Introduction
Digital security used to feel simple: create a password, remember it (or hope you do), and you’re good to go. But the internet has changed faster than our habits. Today, attackers don’t need to “break in” the old-fashioned way; they only need one leaked password, one reused credential, or one careless login attempt to slip into an account that wasn’t built for the threat landscape we face now.
That’s why two-factor authentication (2FA) has become a cornerstone of modern identity security. Whether you’re a casual user who just wants safer logins, a developer building secure apps, or a security architect evaluating authentication frameworks, 2FA answers the same question for all: How do we prove someone is who they claim to be without relying on trust or luck?
At its core, 2FA adds an extra checkpoint, a small step for the user, but a massive obstacle for attackers. It reinforces password-based systems with something stronger, smarter, and significantly harder to steal.
And while the concept sounds simple, the logic behind it has evolved into a sophisticated layer of protection that now underpins customer identity, enterprise access, and zero-trust frameworks worldwide.
As we break down what 2FA is, how it works, and why it remains foundational even in the era of passkeys and passwordless authentication, you’ll see that it isn’t just a security feature; it’s the minimum standard for safeguarding digital identities today.
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-Factor Authentication, or 2FA, is a security process that verifies your identity using two separate and independent factors before allowing access. Think of it as a double-check mechanism that confirms you’re really you, not just someone who happens to know your password.
At a foundational level, 2FA is built on a simple principle: Your identity becomes significantly harder to compromise when verification doesn’t rely on a single piece of information.
To understand it clearly, security professionals categorize authentication methods into three major factors:
-
Something you know — a password, PIN, or secret answer.
-
Something you have — a smartphone, authenticator app, hardware key, or token.
-
Something you are — biometrics such as your fingerprint, face, or voice.
Traditional logins rely only on the first factor. But passwords alone are fragile; they can be guessed, leaked, phished, reused, or even bought on the dark web. With 2FA, the login requires at least two different types of factors, making it exponentially harder for attackers to succeed, even if they already possess one of them.
For beginners, this means an extra step that protects your account from password theft. For developers and identity architects, it means introducing a layered, multi-channel verification system that aligns with modern authentication standards like TOTP, FIDO2, WebAuthn, and risk-based adaptive flows.
2FA is simple on the surface, but its impact on account security is profound; it's the difference between single-point vulnerability and distributed trust.

How 2FA Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Even though 2FA feels like “one extra step,” the logic behind it is a beautifully structured security flow designed to filter out anyone who isn’t the real user, even if they somehow have the user’s password. Understanding this flow helps both beginners appreciate its value and experts evaluate or implement 2FA in their systems.
Let’s walk through how it actually works under the hood:
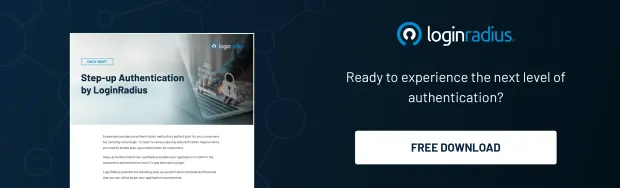
Step 1: The User Attempts to Log In (Primary Authentication)
Everything begins the moment a user enters their username and password. This is the first checkpoint of the factor based on something you know.
But in modern threat landscapes, this step alone is not enough. Attackers often get past this layer by:
-
Buying leaked passwords
-
Running credential-stuffing bots
-
Using phishing pages
-
Guessing weak passwords
Instead of granting instant access after this step, the system triggers the second authentication factor.
Step 2: The System Initiates a Challenge (Secondary Authentication)
Once the first factor is validated, the server says, “Okay, now prove it’s really you.” This is where the magic of 2FA truly kicks in.
The system sends or generates a unique verification challenge tied to something the user has or something the user is. This can take many forms:
-
A TOTP code generated by an authenticator app (Google Authenticator, Authy, Microsoft Authenticator).
-
A push notification asking the user to approve or deny the login.
-
A hardware security key (YubiKey, Feitian, Google Titan) that the user taps or inserts.
-
A biometric match: fingerprint, face recognition, or voice ID.
-
An email OTP or SMS OTP (used widely but less secure due to SIM-swap risks).
Each of these methods generates a one-time, short-lived piece of evidence that only the genuine user should have access to.
Step 3: The User Provides the Second Factor
The user responds to the challenge by entering the code, approving the push, or tapping the hardware key.
This second factor creates an identity signal that is:
-
Unique (no two codes or keys are alike)
-
Time-bound (valid for seconds)
-
Independent from the password
-
Hard to intercept, especially with advanced methods like WebAuthn or FIDO2
This eliminates “single point of failure,” raising the bar against attackers exponentially.
