzing real-time context around every login attempt and making an intelligent decision about the level of verification required. Instead of forcing the same MFA challenge on every user, it evaluates risk first then adjusts the authentication flow accordingly. This creates a balance between strong protection and seamless usability.
This risk-based model is the foundation of modern adaptive MFA, where authentication flows are no longer fixed. Instead, adaptive authentication continuously evaluates context and can even integrate with adaptive SSO, allowing trusted users to move seamlessly across applications without repeated challenges.
Risk Evaluation Begins the Moment a User Tries to Log In
When a login attempt is made, adaptive authentication immediately gathers contextual and behavioral signals. These aren’t just basic checks; they include location patterns, device fingerprints, network quality, historical login behavior, time-of-day consistency, and known threat intelligence.
The system asks intelligent questions such as:
-
Is the user logging in from their usual device?
-
Does the IP address carry any known risk?
-
Has the user behaved differently compared to past sessions?
-
Is the request coming from a suspicious or impossible location?
These signals help form a foundational understanding of whether the attempt looks normal or suspicious.
Assigning a Risk Score to Determine Trustworthiness
Once the contextual data is collected, the authentication engine assigns a risk score. This score determines how much trust the system has in the login attempt. Low-risk sessions can continue without additional friction, while high-risk sessions trigger stronger verification mechanisms.
Adaptive MFA does not rely on static rules it uses dynamic logic, risk scoring algorithms, and sometimes even machine learning models to make smarter decisions over time. The more the system observes user behavior, the better it becomes at distinguishing legitimate patterns from unusual ones.
Responding with the Appropriate Authentication Action
Based on the risk score, the system chooses the correct next step. This is where adaptive MFA becomes truly powerful: it applies the right level of security at the right time, instead of relying on outdated one-size-fits-all challenges.
Typical adaptive responses include:
-
Allow the login with no interruption (low-risk)
-
Silently evaluate more factors in the background (medium-risk)
-
Trigger a step-up authentication challenge like TOTP, push, biometrics, or passkey (high-risk)
-
Deny the login if the activity appears malicious
The result is a system that strengthens security only when necessary while keeping the experience smooth for trusted users.
Continuous Evaluation Throughout the Session
Adaptive authentication doesn’t stop after login. In more advanced implementations, it continues monitoring user actions throughout the session. This means if behavior suddenly becomes suspicious, such as accessing sensitive resources from a risky network, the system can demand verification again or terminate the session entirely.
This continuous, risk-aware model aligns with zero-trust and identity-first security, ensuring that trust is earned and maintained, not assumed.
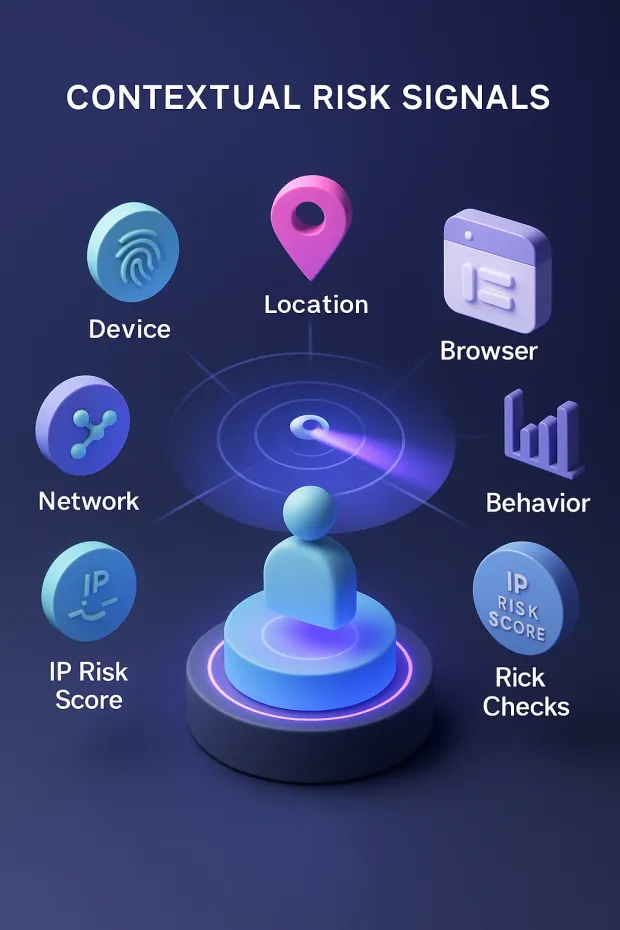
Risk Signals Used in Adaptive MFA
Adaptive MFA is effective because it analyzes a broad range of environmental, behavioral, and contextual signals to understand whether a login attempt is trustworthy. Instead of relying on a single factor, it evaluates multiple dimensions of user activity, creating a layered, intelligent picture of risk.
These signals allow the system to detect anomalies that traditional MFA or 2FA would completely overlook.
Device & Browser Intelligence
Adaptive authentication examines the device being used during login, checking whether it matches known patterns for that user. Everything from device ID to operating system, browser fingerprint, and security posture is evaluated. \
If the user is on a familiar device, the system builds trust. If the login originates from a new or suspicious device, risk levels increase immediately.
Signals it considers include:
-
New or unrecognized devices
-
Jailbroken or rooted devices
-
Browser fingerprint mismatches
Location & IP-Based Risk
User login locations tell a powerful story. Adaptive MFA identifies geographic consistency where a user usually logs in from and flags anomalies.
Risk signals include:
-
Sudden login from a new country
-
Impossible travel (e.g., two locations minutes apart)
-
Suspicious IP ranges, VPN abuse, TOR networks
-
High-risk or blacklisted IPs
These location-based checks help detect account takeover attempts that originate from hacked or remote servers.
User Behavior & Activity Patterns
Behavior acts as a digital fingerprint. Adaptive MFA evaluates how users typically behave — when they log in, how they navigate, and what actions they take.
Signals include:
-
Unusual login times
-
Fast, automated, or bot-like interactions
-
Abnormal click or navigation patterns
-
Sudden changes in typical behavior
Any deviation from normal behavior can trigger additional verification.
Also read: Fix Broken Authentication with Adaptive MFA
Network & Environmental Signals
The quality and type of network also impact risk. Adaptive MFA analyzes whether a user is connecting from a trusted or suspicious environment.
Signals include:
-
Public Wi-Fi or unsecured networks
-
Anonymous or masked connections
-
Repeated failed login attempts from the same network
These signals help filter out automated attacks, credential stuffing, and bot-driven intrusions.
Threat Intelligence & Historical Risk
Adaptive MFA leverages real-time and historical threat data to evaluate credibility. If previous sessions, devices, or IPs associated with the login attempt were risky, the system automatically tightens verification.
Signals include:
-
Known malicious sources
-
Accounts flagged for suspicious behavior
-
Repeated brute-force attempts
This ensures attackers are blocked even if they appear legitimate on the surface.
By combining these signals, adaptive MFA achieves a level of accuracy and sophistication that traditional MFA or 2FA cannot match. It moves authentication from a static “checklist” approach to a dynamic, intelligent system that responds to risk in real time.
