Introduction
We live in an age where the average employee, partner, or customer interacts with dozens of applications every single day, from collaboration platforms and CRMs to analytics dashboards and cloud tools. As digital ecosystems expand, so does the complexity of managing access. Multiple usernames. Endless passwords. Frequent resets. And every login screen? A new opportunity for risk.
That’s the paradox of modern connectivity: the more connected we are, the more fragmented our access becomes. Every organization, regardless of size, is now facing a familiar challenge: how to deliver frictionless access for users while keeping digital identities secure from evolving cyber threats.
Enter Single Sign-On (SSO), powered by SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language), the unsung hero behind seamless authentication experiences. These technologies quietly handle what users often take for granted: the ability to log in once and securely access everything they need without repeatedly entering credentials.
In this blog, we’ll break down what SSO and SAML actually mean, how they work behind the scenes, and why they’ve become indispensable pillars of enterprise cybersecurity and CIAM.
Whether you’re a developer implementing authentication protocols, a security architect refining your access strategy, or a business leader navigating compliance and productivity goals, understanding SAML authentication isn’t optional anymore. It’s the key to balancing convenience, control, and security in today’s identity-driven world.
What Is Single Sign-On (SSO)?
If you’ve ever logged into your email and suddenly gained access to your calendar, documents, and chat tools without re-entering your credentials, you’ve already experienced Single Sign-On (SSO) in action. It’s one of those invisible technologies that quietly makes digital life easier, yet it carries a profound impact on how modern organizations handle identity and security.
At its core, SSO is a user authentication method that allows individuals to access multiple applications using a single set of credentials. Once a user signs in, a trusted authentication session is established, granting access to all connected systems without requiring repeated logins. This not only eliminates password fatigue but also sets the stage for a consistent, secure access experience across platforms, devices, and even organizational boundaries.
But SSO isn’t just about saving time. It’s about redefining trust. In traditional systems, each application verifies a user separately, creating isolated “islands” of authentication and, consequently, multiple vulnerabilities.
With SSO, authentication happens once through a central identity provider (IdP), which securely verifies who you are and then shares that proof of identity with other authorized applications. This approach builds a trust network where identity verification is streamlined, standardized, and far more resilient to attacks like phishing or credential stuffing.

Why Modern Businesses Rely on SSO
In today’s enterprise environment, where remote work, hybrid cloud infrastructure, and SaaS adoption are the norm, SSO has become a strategic necessity rather than a convenience feature.
-
For users, it means frictionless access. They can jump between tools like Slack, Salesforce, or internal portals without juggling multiple logins.
-
For IT teams, it means centralized control. Administrators can monitor sessions, enforce password policies, revoke access instantly, and integrate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for stronger security, all from one console.
-
For security leaders, it means a unified front against identity threats. Fewer passwords to manage means fewer attack surfaces, and centralized authentication helps maintain compliance with standards like SOC 2, GDPR, or ISO 27001.
The Core Principle of SSO: One Identity, Many Doors
The beauty of Single Sign-On lies in its simplicity: you sign in once, and the system handles the rest. But underneath that simplicity is a powerful idea: trust shared across applications.
Imagine walking into a corporate campus. You swipe your access card once at the main gate, and from that moment on, every door you open in your office, the meeting room, or even the cafeteria recognizes that you’re already cleared to enter. You don’t need to keep proving who you are at every door. That’s exactly what SSO does in the digital world.
Once you log in, your identity is verified by a trusted system, and that trust extends across all the connected apps you’re authorized to use. Whether it’s your CRM, analytics dashboard, or project management tool, they all “recognize” you because your identity has already been confirmed.
This simple principle makes life easier for everyone:
-
For users, it means fewer interruptions and a smoother workflow.
-
For teams, it removes the constant password juggling that slows productivity.
-
For organizations, it reduces the risk of weak or reused passwords, one of the most common causes of breaches.
In today’s fast-paced, multi-device world, people expect speed and simplicity. They want to log in once and get on with their work, not spend time remembering passwords or dealing with account lockouts. SSO delivers exactly that: a trusted, consistent way to move through the digital workplace without friction or risk.
It’s a quiet revolution in how we experience security, one login that unlocks everything you need, while still keeping your data safe behind the scenes.
