In today's digital landscape, ensuring secure and seamless user authentication is paramount. With cyber threats evolving, organizations must adopt robust authentication methods to protect user data and maintain trust.
This comprehensive guide gives you insights into various authentication types, their significance, limitations, and emerging trends to help you choose the most effective user authentication methods.
What is User Authentication?
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user/device attempting to access a system, application, or network. It ensures that users/devices are who they claim to be, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.

For instance, when you log into your email account, entering your username and password is a form of user authentication. If you enable two-factor authentication, you might also receive a code on your phone, adding an extra layer of security.
Why is User Authentication Important?
User authentication is a foundational element of digital security. As digital services become deeply integrated into daily life, ensuring that only verified users can access systems, applications, and data is crucial.
Authentication serves not just as a protective barrier but also as a key component of trust, compliance, and operational stability. Let’s understand its importance in today’s modern digital landscape:
Security: Protecting Access to Sensitive Systems
The primary role of authentication mechanisms is to prevent unauthorized access. Inadequate authentication exposes systems to credential stuffing, phishing, and brute-force attacks. Organizations using only basic authentication types, such as passwords, are particularly vulnerable.
Take the case of a banking application. If an attacker manages to obtain login credentials through a phishing scam and no additional verification is in place, unauthorized access could occur. However, if the application uses biometric login or multi-factor authentication, the chances of a breach are significantly reduced.
This is why advanced authentication methods like passkeys or behavioral biometrics are increasingly replacing password-only systems—they minimize risk without increasing user friction.
Compliance: Aligning with Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS mandate the protection of user data, and secure user authentication methods are a critical part of that requirement. Failure to comply with these standards can result in fines, reputational damage, and legal complications.
For instance, a healthcare provider must ensure that only authorized personnel access patient records. Implementing biometric or passkey-based access control helps meet HIPAA’s strict data protection guidelines while also streamlining user login.
Incorporating the right types of authentication methods is therefore not only a best practice but often a legal necessity.
User Trust: Strengthening Brand Confidence
Trust is difficult to earn and easy to lose. With growing awareness of data breaches, users are more concerned than ever about how their data is handled. Authentication methods that prioritize both security and ease of use help build long-term trust.
For example, when a user logs in to an app using a face scan or a synced passkey stored on their device, the experience feels secure and modern. There is no need to remember complex passwords or wait for one-time passcodes. This convenience, backed by robust authentication mechanisms, enhances user satisfaction and confidence.
As competition in digital markets increases, secure and seamless access is becoming a critical part of the customer experience.
Operational Integrity: Preventing System Disruption
Beyond user experience, authentication plays a major role in safeguarding an organization's internal operations. Breaches resulting from weak or outdated authentication types can cripple business continuity. Whether it’s internal tools, partner portals, or customer-facing systems, weak access controls can lead to serious disruptions.
Consider a scenario where an employee's account is compromised due to a reused password. Without secondary authentication checks, an attacker could gain access to sensitive documents or systems, halting workflows and triggering crisis response procedures.
By implementing various authentication methods such as adaptive MFA or device-based verification, organizations ensure that their systems remain resilient and secure—even if one layer is breached.
Common Authentication Types
Choosing the right authentication methods begins with understanding the fundamental types available. Each type plays a specific role in verifying identity, and when combined thoughtfully, they form a robust defense against unauthorized access.
Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA)
This is the most familiar form of authentication, relying on information the user knows—like passwords, security questions, or PINs. While common, it's also increasingly vulnerable to attacks if used alone.
With growing concerns around password fatigue, more secure variations such as PIN-based approaches are being explored. You can learn more about how PIN authentication is evolving in secure systems in this detailed overview.
Possession-Based Authentication
This method depends on something the user physically has—like a smartphone, hardware token, or smart card. It's often used in two-factor authentication to reinforce security after the initial login.
As digital ecosystems expand, token-based access control is becoming more widespread. Here's an insightful breakdown on how token authentication works and when it’s most effective: What Is Token Authentication?.
Inherence-Based Authentication
Often referred to as biometric authentication, this type verifies identity through biological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or even retina scans.

It offers a high level of security with minimal user friction, particularly in mobile environments. If you’re curious about how biometrics are shaping mobile security experiences, check out this comprehensive article.
Behavioral-Based Authentication
This approach evaluates patterns in user behavior—such as typing rhythm, device usage, or mouse movement—to detect anomalies in real-time. It functions silently in the background and adds a subtle yet effective layer of security. To understand how behavioral signals are shaping risk-based access control, explore this discussion on adaptive authentication.