Step 4: The Server Validates the Second Factor
Now the server performs a verification handshake.
Depending on the method, it uses:
-
Cryptographic validation (for TOTP, WebAuthn, and security keys)
-
Signed challenges (push notifications)
-
Secure hashing and comparison (OTP codes)
-
Public-private key verification (passkeys, FIDO2 keys)
If the verification checks out, the user is authenticated. If not, the attempt is blocked even if the password was correct.
For developers, this is where standards like RFC 6238, FIDO2, and WebAuthn APIs come into play, ensuring secure implementation and interoperability.
Step 5: Session Established (Secure Access Granted)
After successful validation of both factors, the system creates a secure session using:
-
Tokens (JWT/OIDC)
-
Session cookies
-
Encrypted session IDs
This session lets the user move through the app without re-entering the second factor repeatedly (unless risk signals trigger another check).
Types of 2FA Methods
Two-factor authentication isn’t a single technology; it's an ecosystem of methods, each designed with different balances of convenience, security, and implementation complexity. Understanding these options helps individuals choose safer login methods and helps developers or architects design authentication flows that scale without compromising user experience.
Below are the most widely used 2FA methods today, broken down by how they work and when they should be used.
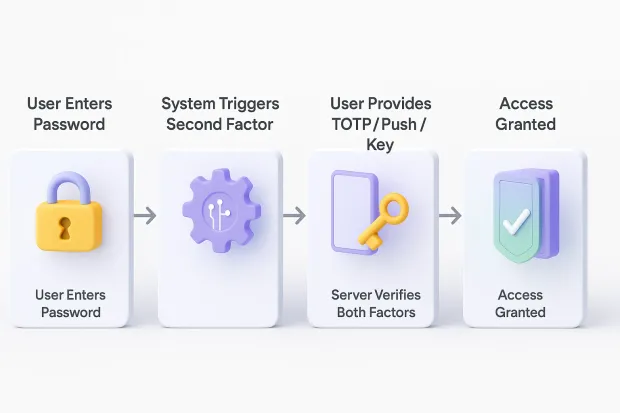
1. SMS One-Time Passcodes (SMS OTP)
SMS 2FA sends a six-digit or short-lived code to your mobile number.
How it works: The server generates a unique OTP and sends it over the mobile network to the user's phone. The user enters it to complete login.
Why it’s popular:
-
Extremely easy to deploy
-
Works on any mobile device
-
Familiar to both technical and non-technical users
Security considerations: While better than password-only logins, SMS OTP has well-known weaknesses:
-
Vulnerable to SIM-swap attacks
-
Exposed to SS7 network weaknesses
-
Susceptible to phishing
Best for: Low-risk applications, fast rollouts, massive user bases with mixed technical proficiency.
2. TOTP (Time-Based One-Time Passwords)
This is the most widely recommended upgrade from SMS.
How it works: Apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, and Microsoft Authenticator generate a new 6-digit code every 30 seconds using a shared secret and time-based algorithm (RFC 6238).
Advantages:
-
Works offline
-
Extremely hard to intercept
-
No telecom dependency
-
Free to use
Weaknesses:
-
Users might lose their device
-
Requires a small onboarding effort
Best for: SaaS platforms, enterprise systems, banking, developer tools, and any app needing scalable, secure 2FA.
3. Push Notification Authentication
A seamless 2FA method that sends a login approval request to the user’s smartphone.
How it works: The user receives a push alert (e.g., “Approve this login?”). They tap Approve to complete the authentication.
Why it’s loved:
-
Frictionless
-
Fast
-
User-friendly
Security considerations:
-
Can be vulnerable to MFA fatigue attacks where users tap “approve” out of habit.
-
Should include contextual information: location, device, IP, app details.
Best for: Consumer apps, enterprise logins, and organizations prioritizing UX.
4. Hardware Security Keys (U2F, FIDO2, WebAuthn)
The strongest and most phishing-resistant form of 2FA available today.
How it works: A physical key like a YubiKey or Feitian key uses public-key cryptography to verify the user. You plug it into a USB port or tap it using NFC.
Advantages:
-
Immune to phishing
-
No codes to enter
-
Extremely low attack surface
-
Works offline
Weaknesses:
-
Requires purchasing physical keys
-
Slight learning curve for users
-
Risk of device loss (can be mitigated with backups)
Best for: Enterprises, developers, IT admins, privileged accounts, regulated industries (finance, healthcare, government).
5. Biometric 2FA (Fingerprint, Face ID, Voice)
Biometrics offer frictionless 2FA your body becomes your second factor.
How it works: Encrypted biometric data on the device verifies identity locally (never sent to servers).