Security Benefits of SSO
When people hear “Single Sign-On,” their first thought is usually convenience, but its biggest strength lies in security. In fact, SSO is one of those rare technologies that make life easier and safer at the same time.
Every login is a potential entry point for attackers. The more passwords your users manage, the more vulnerable your organization becomes. People reuse passwords, store them in plain text, or fall for phishing emails, and cybercriminals count on that. SSO helps change the game.
By centralizing authentication through a trusted, secure identity provider, SSO minimizes the number of times users enter their credentials. Fewer passwords mean fewer chances for theft, exposure, or misuse. This drastically reduces common attack surfaces, such as password spraying and credential stuffing, two of the leading causes of data breaches today.
1. One Login, Stronger Controls
Instead of forcing users to remember dozens of passwords, SSO creates a single, protected gateway. Organizations can strengthen this gateway with modern security controls such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) or adaptive risk analysis. That means even if an attacker gets hold of a password, they’ll still face another layer of verification, keeping your data safe behind multiple layers of defense.
2. Centralized Oversight and Rapid Response
From an administrative standpoint, SSO also gives IT and security teams greater visibility. They can monitor access patterns, set session timeouts, revoke user access instantly, and enforce password policies consistently across all applications. When someone leaves the organization, one action at the identity provider instantly revokes access everywhere, no lingering logins, no forgotten accounts.
3. Trust That Scales
Perhaps the most overlooked advantage of SSO is trust. When authentication flows through a single, verified channel, both users and systems operate with confidence. It’s easier to comply with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR, and it aligns with modern frameworks like Zero Trust Security, where every access request must be verified.
In short, SSO is more than a convenience feature; it’s a shield. It reduces human error, consolidates security controls, and strengthens organizational resilience against identity-based threats.
Because true security isn’t about making access harder, it’s about making it smarter.
What Is SAML? The Backbone of Secure Single Sign-On
Now that we’ve explored what Single Sign-On (SSO) does, it’s time to meet the framework that makes it all possible: SAML, short for Security Assertion Markup Language.
At first glance, the name might sound like something only a developer would care about. But in reality, SAML quietly powers most of the login experiences you already trust, from your workplace apps to your university portals and cloud dashboards. It’s the digital handshake that happens behind the scenes, confirming, “Yes, this user really is who they claim to be.”
Think of SAML as the translator between two worlds:
-
One world is the Identity Provider (IdP), the system that knows who you are and verifies your login.
-
The other world is the Service Provider (SP,) the application you’re trying to access.
SAML enables these two systems to speak a common language of trust. When you sign in through your company portal (the IdP), SAML securely passes a digital “assertion” to the service provider, confirming that your identity has already been verified. The result? Instant access without re-entering your credentials.
Why SAML Matters Today
In today’s hybrid cloud world, where employees use SaaS apps, customers log into branded portals, and partners access shared systems, SAML acts as the glue that binds them all together. It ensures that identity travels safely across platforms and boundaries without exposing passwords or sensitive data.
For organizations, this means:
-
Secure authentication without storing credentials in every app.
-
Consistent user experience across multiple services.
-
Faster onboarding and offboarding, since access is managed from one trusted point.
And for users? It means a login experience that feels simple, safe, and seamless — exactly the way it should.
SAML has been around for years, but its relevance has only grown stronger with time. It’s not just a legacy standard; it’s a trusted foundation for enterprise identity federation worldwide. Many modern authentication frameworks, including cloud-native IAM and CIAM platforms, still rely on SAML to ensure secure, unified access at scale.
In essence, SAML is the trust bridge behind the magic of SSO, quietly proving your identity, protecting your credentials, and keeping every login secure, without slowing you down.