Top User Authentication Methods
Selecting the right user authentication methods is vital for balancing security and user experience. Here are some of the most effective methods:
1. Passwordless Authentication
Eliminates the need for traditional passwords by using alternatives like biometrics or magic links. This method reduces the risk of password-related breaches and enhances user convenience. A common example is logging into an app using facial recognition or a fingerprint scan.
One of the most promising advancements in this space is the use of passkeys - a secure, phishing-resistant alternative based on FIDO2 standards. Passkeys allow users to authenticate with biometrics or device-level PINs, removing the need for passwords entirely while enhancing protection against credential-based attacks.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) strengthens security by requiring users to verify their identity using two or more distinct factors—typically a combination of something they know, have, or are. This approach makes it much harder for attackers to gain access with just stolen credentials.
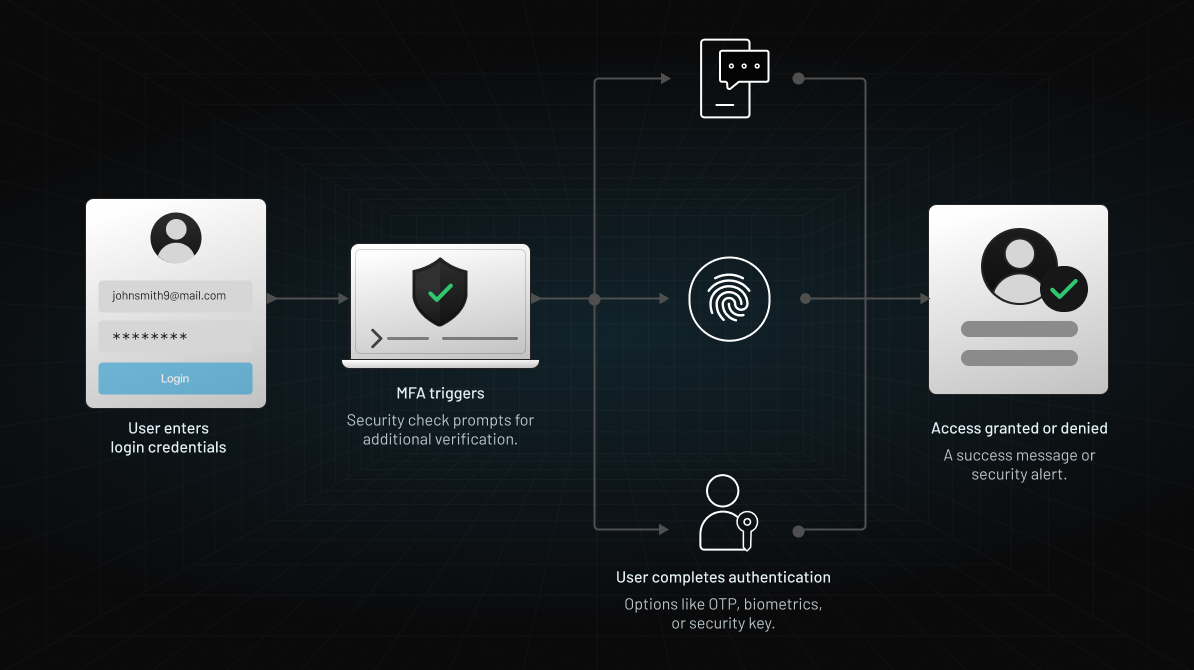
For instance, logging into an online account may involve entering a password and then confirming a code sent to the user's phone. MFA is now a standard across many industries, offering a practical balance between usability and security. You can learn more about how MFA works and where it fits into a strong authentication strategy in this LoginRadius MFA blog.
3. Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication uses the user’s inherent biological characteristics—such as fingerprints, facial features, or even iris patterns—to verify identity. This method is both secure and intuitive, as it relies on traits that are extremely difficult to replicate.
It’s commonly used in mobile devices and modern applications to streamline access while maintaining high levels of security. The growing adoption of biometrics, especially in mobile apps, is explored in depth in this biometric authentication guide.
4. Token-Based Authentication
This method involves issuing a unique physical or virtual token to the user, which is required during the authentication process. These tokens typically generate time-sensitive, one-time passcodes that significantly reduce the risk of credential theft.
For example, a user might carry a hardware token that refreshes a code every 30–60 seconds, or use a software-based token app on their smartphone. While effective, token-based systems come with trade-offs. You can explore the full spectrum of advantages and drawbacks in this detailed analysis on token authentication.
5. Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On allows users to log in once and gain access to a suite of connected applications without needing to re-authenticate. It simplifies user workflows while reducing password fatigue and administrative overhead.