Adaptive MFA Benefits
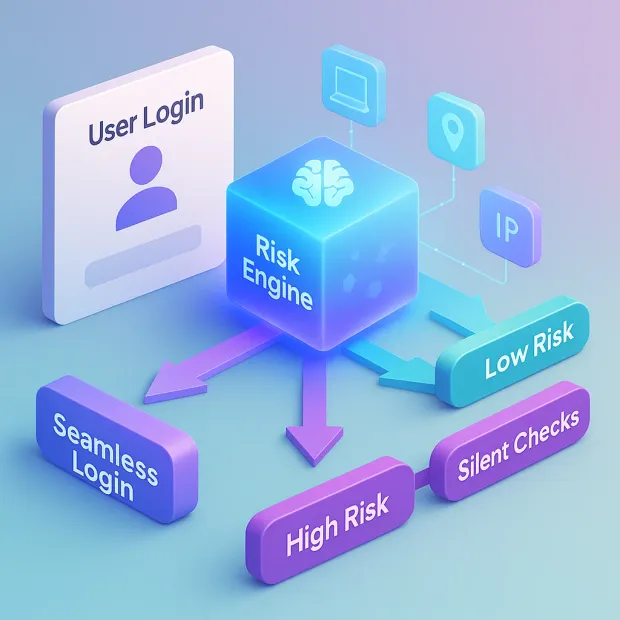
Adaptive MFA delivers a level of protection and user experience that traditional MFA and 2FA cannot match. By analyzing real-time context and responding intelligently, it enhances security while reducing friction a rare combination in the authentication world.
Below are the most important benefits, explained in an elaborated yet easy-to-follow format.
1. Stronger Security Through Real-Time Risk Analysis
Adaptive MFA evaluates multiple risk signals, including device behavior, IP reputation, user patterns, network trust, and threat intelligence, to determine whether a login attempt is legitimate.
This real-time risk analysis helps the system catch suspicious activity before a user even reaches the login screen. Attackers trying to bypass authentication, launch credential stuffing, or attempt account takeovers are intercepted instantly.
Because decisions are based on data and behavior rather than fixed rules, the system becomes smarter and more resilient over time.
2. Reduced Friction for Low-Risk Users
One of the biggest drawbacks of traditional MFA is the unnecessary friction it creates. Every login feels the same, even if the user is clearly authentic.
Adaptive MFA changes this by allowing low-risk users to authenticate seamlessly without extra steps. When the system recognizes a trusted device, familiar location, and normal behavior, it lets the user log in without OTPs, prompts, or secondary checks.
This creates a smoother user experience, reduces login fatigue, and significantly increases conversion rates, especially for consumer-facing applications.
3. Targeted Step-Up Challenges Only When Needed
Adaptive MFA provides step-up authentication only when a login attempt truly appears risky. Instead of forcing every user to complete a full MFA flow, the system challenges only those who exhibit unusual or suspicious patterns.
This targeted approach ensures that security is enforced where it matters most while legitimate users enjoy a hassle-free experience. It also reduces OTP dependency, SMS delivery failures, and push-notification fatigue.
4. Better Protection Against Modern Attacks
Traditional MFA struggles against advanced threats like real-time phishing, bot-driven attacks, SIM-swapping, and adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) scenarios.
Adaptive MFA uses risk intelligence and contextual signals to flag these anomalies instantly. If an attacker is trying to log in from a compromised IP, unusual region, or suspicious device, the system forces a strong step-up or blocks the attempt altogether.
This makes adaptive MFA one of the most effective defenses against modern account takeover attempts.
5. Improved Login Success Rates & Lower Abandonment
Every extra login step increases the risk of user abandonment, especially during signup or checkout. Adaptive MFA optimizes login and registration flows by minimizing obstacles for legitimate users.
This results in:
-
Higher login completion
-
Better onboarding success
-
Lower churn
-
A smoother authentication experience across devices
It’s a major advantage for high-traffic consumer applications where user experience directly impacts revenue.
6. Lower Support Costs & Reduced Operational Overhead
Most support tickets in authentication are due to MFA issues: lost devices, SMS delays, OTP errors, or inability to access codes.
Adaptive MFA reduces reliance on OTP-heavy flows, meaning fewer problems for users and fewer escalations for support teams. Organizations save time and resources because the system intelligently avoids unnecessary MFA challenges and reduces points of failure.
7. Seamless Global Compatibility for Diverse User Bases
In global apps, SMS delays, device limitations, and connectivity issues can drastically impact MFA performance. Adaptive MFA helps overcome these challenges by offering alternative paths and adjusting requirements based on device capability and network context.
Whether the user is on a high-end smartphone, a low-bandwidth network, or an unfamiliar region, adaptive MFA ensures the right authentication flow is delivered.
8. A Future-Proof Approach to Zero-Trust Security
Adaptive MFA aligns naturally with zero-trust principles: never trust, always verify.
It continuously evaluates user behavior and device signals, ensuring that authentication isn’t a one-time checkpoint but an ongoing assessment. This makes it ideal for modern CIAM architectures that require intelligent, dynamic, and user-first security.
Adaptive MFA vs Traditional MFA vs 2FA
Understanding the differences between Adaptive MFA, Traditional MFA, and 2FA is essential for choosing the right security model. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they deliver very different levels of protection, user experience, and intelligence.
This section breaks down those differences in a clear, practical way for both beginners and experts.
How 2FA Works: A Static Second Step for Basic Security
2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) adds a second layer of security on top of a password, typically through SMS OTP, TOTP apps, email codes, or push notifications.
While it significantly improves security compared to password-only logins, 2FA is still a static process every login triggers the same challenge, regardless of context or risk.
Limitations include:
-
Vulnerability to SIM-swaps, OTP interception, and phishing
-
Extra friction for every user, even trusted ones
-
High dependency on reliable devices or networks
-
No real intelligence about unusual login behavior
2FA strengthens security, but it does not adapt to evolving threats or user context.
How Traditional MFA Works: More Factors, but Still Static
Traditional MFA expands on 2FA by offering multiple factor types passwords, OTPs, security keys, or biometrics but the logic remains similar: All users must complete the same MFA steps every time.
While it’s more flexible and secure than basic 2FA, it still follows rigid rules:
-
Every login triggers MFA
-
No evaluation of risk or behavior
-
No contextual adjustments
-
More friction for high-volume consumer apps
Traditional MFA improves security but sacrifices user convenience by treating every login attempt equally regardless of whether the user is safe or suspicious.
How Adaptive MFA Works: Intelligent, Context-Aware, User-Friendly
Adaptive MFA is the evolution of MFA. Instead of using fixed rules, it evaluates risk signals in real time device trust, location anomalies, behavior deviations, IP reputation, and threat intelligence.
Based on these insights, the system decides whether to allow the user through seamlessly or require additional verification.