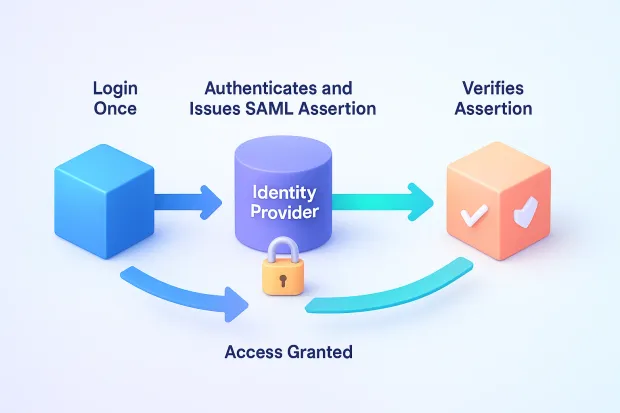
The Role of SAML in Authentication: Building a Bridge of Trust
To understand the role of SAML in authentication, let’s start with a simple truth: the internet is built on trust, and trust needs proof.
When you access an app, that app needs to be absolutely sure you are who you say you are. But verifying your identity directly every time isn’t practical, especially when you’re using dozens of different services throughout your day. That’s where SAML steps in as the trusted middleman that makes the verification process smooth, consistent, and secure.
How SAML Fits Into the Login Story
Imagine you’re checking into a hotel. At the front desk, you show your ID once, and they hand you a keycard. That keycard now gives you access to your room, the gym, and maybe even the breakfast lounge without having to show your ID again.
Here’s what happens behind the scenes
-
You try to access an application (like a CRM or a cloud dashboard).
-
The app says, “Wait, I don’t handle authentication myself. Let me check with someone who does.”
-
It sends a request to your Identity Provider (IdP) a trusted system that manages your login credentials.
-
The IdP verifies your identity (via password, MFA, or other secure methods).
-
Once verified, the IdP sends back a SAML assertion a digitally signed confirmation that says, “Yes, this user is authenticated.”
-
The app (known as the Service Provider) reads that assertion and grants you access instantly and securely.
You never have to enter your credentials into every app because SAML takes care of the heavy lifting in the background.
Understanding SAML Assertions
If SAML is the framework that connects trust between systems, then SAML assertions are the proof that makes that trust possible.
Think of an assertion as a digital passport, one that carries verified details about who you are, where you came from, and what you’re allowed to access. When you travel internationally, border control doesn’t need to know your whole life story, just that your passport is valid and issued by a trusted authority. In the same way, SAML assertions carry only the essential, verified information that a service needs to grant you access.
What Exactly Is a SAML Assertion?
A SAML assertion is a small, secure package of information created by your Identity Provider (IdP) once it verifies your identity. It’s then sent to the Service Provider (SP) the application you’re trying to access as proof that you’re already authenticated.
Inside this package are three key types of information:
-
Authentication statements: confirm that you successfully logged in, when, and how.
-
Attribute statements: include additional details about you, such as your name, email, or user role.
-
Authorization statements: specify what you’re allowed to do once you’re in the application.
Together, these statements form a complete identity picture that is enough for the service to know who you are and what permissions to grant.
Why SAML Assertions Matter
SAML assertions eliminate the need for users to send their passwords everywhere. Instead of multiple apps each storing and verifying your credentials, the assertion itself becomes the proof of your identity. It’s digitally signed by the identity provider, which means it can’t be altered or forged without detection.
That’s why service providers trust these assertions: they’re not just data; they’re cryptographically sealed promises from a system they trust.
Advantages of Using SAML
Whether you’re an employee signing into your daily tools, a customer accessing an online portal, or an IT admin managing hundreds of accounts, SAML brings order to the chaos of modern login systems. Let’s look at how it creates value for everyone involved.
1. Enhanced Security
Every password entered into an application is a potential weak spot. SAML minimizes that risk by allowing users to authenticate just once through a trusted identity provider (IdP). This reduces the number of stored credentials, lowers the risk of phishing and credential theft, and centralizes all authentication events in one secure location.
Because authentication happens in one trusted environment, organizations can also apply advanced security policies like multi-factor authentication (MFA), risk-based verification, and adaptive access controls to strengthen protection at the source.
In short, SAML replaces multiple small locks with one smart, reinforced gate that’s easier to secure and monitor.
2. Seamless User Experience
For users, SAML transforms login from a daily frustration into a background process. No more juggling dozens of passwords or being interrupted by repetitive login prompts. Once signed in, they can move between tools, email, CRM, analytics, and HR systems without a second thought.
This frictionless access experience builds trust, boosts productivity, and ensures users stay focused on what matters: their work, not their credentials.