In enterprise environments, SSO can provide seamless access to systems such as email platforms, HR tools, and CRMs. To understand how SSO improves productivity and security across ecosystems, this comprehensive overview offers valuable insights.
6. Adaptive/Risk-based Authentication
Adaptive/risk-based authentication analyzes patterns in how users interact with systems, such as IP address, time of access, location, and device usage. By establishing a behavioral baseline, the system can flag anomalies that suggest fraudulent activity, even if login credentials appear valid.
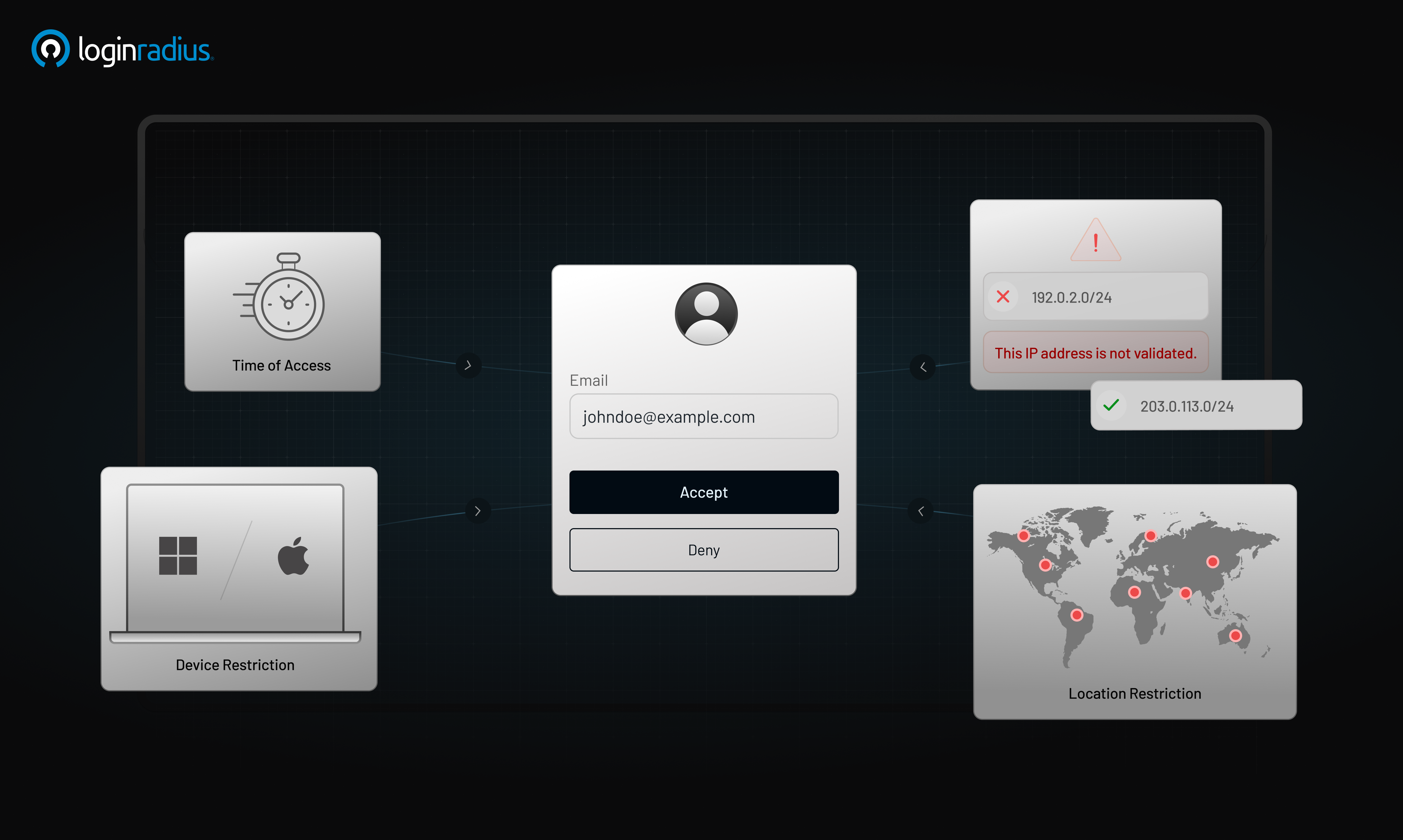
For instance, a login attempt from a device with unusual typing cadence or location may trigger additional verification. This concept is central to risk-based and adaptive authentication strategies. Learn how behavioral signals contribute to stronger identity verification in this article on risk-based authentication.