Key advantages:
-
Step-up challenges only when something looks risky
-
Seamless, frictionless experience for trusted users
-
Blocks or challenges suspicious activity instantly
-
Continuous learning and behavior analysis
-
Ideal for modern CIAM, zero-trust, and high-scale consumer apps
Adaptive MFA brings balance: maximum security with minimum friction.
The Clear Difference: Static vs Smart Authentication

The biggest distinction comes down to intelligence:
-
2FA = static second step
-
Traditional MFA = multiple static steps
-
Adaptive MFA = dynamic, risk-based decisions
Organizations choosing between them should consider their user base, threat landscape, and long-term authentication strategy. While 2FA and traditional MFA remain useful, only adaptive MFA meets the demands of today’s identity-first, phishing-heavy, high-risk digital environment.
Adaptive MFA in CIAM
Adaptive MFA becomes even more valuable when viewed through the lens of Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM). Unlike workforce identity, where users are internal and controlled, customer identity environments serve millions of unpredictable, diverse, global users. This scale and unpredictability make static authentication models inefficient, expensive, and often frustrating for real customers.
In advanced CIAM implementations, adaptive MFA often works alongside adaptive SSO, enabling frictionless access across multiple applications while still enforcing step-up authentication whenever risk thresholds are crossed.
Adaptive MFA solves these challenges by offering security that grows smarter without disrupting the user journey.
Designed for High-Volume Consumer Login Flows
Consumer applications experience unpredictable login spikes from flash sales to seasonal peaks. Traditional MFA introduces friction that can choke conversion during these high-traffic moments.
Adaptive MFA ensures that trusted customers pass through login quickly, reducing queue times, OTP delays, and other bottlenecks. It keeps authentication fast even during peak usage.
This is especially important for industries like retail, media, gaming, travel, and eCommerce where every second counts during login.
Reduces Abandonment and Improves Conversion Rates
Customer-facing platforms live or die by smooth user journeys. Static MFA creates friction every time a user logs in, increasing the likelihood of drop-offs during registration, checkout, or everyday access.
Adaptive MFA challenges users only when necessary, meaning more seamless sign-ins and fewer reasons for users to abandon the flow. This directly boosts conversion, retention, and session completion rates.
Protects Against Account Takeovers (ATO) at Scale
Large user bases are prime targets for account takeover attacks. Credential stuffing, bot assaults, password reuse, and phishing campaigns can hit millions of accounts at once.
Adaptive MFA doesn’t just add a second factor it uses real-time intelligence to identify anomalous activity and block, challenge, or flag suspicious attempts automatically.
This proactive, dynamic defense is critical for CIAM environments, where user trust and brand reputation are at stake.
Customizable for Global, Diverse User Groups
Not all users have the same devices, capabilities, or connectivity. OTPs might fail for users in certain regions. Push notifications might not work for others.
Adaptive MFA adjusts the authentication flow based on user context, making global compatibility far more achievable. It can even tailor authentication methods based on local regulations, device types, or risk levels.
This flexibility makes it ideal for multinational platforms with varied user behavior.
Aligned with Modern Identity-First & Zero-Trust Strategies
CIAM has evolved from simply managing user accounts to becoming the first line of security in a zero-trust environment. In a world where threats bypass infrastructure and target users directly, adaptive authentication ensures verification happens intelligently and continuously.
Instead of assuming trust after login, adaptive MFA keeps evaluating context throughout the session perfect for modern, identity-first security designs.
Real-World Use Cases & Industry Scenarios
Adaptive MFA is not just a theoretical improvement it solves real challenges across industries where user behavior, risk patterns, and customer expectations vary widely. Because it balances strong protection with low friction, adaptive authentication fits naturally into any sector that prioritizes secure and seamless customer experiences.
1. Banking and Financial Services
Financial services face some of the highest levels of fraud, credential stuffing, phishing, and account takeover attempts. Adaptive MFA helps banks distinguish between trusted customers and suspicious behavior instantly.
For example, if a user logs in from their usual device and city, the system grants access without extra steps. But if the same account is accessed from a risky network or a new country, adaptive MFA automatically enforces stronger step-up checks like biometrics or security keys.
This preserves user convenience while maintaining airtight protection across digital banking, mobile apps, and fintech platforms.
2. Retail & eCommerce
Checkout friction kills conversions. For online retailers, adding extra MFA steps at the wrong moment can directly impact revenue.
Adaptive MFA keeps trusted shoppers moving quickly by allowing seamless logins during everyday purchases. When something seems off, such as an unusual shipping address, a suspicious IP address, or an impossible travel route, the system triggers additional verification.
This approach reduces abandoned carts, lowers fraud, and helps retailers maintain a smooth buying experience across global markets.
3. SaaS Platforms & Enterprise Applications
SaaS platforms serve diverse user personas from everyday employees to high-privilege admin accounts, each with different risk levels. Adaptive MFA allows SaaS providers to tailor authentication based on user roles, device types, and behavior patterns.
High-risk admin actions can require stronger verification, while routine user logins can remain frictionless. This creates a balanced security model across self-service portals, dashboards, and multi-tenant SaaS environments.
4. Healthcare & Regulated Industries
Healthcare systems must balance strict compliance requirements with real-world usability for doctors, staff, and patients. Adaptive MFA helps maintain HIPAA- and PHI-compliant access without constantly interrupting workflows.
It ensures sensitive data access requires strong verification, while low-risk sessions like checking appointment schedules or accessing patient portals remain smooth and fast.
5. Media, Gaming & High-Traffic Consumer Apps
Apps with millions of users face unique challenges: bot attacks, massive login surges, and global usage patterns. Static MFA cannot scale efficiently in this environment.
Adaptive MFA intelligently handles spikes by reducing unnecessary steps for legitimate users and focusing computational effort on suspicious activity. This creates a secure and high-performance login experience for platforms built around entertainment, video streaming, or gaming.
6. Government Services & Public Portals
Government applications require strong authentication due to sensitive citizen data. Adaptive MFA provides security without overwhelming users.
By analyzing risk context location, behavior, and device trust it allows low-risk routine tasks to be completed smoothly while protecting sensitive interactions behind stronger verification layers.
The Future of Adaptive Authentication
Adaptive MFA is not just a trend; it is the foundation of the next generation of digital identity security. As threats evolve and user expectations rise, authentication must become smarter, more context-aware, and less intrusive.
As identity ecosystems mature, adaptive authentication combined with adaptive MFA will become the default security model for customer identity, replacing static MFA entirely in high-scale, zero-trust environments.
The future of adaptive authentication reflects this shift, blending intelligence, automation, and seamless user experience into a unified security model.
AI-Driven Risk Engines Will Power Authentication Decisions
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, static rules will no longer be enough. The next wave of adaptive MFA will rely heavily on AI and machine learning to analyze patterns, detect anomalies, and predict malicious activity before it happens.
These AI-driven risk engines will learn from millions of signals across devices, behaviors, and environments, offering more accurate and real-time threat assessments than manual interventions ever could.
Continuous Authentication Will Replace One-Time Verification
Today’s authentication often ends at login. Once a user gains access, the session is trusted until manually revoked. Future adaptive systems will continuously evaluate user behavior, device stability, and environmental trust not just at the moment of login, but throughout the entire session.