3. Reduced Administrative Burden
Managing multiple user accounts across different systems can be a nightmare for IT teams. SAML makes this effortless by centralizing identity management.
Admins can create, update, or deactivate user accounts from one place with changes automatically reflected across all connected applications.
It’s not just about efficiency; it’s about precision. When employees leave, their access can be revoked instantly, closing potential security gaps and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
4. Scalability for Growing Organizations
As businesses expand, they inevitably add more tools, users, and integrations. SAML scales with them.
Instead of setting up new logins for every app or service, organizations can easily plug them into the same trusted authentication framework. That means faster onboarding, consistent access policies, and fewer integration headaches even in complex, multi-cloud environments.
5. Compliance and Audit Readiness
With privacy regulations tightening worldwide, organizations are under constant pressure to prove they handle identity data responsibly. SAML supports this by providing transparent, traceable authentication flows.
Security logs, access histories, and event tracking all live in one place, making compliance with standards like GDPR, SOC 2, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 far simpler and more reliable.
In essence, SAML isn’t just a protocol it’s a productivity enabler and a security cornerstone. It helps organizations move faster, stay safer, and deliver experiences users genuinely appreciate. By consolidating how identities are verified and trusted, SAML becomes the quiet force behind secure growth and digital confidence.
It’s no wonder that SAML remains one of the most trusted standards in enterprise identity management, even as newer technologies like OIDC and OAuth evolve alongside it. Because when it comes to balancing usability with security, SAML continues to get it just right.
SAML Integration and Benefits: Connecting Systems, Simplifying Security
Integrating SAML into your authentication process is like connecting all your digital doors to one smart, trusted key. It brings together different applications, platforms, and services under a single, secure identity framework, creating a smooth, unified experience for users while giving organizations stronger control and visibility over access.
In a world where companies rely on dozens (sometimes hundreds) of applications from HR and finance to analytics and cloud tools, SAML acts as the common language of trust that makes secure, frictionless login possible everywhere.
1. Streamlined User Experience
With SAML integrated into a Single Sign-On (SSO) system, users log in once and gain access to all connected applications. No more repetitive logins. No more password overload. Just one secure entry point that unlocks everything they need to get work done.
That ease of movement across platforms improves not only productivity but also user satisfaction. Employees and customers alike experience fewer barriers, faster access, and the peace of mind that comes from a login process that “just works.”
2. Centralized Identity Management
For IT and security teams, SAML is a lifesaver. Instead of managing logins and credentials across dozens of apps, everything flows through one secure identity provider (IdP).
That means:
-
Faster onboarding: Add a new user once, and they automatically gain access to all authorized apps.
-
Instant offboarding: Disable a user in the IdP, and access is revoked everywhere immediately.
-
Consistent policies: MFA, password rules, and access permissions are managed centrally, ensuring uniform security across the organization.
In short, SAML simplifies what used to be a complex web of accounts and credentials into a single, unified system of control.
3. Stronger Security and Risk Reduction
Every extra password is another potential breach point. SAML reduces these risks by centralizing authentication and minimizing password exposure.
Since login credentials never pass directly through individual apps, the chances of phishing, brute-force attacks, or credential leaks are drastically reduced. And when paired with advanced measures like adaptive MFA or device-based verification, organizations can detect unusual login behavior and apply step-up authentication instantly.
This layered approach strengthens security without disrupting the user experience, something every modern organization strives for.
4. Scalability for Growth
As companies expand adding more teams, apps, or even new business units SAML-based authentication scales right alongside them.
Whether it’s onboarding hundreds of new employees or integrating new SaaS tools, everything plugs into the same identity ecosystem. You don’t have to reinvent the wheel each time; just connect the new service provider to the existing SAML framework, and it becomes part of the trusted network.
That’s what makes SAML ideal for fast-growing organizations that need both agility and enterprise-grade security.
5. Compliance and Governance Made Easier
Today’s regulatory landscape from GDPR and HIPAA to SOC 2 and ISO 27001, demands transparency and accountability in how identities are managed.
SAML helps organizations meet these requirements effortlessly. Every login attempt, authentication event, and session is traceable through a single, auditable system.
This not only simplifies compliance reporting but also ensures that data access is always backed by verifiable, centralized logs.