Limitations of Old Authentication Methods
Traditional authentication methods, such as relying solely on passwords, have significant drawbacks:
-
Vulnerability to Attacks: Easily compromised through phishing, brute force, or credential stuffing.
-
User Frustration: Managing multiple complex passwords can lead to poor practices like reuse or weak passwords.
-
Maintenance Overhead: Frequent password resets and account recoveries burden IT support.
These limitations necessitate the adoption of more secure and user-friendly authentication mechanisms.
Which Authentication Method is the Safest One?
While no authentication method is entirely immune to cyber threats, certain user authentication methods offer far stronger protection than others, especially when they eliminate human error and remove reliance on passwords.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) continues to be one of the most secure approaches, particularly when it includes advanced authentication methods such as biometrics (like fingerprint or facial recognition) and behavioral analytics. However, even MFA has vulnerabilities when traditional passwords are one of the factors.
This is where passkeys come into play—representing a major leap forward in secure and user-friendly authentication.
What Are Passkeys?
Passkeys are a modern, phishing-resistant alternative to passwords. Built on FIDO (Fast Identity Online) and WebAuthn standards, passkeys allow users to authenticate using biometrics (such as fingerprint or Face ID) or PINs linked to their device, without ever typing a password. They are stored locally on a user's device and synced securely via cloud services like iCloud or Google Password Manager.
Why Are Passkeys Safer?
-
Phishing-Proof: Since there’s no password to steal or enter, phishing attacks become ineffective.
-
No Shared Secrets: Passkeys never leave the user’s device—authentication is done via cryptographic key pairs, minimizing the risk of server-side breaches.
-
Frictionless Experience: Logging in becomes seamless—users simply use biometrics or a device screen lock.
-
Device-Bound Security: The private key never leaves the device, ensuring tight control and reducing attack vectors.
For instance, instead of entering a username and password, a user simply unlocks their phone with a fingerprint to sign into an app. The public key stored on the server verifies the cryptographic handshake—secure, fast, and user-friendly.
Combining MFA and Passkeys: For ultra-sensitive systems, combining passkeys with another factor (like location-based or behavioral authentication) creates a near-impenetrable defense. Here’s where risk-based authentication comes into play. Learn more about risk-based authentication:
Why LoginRadius Passkeys?
At LoginRadius, we understand that evolving threats demand smarter, more secure, and user-centric solutions. That’s why we offer Passkey Authentication as part of our modern CIAM platform, empowering organizations to deliver seamless and secure login experiences.
Key Benefits of LoginRadius Passkeys
Seamless Security Without Passwords
LoginRadius passkeys eliminate password fatigue and reduce vulnerabilities by using FIDO2 and WebAuthn protocols, ensuring each login is private and unphishable.
Device-Centric Authentication
Our solution ties passkeys to users’ trusted devices, leveraging local biometric authentication. Whether it’s a fingerprint on a phone or Face ID on a Mac, users enjoy smooth and secure access.
Cross-Platform Support
LoginRadius ensures passkey synchronization across ecosystems like iOS, Android, and desktop environments—making it ideal for modern, multi-device user experiences.
Easy Developer Integration
Our API-first architecture lets your dev team integrate passkey authentication into apps quickly using our robust SDKs and pre-built UI components.
Enhanced User Experience + Compliance
Passkeys not only enhance user trust and reduce login friction but also help organizations meet compliance requirements (like GDPR and HIPAA) with minimal effort.
How to Implement LoginRadius Passkeys
Implementing passkeys with LoginRadius is quick and developer-friendly, designed to deliver secure, passwordless logins with minimal setup.
1. Enable Passkeys in the Console
Start by logging into the LoginRadius Admin Console. Under Authentication Methods, enable Passkey (FIDO2/WebAuthn) support for your application.