This continuous evaluation will reduce lateral movement attacks, insider threats, and hijacked session exploits without increasing user friction.
Passwordless + Adaptive MFA Will Become the New Standard
Passwordless authentication solves a major portion of today’s security challenges, but when combined with adaptive MFA, it becomes significantly more powerful.
Passkeys, WebAuthn, and device-bound biometrics already provide high security and low friction. Adaptive intelligence elevates them further by deciding when a user needs additional verification or when the device alone is enough. This combination creates a seamless, phishing-resistant, future-proof authentication model.
Identity-First Security Will Drive Authentication Architecture
The industry is shifting from network-centric to identity-centric security. Instead of relying on firewalls or VPNs as the primary defense, authentication becomes the first and most critical checkpoint.
Adaptive MFA aligns perfectly with this philosophy: it treats every login attempt as a potential risk, evaluates context dynamically, and enforces trust step by step.
Regulatory Pressure Will Push Organizations Toward Smarter MFA
Global privacy and security standards are becoming increasingly stringent. Regulations such as GDPR, PSD2, and HIPAA, as well as industry best practices, increasingly require risk-based authentication for sensitive operations.
Adaptive MFA satisfies these expectations by identifying risky scenarios automatically and enforcing the right level of verification without bottlenecking users.
Adaptive authentication represents the ideal balance between protection and usability. As the digital ecosystem continues to expand and identity threats become more complex, adaptive MFA will evolve into the backbone of modern CIAM an intelligent, predictive system that continuously adjusts security in ways users barely notice.
Conclusion
Adaptive MFA represents the natural evolution of authentication in a world where threats are unpredictable and user expectations demand speed. Unlike traditional MFA or 2FA, which apply static rules to every login, adaptive authentication intelligently adjusts to context, behavior, and real-time risk.
The result is a system that protects users with precision while keeping their experience as smooth as possible.
For organizations operating at scale, whether in retail, finance, SaaS, gaming, or global consumer environments, adaptive MFA offers the best of both worlds: stronger defense against account takeovers and dramatically reduced friction for trusted users. It aligns perfectly with identity-first security models, zero-trust frameworks, and modern CIAM strategies that prioritize both security and usability.
As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated and digital identity becomes a core part of brand trust, adaptive MFA isn’t just a nice-to-have, it's a competitive advantage. Platforms that adopt risk-based, context-aware authentication will deliver safer, smarter, and more user-friendly experiences that stand out in crowded markets.
Ready to Deliver Smarter, Adaptive Authentication?
LoginRadius helps organizations transition from static MFA to a fully intelligent, adaptive security model without sacrificing user experience.
With LoginRadius, you can enable:
-
Adaptive MFA with real-time risk scoring
-
Phishing-resistant authentication (WebAuthn, biometrics, passkeys)
-
Seamless passwordless login flows
-
Device intelligence, IP risk analysis, and behavioral signals
-
Scalable CIAM built for global consumer applications
-
Low-friction authentication that boosts conversion and trust
If you're ready to see how adaptive authentication can transform your customer experience:
Book a quick demo with LoginRadius and explore the future of secure, frictionless login.
FAQs
Q: What is Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication?
A: Adaptive multi-factor authentication (Adaptive MFA) uses contextual and behavioral signals—like device, location, and IP risk—to decide whether a user needs additional verification. It strengthens security while reducing friction for trusted users.
Q: How is Adaptive MFA different from traditional MFA?
A: Traditional MFA challenges every user the same way, while Adaptive MFA intelligently adjusts verification based on real-time risk. Users only face step-up checks when something looks suspicious, making the login flow smoother.
Q: What signals does Adaptive MFA analyze?
A: It evaluates device fingerprints, location consistency, network trust, behavior patterns, IP reputation, and threat intelligence. These signals help determine whether a login should be seamless, challenged, or blocked.
Q: Is Adaptive MFA better than 2FA?
A: Yes. 2FA adds a static second step, but Adaptive MFA uses dynamic context and real-time risk scoring to protect users more accurately. It offers stronger security with minimal user friction.

Featured Posts
Adaptive MFA vs MFA: The Smarter Choice for Modern Security
Security Keys vs TOTP vs Push: Which Authentication Method Is the Strongest?
2FA Benefits & Risks: Real Tradeoffs Behind Modern Authentication
Beginner’s Guide to Authentication and Authorization in Digital Security
A Complete Guide to Adaptive MFA for Modern CIAM
What Is OTP?
The Rise of Agentic IAM: Securing Agents Before They Go Rogue
What Is Single Sign-On (SSO)?
Your Identity Security Playbook: Stop Fraud, Catch Threats, and Make Customers Love Your Security
Passwordless & MFA in 2026: Passkeys, Push MFA, Device Trust, and Continuous Authentication
What Is Biometric Security?
What Is Device ID?
What Is Dynamic Access Control?
What Is 2FA and How It Works: Guide to Modern Authentication
What Is SMART on FHIR?
2FA in 2025: How Leading Providers Keep Digital Identities Safe
What Is a YubiKey?
Biometric Authentication Methods: How They Work & When to Use Them
Compliance Management: Processes, Systems & Best Practices
RBAC and Access Management: The Foundation of Secure IAM
How Does SAML Authentication Work?
ID Token vs. Access Token: Understand the Difference
AI-Driven Fraud Detection: The Future of Digital Trust
OIDC Authentication: How Modern Apps Verify Identity
A Complete Guide to 2FA Authentication in 2025: Methods, Risks, and Modern Best Practices
Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2025: Why Businesses Can’t Afford to Look Away
Secure Customer Experiences with Phone Authentication: Why Mobile Matters
Best Descope CIAM Alternatives in 2025
Passwordless Login: Technical Workflows, Business ROI, and Regional Adoption
Top 10 Frontegg Alternatives to Consider in 2025
Identity and Access Management in Banking: Why It’s Crucial for Security and Customer Experience
Top 10 FusionAuth Alternatives in 2025
Unlocking Secure Digital Experiences with Authorization as a Service
CIAM Platform Integrations: The Key to a Strong Customer Identity Strategy
Email is Hacked! 7 Immediate Steps to Follow
Data Governance in Healthcare: Best Practices & Future Trends
Why Social Login is a Game-Changer for eCommerce Login
Top WordPress Social Plugin Picks for Seamless Logins
Why Privacy-First Companies Choose Canada for Data Storage
Top Auth0 Alternatives for 2025: Simpler, Faster, and More Flexible CIAM Options
What Are Digital Certificates and How Do They Secure the Web
Why Hosting Your CIAM Solution in a Canadian Data Center Gives You the Edge
B2B IAM vs Workforce IAM: What Enterprises Must Know
Access Control in Security: What It Is and Why It Matters
The Making of The Power of Digital Identity: A Candid Interview with Rakesh Soni
What is Certificate-Based Authentication and Why It’s Used
6 Key Ecommerce Challenges in 2025 (And How CIAM Solves Them)
B2B vs B2C Authentication- A Quick Guide
Password Best Practices for Stronger Security
Building Community Beyond Borders: Our Thailand Story
1FA vs 2FA vs MFA: Which Method Secures You Best?