In other words, SAML gives security and compliance teams something priceless: clarity and control in a world full of complexity.
Implementing SAML for Authentication
By now, it’s clear that SAML is more than just a technical protocol; it’s the foundation of secure, seamless access in modern organizations. But how do you actually bring it to life?
Implementing SAML for authentication isn’t about complicated coding or endless configuration, it’s about establishing a chain of trust between the systems that verify identity and the applications that need it.
Let’s walk through how that happens, step by step.
1. Choose a Reliable Identity Provider (IdP)
Every successful SAML setup starts with choosing the right Identity Provider, the heart of your authentication ecosystem. This is the system that verifies who your users are and securely communicates that proof to other applications.
When selecting an IdP, consider a few key factors:
-
Ease of integration: It should support SAML 2.0 and integrate smoothly with your existing applications.
-
Security strength: Look for advanced features like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), adaptive risk checks, and encryption.
-
Scalability: As your organization grows, your IdP should handle thousands (or even millions) of identities effortlessly.
2. Configure Your Identity Provider
Once you’ve selected your IdP, the next step is to set it up to recognize your users and their access needs.
This includes connecting it to your user directory (like Active Directory or a cloud database), defining user attributes (like name, role, or department), and setting security policies for login.
Think of this step as teaching your IdP who’s who in your organization so it can make accurate, informed authentication decisions every time someone tries to log in.
3. Connect Your Service Providers (Applications)
Next, it’s time to connect the apps and platforms that your users need access to; these are your Service Providers (SPs).
Each SP needs to know two things:
-
Which IdP should it trust for authentication?
-
What information (like username or role) should it receive when a user logs in.
This connection is usually done through a simple exchange of configuration data known as metadata, a secure set of details that allows both systems to identify each other and communicate safely.
Once set up, users can log in through the IdP and be instantly recognized by every connected application, no extra logins, no password repetition.
4. Test the Integration
Before rolling out SAML organization-wide, it’s crucial to test.
Log in as a user, switch between apps, and ensure that:
-
Authentication works seamlessly.
-
User attributes are correctly passed.
-
Sessions remain secure, and the out is as expected.
This step is where theory meets experience, confirming that your authentication flow truly feels smooth, secure, and natural.
5. Train, Monitor, and Evolve
A great SAML integration doesn’t end with launch it evolves. Train users on how SSO works, encourage adoption, and keep a close eye on metrics like login success rates, session durations, and security alerts.
Over time, integrate additional safeguards like adaptive MFA or real-time anomaly detection to keep your security posture strong as your organization grows.
Conclusion
In an age where every click, login, and data exchange matters, secure access has become the new foundation of digital trust. SAML and Single Sign-On (SSO) together represent more than just a login solution; they are the bridge between security and simplicity, helping organizations safeguard their digital ecosystems without compromising user experience.
By implementing SAML-based authentication, companies can finally replace password chaos with clarity. Users log in once and move freely, IT teams gain centralized control, and security leaders strengthen their defense against evolving identity threats. It’s a rare win-win, effortless for users, powerful for enterprises.
Book a Demo to see how LoginRadius helps global brands create seamless, secure, and scalable login experiences powered by modern CIAM and SAML integration. Because in today’s identity-first world, security shouldn’t stop the experience; it should drive it.
FAQ’s
Q: What is SAML authentication and how does it work?
A: SAML is a security standard that lets an Identity Provider verify a user once and securely pass that verified identity to applications. This enables passwordless access across multiple systems through trusted SAML assertions.
Q: How does SAML support Single Sign-On (SSO)?
A: SAML enables SSO by allowing users to log in once through a central Identity Provider and access all connected apps without re-entering credentials. It creates a seamless, secure login experience across platforms.
Q: What are the main benefits of using SAML for authentication?
A: SAML centralizes identity management, reduces password exposure, and enhances security with stronger policies. It also delivers frictionless access and supports compliance with regulatory standards.
Q: How is SAML different from OAuth or OpenID Connect (OIDC)?
A: SAML is ideal for enterprise SSO using XML-based assertions, while OAuth and OIDC are better for API and consumer app authentication using JSON-based tokens. Each serves different modern identity needs.