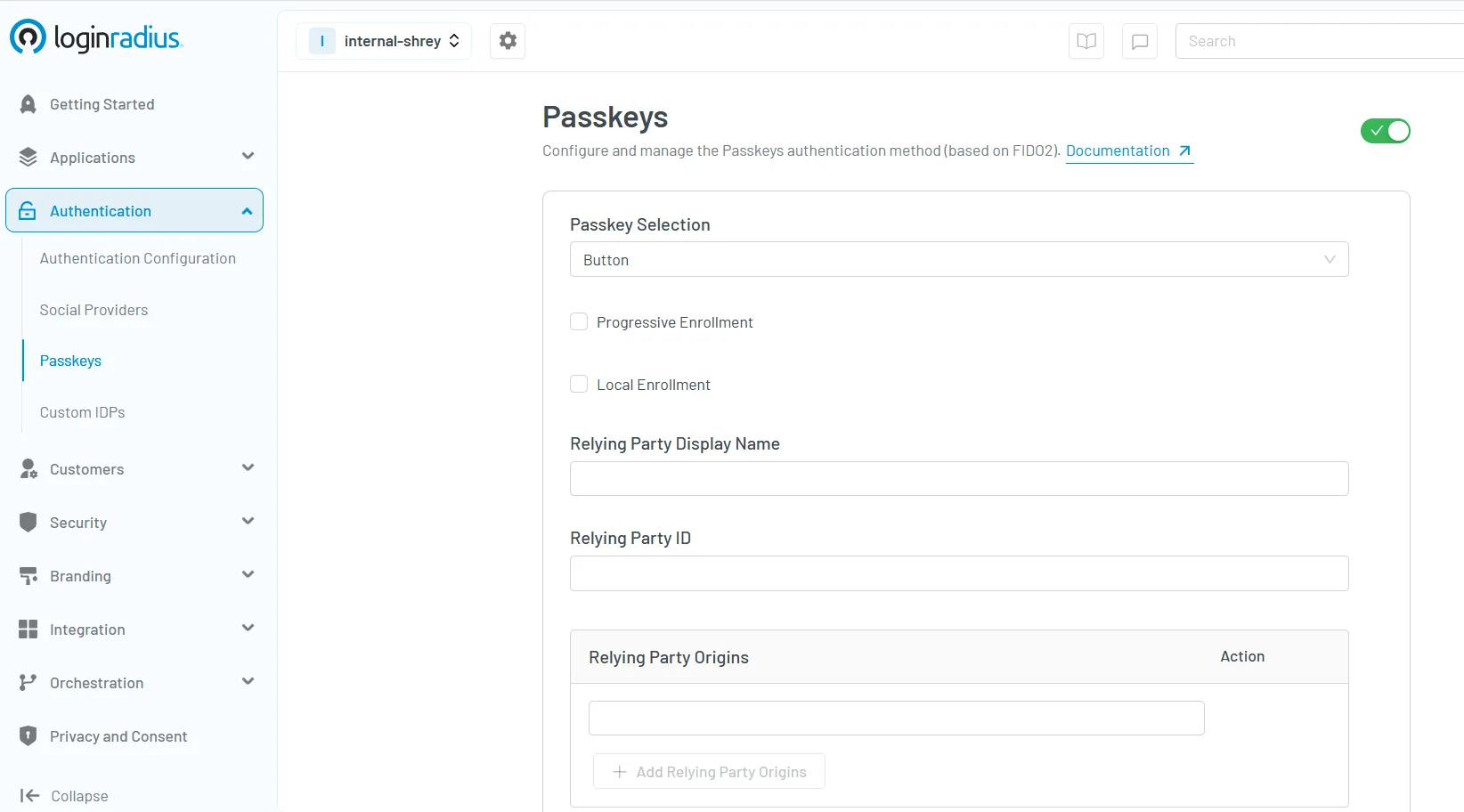
2. Register Passkeys via API
Use the /passkey/register endpoint to allow users to enroll using device biometrics or screen lock. The public key is securely stored and tied to the user profile.
3. Authenticate Seamlessly
Once registered, users can log in using the /passkey/login endpoint. The authentication is instant, using a secure cryptographic handshake with the user’s device.
4. Monitor and Manage
Track passkey adoption, manage device registrations, and customize login flows directly from the LoginRadius dashboard.
For detailed API integration steps, visit the LoginRadius Passkey Docs.
Conclusion
Securing digital access begins with choosing the right authentication methods—ones that are not only resilient against modern threats but also intuitive for users. From passwordless logins and MFA to emerging technologies like passkeys, the goal is clear: protect identities without adding friction.
As the threat landscape evolves, so must your authentication strategy. Whether you're starting fresh or looking to upgrade existing systems, LoginRadius offers the tools, flexibility, and expert support to help you implement secure and scalable user authentication.
Have questions or need help getting started? Contact the LoginRadius team to explore how we can support your authentication goals.
FAQs
1. Which is the most secure method to authenticate a user?
A. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), especially when incorporating biometric and behavioral factors, is considered highly secure due to its layered approach.
2. What are examples of biometric authentication methods?
A. Common biometric methods include fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, voice recognition, and retina scanning.
3. What is the best API for user authentication?
A. The best API depends on specific requirements. LoginRadius provides robust authentication APIs that support various methods, including MFA, SSO, and passwordless authentication, catering to diverse organizational needs.