B2B IAM Best Practices and Architecture Guide
Adding Partner IAM With LoginRadius: A Complete Guide to B2B Identity Management
What is User Authentication, and Why is it Important?
What is Partner IAM / B2B IAM - A Complete Guide
Still Bending Workforce IAM for Your B2B Networks? Introducing LoginRadius Partner IAM—Built from the Ground Up
What is Biometric Authentication and How It's Changing Login
Location-Based Data Residency Boosts Trust and Conversions
The Impact of AI on Cybersecurity
PINs vs Passwords: Which is More Secure?
Why Global Businesses Trust Canada for Data Hosting Services
Passkeys vs Passwords: The Upgrade Your Security Needs
What is the Best Way to Authenticate Users?
Canada as a Global Hub for Privacy-First CIAM Platforms
How to Choose a Strong Password- A Quick Guide
A Complete Guide to Device Authentication Methods
What is a One-Time Password (OTP) ? – A Complete Guide
A Quick Guide to Username and Password Authentication
Types of Authentication and Identity Verification
What is Strong Authentication in Cybersecurity?
Top 9 User Authentication Methods to Stay Secure in 2025
Authentication vs Authorization: Key Differences, Real Examples & Best Practices
Guide to Authentication Methods & Choosing the Right One
Identification and Authentication: A Quick Comparison
Understanding Authentication, Authorization, and Encryption
Introducing the LoginRadius Trust Center: Always Up-to-Date and at Your Fingertips
What is Token Authentication and How Does It Work?
What is OTP Authentication and How Does it Work?
What is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)?
LoginRadius Launches Next-Generation CIAM Console: Self-Serve, No-Code, and Built for Speed
Quick Guide to Single-factor, Two-factor, and Multi-factor Authentication
Democratizing Authentication: Introducing LoginRadius' Free Forever Developer Plan
Mobile Authentication: Everything You Need to Know
What is Push Notification Authentication and How It Works?
Code Less, Build More: Unveiling LoginRadius' AI-Powered Developer Documentation
Types of Multi Factor Authentication & How to Pick the Best
Risk-Based Authentication vs. MFA: Key Differences Explained
Revamped & Ready: Introducing the New Developer-First LoginRadius Website
What is SCIM? A Developer's Guide to Understanding and Using SCIM
RBAC vs ABAC: A Developer’s Guide to Choosing the Right Fit
CISOs’ Top Cybersecurity Threats 2025: Scattered Spider, Deepfakes, and More
LoginRadius 2024: A Year of CIAM Innovations
What is Passkey Authentication - A Complete Guide
How AI-Enabled Cybersecurity Solutions Are Strengthening Our Online Security
What is Identity Orchestration
LoginRadius Releases 2024 Consumer Identity Report, Highlights the Shifting Trends in Consumer Preferences
Celebrating 8th Year Milestone: How Our Collaboration with a Leading Healthcare Company Transformed Millions of Lives
Unlock Your Digital Freedom: How Automating Passwordless Authentication Can Transform Your Security
How To Secure GenAI by Implementing RBAC In The Enterprise
The Hidden Pitfalls: Why Most CIAM Systems Fail Under Pressure
No More Login Hassles: Effortless Migration to LoginRadius Awaits
How Cookie Management Supports GDPR and CCPA Compliance
LoginRadius Launches Identity Orchestration for Seamless Identity Workflows
Passkeys: Unlocking Benefits for a Better Online Shopping Experience
AI and the Changing Face of Enterprise Security Threats
Leading the Charge in Customer IAM: LoginRadius Recognized as an Overall Leader by KuppingerCole
Gearing Up for Better Customer Experiences? Choose No-Code Identity Orchestration
Announcement - LoginRadius Launches PassKeys to Redefine Authentication Security and User Experience
Decoding the Rise of Zero-Trust Adoption in Government Sector
Say Goodbye to Passwords: How Passkeys Are Reinventing Online Security
Announcement - LoginRadius Unveils the Future of Authentication with Push Notification MFA
Is Your CIAM Adapting to Global Needs? 6 Key Areas to Win Privacy-Concerned Customers
The Growing Threat of Identity-Based Attacks and the Need for an Advanced Identity Security Approach
How AI Is Changing the Game in User Authentication
eIDAS 2.0: The Digital Revolution Is Here – Is Your Business Ready to Comply?
A Quick Guide To Choosing The Right Zero Trust Vendor
Cloud Security Governance: Protecting Assets in the Digital Frontier
What is Silver SAML Vulnerability and How Can We Protect Our Digital Identities?
Identity Security for Device Trust: Navigating 2024 & Beyond
Exciting Leadership Updates Amid Strategic Growth at LoginRadius
From Past to Present: User Authentication's Evolution and Challenges
How Does Multi-Tenancy in Customer IAM Solutions Boost Security?
How No/Low Code CIAM Balances Security and User Engagement?
Beyond Passwords: Navigating Tomorrow's Authentication Landscape
How does identity management address the top 5 security challenges in B2B SaaS?
Reinforcing Security with Advanced Risk-Based Authentication in 2024 & Beyond
2FA vs MFA: Understanding the Differences
Okta Token Theft Implicated in Cloudflare's Security Breach
Voice OTP by LoginRadius: Revolutionizing Secure and Seamless User Authentication
Which is Safer: Biometric or Password?
7 Reasons to Use Biometric Authentication for Multi-Factor Authentication
Exploring Digital Identity Verification with Effective Crucial Data Checks
5 Reasons Why LoginRadius Leads the Way in the CIAM Landscape in 2024 & Beyond
Above the Horizon: Exploring the Power of a Strong Cloud Identity Platform
Streamlining Authentication: Elevate User Experience with LoginRadius AutoLookup
A Journey Through Our Top 10 Blogs from 2023
Now and Beyond- Staying Ahead with the 10 Key Cybersecurity Trends of 2024
B2B SaaS SSO Login: Exploring Enterprise Considerations in 2024
Securing Corporate Applications: A Comprehensive Guide to Enterprise Application Security
Strengthening Security Measures: The Role of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Securing the Throne: Privileged Access Management (PAM) Best Practices Unveiled
7 Common Authentication Vulnerabilities to Steer Clear of
What is Identity Lifecycle Management?
Strengthening Security and Compliance: The Role of Identity Governance
Understanding the Okta Hack: Breach in Customer Support and Lessons for Organizations
Managing Generative AI Security Risks in the Enterprise- A Quick Guide
Empowering Your Security: Exploring the Advantages of Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP)
The Future of Personalization: Embracing Zero-Party Data
Comprehensive Guide to Flexible CIAM Deployment Options with LoginRadius
Small Steps, Big Shields: Navigating Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2023 Safely
Streamlining Access with Converged Identity Platforms
How Retailers Can Balance Privacy While Foiling Thieves
The Power of No-code Customer IAM in Reducing Churn
CIAM: Enhancing Security & Building Consumer Trust-All At Once
Maintaining Trust: Customer Identity Verification Challenges & Best Practices
Unlocking Smartphone Security: How to Hackproof Your Smartphone
Phishing-Resistant MFA Login for Mobile Applications: Strategies and Challenges
True Passwordless Authentication: Stronger Defense Against Cyberattacks
Identity Governance vs. Identity Management: Navigating the Differences
Navigating Identity Verification Challenges in Regulated Industries: 7 Effective Solutions
Enhancing Security: Leveraging 5 Real-Time Techniques to Detect Phishing Attacks
A Comprehensive Guide to the Five A's of Cloud Identity Management
Understanding the Difference Between Identity Access Management On-Premise and Cloud
Learn the Impact of Identity Theft on Businesses in 2023
LDAP Authentication: Meaning and How it Works?
7 Things Your Security Team Need To Know Before Creating A CIAM Strategy
Choosing Between Self-Managed and Service-Based SSO Solutions: A Comprehensive Comparison
What is Cloud Identity and its Benefits?
The Legal Implications of SSO: Privacy, Security, and Compliance
Data Privacy Laws for 2023: A Closer Look at 9 Key Regulations
4 Reasons Why SSO Integrations Are a Must-Have For Online Businesses
Consumer vs. Enterprise: Navigating the Dual Nature of Digital Identity
LoginRadius Releases Consumer Identity Trend Report 2023, Highlights The Future of Customer Identity
What is a Password Vault and How Does it Work?
How a Culture of Identity Governance Empowers Digital Transformation?
Securing the Digital Frontier: The Power of AI in Next-Gen CIAM
Replatforming 101: Everything You Need to Know
Best Practices for Username and Password Authentication
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right CIAM Solution
How to Use Identity Management at Every Stage of the Customer Journey?
Protecting Your Cloud Data: The Power of SaaS Security and IAM Governance
The Rise of Account Creation Fraud: What You Need to Know
Why Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Businesses Must Take A Strategic Approach To CIAM?
What are Self-Sovereign Identities?
7 Uncommon Cyber Attacks in 2023: Why Your Organization Needs To Be Ready For The Worst-Case Scenarios
Identity Modernization: What Is It & Why Should You Care?
A Lot Can Happen In The Cloud: Multi-Cloud Environment and its Optimization Challenges
Can Security and User Experience Co-Exist in the Authenticating and Authorizing Space?
Business On The Move: How Just-in-Time Migrations Are Making Smooth CIAM Transitions
3 Digital Onboarding Trends To Watch In 2023 (And What You Can Do About It Now)
6 Tips to Prevent Accidental Data Exposure Within Your Company
Top Priorities for Customer IAM Leaders in 2023 and How to Prepare
Electronic Theatre Controls: A LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Distributed Multi-Cloud Identity Management and Its Endless Business Benefits
How The Age Of Smart Credentials Is Rewriting The Rules For Physical Verification?
Incident Response Vs. Disaster Recovery: What’s The Difference and Which Do You Need?
The Customer Experience is About to Get Even Better With Passive Authentication
What is Dynamic Authorization & Why Does it Matter?
What’s the Difference Between Attack Surface and Attack Vector?
How Identity-Based Access Ensures Robust Infrastructure Security Amidst the Growing Identity Crisis?
2FA Bypass Attacks- Everything You Should Know
IAM vs. Customer IAM: Understanding the Role of CIAM in Accelerating Business Growth
Why MFA Fatigue Attacks May Soon Be Your Worst Nightmare?
InfoSec Director, Alok Patidar Answers Your Most Difficult Questions on Cybersecurity
Understanding MITRE ATT&CK Framework?
Identity Fabric vs. Zero Trust: Is One a Better Alternative Than The Other?
The Role of Customer Identity Management in IoT Security: How It's a Must!
Securing Centralized Access Without Compromising User Experience
User Authentication in the Metaverse: What’s Changing?
LoginRadius Pledges To Raise Awareness This Cybersecurity Month
Public Cloud Risks - Is Your Organization Prepared for Cloud Threats?
What Brands Need to Know for Building the Future of Data Compliance?
Okta Identity Credentials on the Radar of Oktapus Phishing Campaign
BC Municipality Digitizes its Citizen Services. LoginRadius Brings Identity to the Table.
The Role of Customer Authentication in Paving the Way for Digital Agility
What Brands Need to Know for Building the Future of Data Compliance?
6 Alternative Authentication Methods For Your Online Customers
Implementing Zero Trust? Make Sure You're Doing It Correctly
What is Federated SSO (Single Sign-On)?
MFA Prompt Bombing: Is it a New Threat Vector to Worry About?
Privacy-Centric Enhancements: CEO Rakesh Soni Shares His Thoughts on Shifting Data Strategies
The Role of Identity Management in Securing Your Citizen’s Data
Why is Data Privacy an Immediate Enterprise Priority?
What is Out-of-Band Authentication?
How Can Enterprises Use SSO to Boost Data Collection?
Why Your Business Needs A Simple Passwordless Experience (Minus the User Friction)
Will Apple’s ‘Lockdown Mode’ Reduce State-Sponsored Attacks?
Authentication, Identity Verification, and Identification: What's the Difference
IoT Botnet Attacks: Are They the Next Big Threat to Enterprises?
Skiperformance - a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Cross-Device Authentication and Tracking: The Opportunities and Underlying Privacy Risks
How Identity Modernization Will Thrive Business Success in 2022 and Beyond
The Pros & Cons of Reusable Digital Identity: What You Need To Know
What is Cloud Security and How it Works?
Age of No-Code Technologies: Identification and Authentication
SSO vs. Social Login: What’s the Difference? [Infographic]
Planning a Digital Makeover For Your Business? LoginRadius CIAM Can Help!
What is Cloud Computing?
Authentication vs Login - What’s the Difference?
How a Simple Password Reset Can Ruin Your Customer's Experience
GovTech is On The Rise: How Can This Technology Improve Government Services?
5 Access Management Best Practices and Benefits For Businesses
LoginRadius Releases Consumer Identity Trend Report 2022, Key Login Methods Highlighted
BITB Attacks: The New Destructive Phishing Technique
5 Reasons Why You Need to Strengthen Your Identity Authentication
What is the Difference Between MFA vs. SSO?
What is Login Authentication?
5 Ways to Improve Your Customer Verification Process
5 Myths About Phishing You Should Know
4 Common Security Issues Found In Password-Based Login
Personal Information and PII - What’s the Difference?
OTT Platforms and CIAM: How Identity Management Ensures Millions of Viewers to Scale with Ease
Is the Rise of Machine Identity Posing a Threat to Enterprise Security?
LoginRadius Integrates Search in Navigation for Better Customer Experience
5 Privacy Threats in Social Media You Should Know in 2022
Importance of Multi-factor Authentication for SSO
How LoginRadius Creates a Perfect Harmony of UX and Security
Smart Cities and Cyber Security Trends to Watch Out in 2022
Harry Rosen, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Top 7 Security Tips from LoginRadius’ Cybersecurity Expert to Follow in 2023
Top 7 Security Tips from LoginRadius’ Cybersecurity Expert to Follow in 2023
This Is How Scammers Get Your Email Address & How to Stop Them
Will Decentralized Auth Change the Perception of Consumer Identities in 2022?
Emerging Threat of Deepfakes: How To Identify And Prepare Against It
Everything You Need to Know Before Buying Cyber Insurance in 2022
5 Challenges for Government Adoption of Citizens’ Access Control
Are You Thinking of Token Management for Your API Product? Think about JWT!
LoginRadius Launches M2M Authorization for Seamless Business Operations
LoginRadius Offers PerfectMind Integration for a Seamless UX
Take Control of Your CIAM Environment with LoginRadius' Private Cloud
10 Tips From CIAM Experts to Reduce the Attack Surface of User Authentication
How LoginRadius Webhook Allows You to Sync Your Data in Real-Time
Federated Identity Management vs. SSO: What's The Difference?
How to Evaluate the Quality of Your User Authentication System
How LoginRadius Offers Customer-Centric Capabilities that Drive ROI
3 Best Stages of IT Security for Implementing Gartner's CARTA
How to Choose the Right User Authentication Option for your Product
An Introduction to Financial-Grade API (FAPI) for Open Banking
Why is PKI The Future of Secure Communications
How to Find the Right SSO Strategy that Fits Your Business
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Businesses in 2023 & Beyond [Infographic]
SSO Integration: How to Secure the Customer Experience on Loyalty Platforms
The Top 5 Trends in CIAM We’ve Watched in 2021
The Major Challenges of Customer Identification in the Retail Industry
Cybersecurity Awareness Month: Predicting the Deadliest Cyber Attacks in 2022
LoginRadius Delivers a Seamless User Experience that Increases Conversions through Enhanced Progressive Profiling
Avoid these Common Mistakes When Dealing with Data Breaches
Tiroler Tageszeitung (TT), a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
What are Security Keys? What are its Advantages?
Everything You Need to Know About OAuth and How it Works
Decentralized Authentication: What Is It And How It Is Changing the Industry
Getting Started with OpenID Connect
Discover the Benefits of Re-Authentication for Enhanced Security
Stand Out from the Crowd: Improve Your Customer Support with CIAM
Why Should You be Customizing Your Identity System to Your Needs
SMS Authentication — Can it Really Protect Your Business?
How Poor Login Concurrency can Impact OTT Platforms' Business
A Comprehensive Guide to Privileged Access Management (PAM)
How Cities Can Improve Civilians’ Digital Experience with Unified Identity
Refresh Tokens: When to Use Them and How They Interact with JWTs
How Progressive Disclosure Makes Your User's Onboarding Easy
What is Digital Identity Verification and Why is it Necessary?
How OTT Services can Simplify Authentication on Various Devices
A Beginner's Guide to Zero Trust Security Model
What is Identity Security?
What is a Token? What are its Pros and Cons?
How to Scale Your Business Quickly with Identity Management
How to Manage Situation After a Data Breach
How to Strike the Right Balance Between Security and Consumer Experience
How NIST is Changing Password Creation in 2021
COVID-19 and Beyond: 5 Risk Management Essentials for Your Enterprise
How WebAuth Secures Your Users’ Login
Adaptive Authentication- Is it the Next Breakthrough in Customer Authentication?
The Rise of BYOI (Bring your own Identity)
Understanding PII Compliance: A Key to Enterprise Data Security
Cyber Security Round-Up: What Happened in June 2021
How Businesses are Experiencing Digital Transformation with Consumer IAM
What is SAML SSO?
LoginRadius Offers Additional Security Layer through Newly-Enhanced Step-up Authentication Feature
Why Big Merchants Need to Deliver a Unified Consumer Experience?
All About Google One Tap Login—Explained!
What to Do if Someone Steals Your JSON Web Token?
What is Web SSO
Working With Industry Authorization: A Beginner's Guide to OAuth 2.0
Password History, Expiration, and Complexity: Explained!
SAML vs OIDC: How to Choose the Right SSO Protocol for Your Business
10 Reasons For Businesses to Implement SASE with a Zero Trust Strategy
Move beyond Traditional Risk Management with Holistic APIs
Identity Providers Explained: How IdPs Power SSO, SAML, and OIDC
What is User Session Management?
How Entertainment Companies Use the LoginRadius CIAM platform
Consumer Data Protection: How to Handle Data Breaches in Your Business
Top 5 User Provisioning Mistakes Enterprises Should Avoid in 2021
How Secure is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
The Changing Role of Identity Management in Enterprise Decision-Making
5 Reasons Why Cloud Governance Matters For Your Business
Implementing Effective Social Authentication Solution with LoginRadius
The Future of Authentication is Passwordless With Magic links
Handling Scalability and Enhancing Security with LoginRadius
Maintaining Quality Data Security Practices
Introduction to Mobile Biometric Authentication
Data Security in Hospitality: Best Practices for Operating In a Post-COVID Era
The Role of Identity management in the media industry
A Detailed Guide on How UX/UI Affects Registration
What Is a Salt and How Does It Boost Security?
Login Using Microsoft Account
A Detail Guide to Consent Management and Processing Data
Workflow Automation- What is it and Why Do You Need It?
How Companies can Enable Account security for their Consumers
What is Progressive Profiling and How it Works?
Password Spraying: What Is It And How To Prevent It?
5 Tips to Prevent OAuth Authentication Vulnerabilities
Calculating ROI, Build vs Buy (Part 1)
Identity Theft Frauds- Staying Ahead in 2021
What is privacy compliance and why is it so important?
Authentication Explained: What it is, How it Works, and Why it Matters in Cybersecurity
What are Federated Identity Providers?
Login with Google Apps
What is Passwordless Login?
What is Standard Login
IoT authentication in the airline industry
Announcement - Authentication API Analytics to Evaluate the Performance of LoginRadius APIs for Your Applications
Multi-Factor Authentication - A Beginner’s Guide
Single Sign-On- A Beginner’s Guide
Top 10 Cybersecurity Predictions for 2021 That SMBs Must Know
How to Put Yourself In Control of Your Data by Leveraging LoginRadius' SSO
What Is User Management?
How CIAM Will Address The 5 Most Popular Issues In The Utility Industry
CIAM Continues to Draw Attention as Okta acquires Auth0
Protecting a Unified Cloud Platform through Cloud Security Management
What is Continuous Authentication
What is Brute Force Attack
What is Identity Authentication: How It Works and What’s Ahead
What is the Power of PIN Authentication Security?
What is Risk-Based Authentication (RBA)?
SaaS IAM for B2B: The Key to Secure, Scalable Partner Access
Understanding the Difference Between Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Cloud [Infographic]
What is Phone Login
Why Organizations Must Use API-Driven CIAM for Digital Agility
Why Do Consumers Prefer Social Login [Infographic]
5 Best Practices of Implementing Business Resilience during a Data Breach
What is Broken Authentication Vulnerability and How to Prevent It?
Announcement - LoginRadius Introduces Convenient and Secure Biometric Authentication for Mobile Apps
6 Strategies to Secure Your Cloud Operations Against Today's Cyber Threats
Announcement - LoginRadius Introduces Password Policy to Ensure Best Practices for Businesses and Consumers
How Is New Age Ciam Revolutionizing Consumer Experience?
What is Federated Identity Management
7 Common Web Application Security Threats
Identity Management in Cloud Computing
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Announcement - LoginRadius Announces Identity Brokering To Establish Trust Between Identity and Service Providers
5 Ways User Onboarding Software Can Revamp Your Application
How to secure an email address on your website
What is Formjacking
DNS Cache Poisoning: Why Is It Dangerous for Your Business
How to Set Up Two-factor Authentication on All Your Online Accounts?
What is Digital Transformation
The Do's and Don'ts of Choosing a Secure Password
How To Secure Your Contact Form From Bot Attacks
What is Identity Proofing and Why is it Important?
Identity Governance in CIAM: Taking Control of Your Data
Announcement: LoginRadius Embraces Privacy Policy Management Amid Heightened Regulatory Updates
Login Security: 7 Best Practice to Keep Your Online Accounts Secure
9 Data Security Best Practices For your Business
How To Make Sure Your Phone Isn’t Hacked
Safe Data Act: A New Privacy Law in the Town
Email is Hacked!: 7 Immediate Steps To Follow
Announcement - LoginRadius Smart and IoT Authentication to Offer Hassle-Free Login for Input-Constrained Devices
Announcement - LoginRadius Announces Authentication and SSO for Native Mobile Apps
9 Identity and Access Management Best Practices for 2021
E-commerce Security: 5 Ways to Enhance Data Protection During the Shopping Season
Identity Management in Healthcare: Analyzing the Industry Needs
Identity Management for Developers: Why it's required more than ever
Announcement - LoginRadius Launches Passwordless Login with Magic Link or OTP, Keeps Barriers Low During Registration and Login
Announcement - LoginRadius Simplifies the Implementation of Federated SSO With Federated Identity Management
Best IDaaS Provider - Why Loginradius is Considered as the Best IDaaS Solution
Social Engineering Attacks: Prevention and Best Practices [Infographic]
Announcement – LoginRadius Announces the Availability of User Management
Consumer Identity Management for the CMO, CISO, and CIO
Announcement - LoginRadius Delivers Exceptional Authentication With The Launch Of Identity Experience Framework
Best SSO Provider: Why LoginRadius Is Considered As The Best SSO Solution
Single-Page Applications: Building A Secure Login Pathway with LoginRadius
LoginRadius Releases Consumer Digital Identity Trend Report 2020
Securing Enterprise Mobile Apps with LoginRadius
Data Governance Best Practices for Enterprises
Top 10 Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Build vs Buy: Securing Customer Identity with Loginradius
LoginRadius Identity Import Manager, An Automated Feature for Seamless Data Migration
Why Identity Management for Education Sector has Become Crucial
LoginRadius Approves Consumer Audit Trail for In-Depth Data Analysis and Risk Assessment
Online Casino and Gambling Industry Is Gaining Momentum, So Is the Cyber Threat
How LoginRadius Future-Proofs Consumer Data Privacy and Security
Authentication and Authorization Defined: What's the Difference? [Infographic]
LoginRadius Launches Consent Management to Support the EU's GDPR Compliance
Streaming Applications: How to Secure Your Customer Data
Protecting Organization From Cyber-Threats: Business at Risk During COVID-19
Announcement - LoginRadius China CIAM for Businesses to Benefit From Its Lucrative Market
Why Financial Industry Needs an Identity Management System Now More Than Ever
Announcement - LoginRadius Now Supports PIN Login with Enhanced Features
Corporate Account Takeover Attacks: Detecting and Preventing it
Marriott Data Breach 2020: 5.2 Million Guest Records Were Stolen
How LoginRadius Help Retail and E-commerce Industry to Manage Customer Identities
Announcing New Look of LoginRadius
LoginRadius Announces Its Business Continuity Plan to Fight COVID-19 Outbreak
Unlock the Future of Smart Cities
How LoginRadius Helps Enterprises Stay CCPA Compliant in 2020
Social Login Explained: How “Login with Social Media” Boosts Conversions
Identity as a Service (IDAAS): Managing Digital Identities (Updated)
The Worst Passwords of 2019
Digital Privacy: Securing Consumer Privacy with LoginRadius
One World Identity Report Names LoginRadius a Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) Industry Leader
Benefits of Single Sign-On: Advantages, Security, and ROI Explained
Cloud Security Challenges Today: Expert Advice on Keeping your Business Safe
The Role of Passwordless Authentication in Securing Digital Identity
LoginRadius presents at KuppingerCole Consumer Identity World
Digital Identity Management: 5 Ways to Win Customer Trust
CCPA vs GDPR: Global Compliance Guide [Infographic]
Credential Stuffing: How To Detect And Prevent It
A History of Human Identity in Pictures Part 3
A History of Human Identity in Pictures Part 2
A History of Human Identity in Pictures - Part 1
What is Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) and How does it Work?
Why LoginRadius is the Best Akamai Identity Cloud (Janrain) Alternative
5 Reasons To Know Why B2C Enterprises Should Use Single Sign-On
8 Key Components of a Perfect CIAM Platform
What is CIAM? A Complete Guide to Customer Identity and Access Management
What is Single Sign-On (SSO) and How it Works?
California's CCPA 2.0 Passed: Everything You Need to Know About the New CPRA
IAM vs. CIAM: Which Solution is Right For You?
Looking for a Gigya Alternative? Try LoginRadius, a Superior and Modern Identity Platform
Presenting: Progressive Profiling from LoginRadius
Best Practices for Choosing Good Security Questions
How Do I Know If My Email Has Been Leaked in a Data Breach?
The Death of Passwords [Infographic]
How to Use Multi-Factor Authentication When You Don’t Have Cell Phone Access
The Customer Identity Infrastructure that Cruise Line Passengers Don’t See
Why Your Enterprise Needs a Digital Business Transformation Strategy
Reconsidering Social Login from a Security and Privacy Angle
Improving Customer Experience in the Public Sector
Customer Spotlight - Hydro Ottawa
Digital Transformation: Safeguarding the Customer Experience
Rede Gazeta, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
4 Barriers to Building a Digital Business and How to Overcome Them
LoginRadius Announces $17M Series A Funding from ForgePoint and Microsoft
BroadcastMed, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Why Municipalities Are Investing in Citizen Engagement
Customer Experience is Driving Digital Transformation
Identity Fraud Hits All-Time High in 2017
Phishing Attacks: How to Identify & Avoid Phishing Scams
IFMA, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Canada To Fine Companies For Not Reporting Data Breaches
Mapegy, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Aurora WDC, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
IOM X, a LoginRadius Customer Success Story
Customer Identity Preference Trends Q2 2016
Customer Identity Preference Trends Q1 2016