Advantages:
-
Fast and frictionless
-
Secure local verification
-
Almost impossible to replicate
Weaknesses:
-
Privacy concerns
-
Device-dependent
-
Not always supported on older hardware
Best for: Mobile-centric apps, passwordless flows, secure on-device authentication.
6. Passkeys (The Future of 2FA and Beyond)
Passkeys take authentication beyond 2FA into the world of passwordless, phishing-resistant logins.
How it works: They replace passwords entirely with a cryptographic pair stored securely on your device. You authenticate using biometrics Face ID, Touch ID, or Windows Hello, and the device verifies you with the server through WebAuthn.
Advantages:
-
No passwords at all
-
Zero phishing risk
-
Seamless, one-tap login
-
Perfect for mobile-first or cross-device apps
Weaknesses:
-
Requires ecosystem support (browsers, OS, apps)
-
Needs user awareness and adoption
Best for: Modern SaaS apps, ecommerce platforms, hybrid mobile apps, and any product aiming to eliminate passwords completely.
7. Email OTP (Email One-Time Codes)
A common fallback method when SMS or TOTP isn’t available.
How it works: The system sends a one-time code to the user’s email address.
Pros:
-
Universally accessible
-
Works on any device
-
Easy to onboard
Cons:
-
Relies on email security
-
Slow compared to push or TOTP
Best for: Startups, low-risk apps, backup factors, and user recovery flows.

Why 2FA Matters More Than Ever
The internet has evolved, user behavior has changed, and attackers have become disturbingly efficient. In this environment, relying on passwords alone is like locking your front door but leaving the windows wide open. Two-factor authentication is no longer a “nice-to-have,” it’s the foundation of modern digital trust.
Here’s why 2FA has become essential for individuals, businesses, and any application that collects or stores user identities.
1. Passwords Are No Longer a Reliable Defense
People reuse passwords. They pick weak ones. They store them in screenshots or browser notes.
Even the most sophisticated users are vulnerable because:
-
Passwords can be leaked in data breaches
-
Attackers can run massive credential-stuffing bots
-
AI-powered phishing pages now mimic real login screens perfectly
With just one leaked password, attackers can impersonate a user instantly unless there’s a second factor standing in the way. 2FA breaks this dependency by ensuring that a password is just the first half of the equation, not the whole story.
2. Cybercrime Has Become Automated and Fast
Gone are the days when attacks were manual and slow. Today’s attackers use:
-
Automated botnets
-
AI-generated phishing kits
-
Real-time OTP-stealing tools
-
Proxy-based phishing sites
-
Malware that intercepts SMS codes
2FA interrupts these automated pipelines. Even if a bot knows your password, it can't magically produce a time-based code or tap a hardware key. For attackers, the cost of breaking in suddenly goes from cheap to expensive, which makes your account a far less attractive target.
3. Phishing Is More Advanced Than Ever
Modern phishing attacks don’t just steal passwords they steal entire sessions.
Techniques like:
-
Reverse proxy phishing (EvilProxy, Modlishka)
-
Adversary-in-the-middle attacks
-
OAuth consent phishing
…allow attackers to capture passwords and tokens in real time.
While basic 2FA methods like SMS can still be phished, stronger factors TOTP, push with context, FIDO2/WebAuthn keys stop these attacks entirely by requiring device-bound cryptographic proof.
4. Compliance and Regulations Now Require Strong Authentication
Almost every major security framework mandates 2FA or MFA:
-
PCI DSS for payment data
-
GDPR for personal data protection
-
HIPAA for healthcare access
-
SOC 2 & ISO 27001 for SaaS companies
-
NIST 800-63B for digital identity assurance
-
Financial sector regulations (FFIEC, RBI, SEC)
For growing businesses, 2FA isn't only a security measure — it’s a compliance requirement.
5. User Trust and Brand Credibility Depend on It
Users today are more aware of security risks and value brands that prioritize safety without slowing them down.
Apps that use 2FA (or even better, adaptive MFA or passkeys) see:
-
Higher user confidence
-
Lower account takeovers
-
Reduced churn after security incidents
-
Better long-term retention
Security is no longer “invisible.” It’s a competitive advantage especially in consumer identity.
6. 2FA Reinforces Zero-Trust Architecture
Zero-trust assumes that no identity is trusted by default, even if a user has the correct password or is inside the network.
2FA strengthens zero-trust by validating:
-
The device
-
The location
-
The behavior
-
The context
-
The authenticity of the user
It becomes the first (and often most critical) checkpoint in any modern identity-first security strategy. The web has become a high-speed battlefield where attackers exploit every weakness they can find. 2FA doesn’t eliminate risk completely, nothing can but it dramatically narrows the attack surface and ensures that stolen passwords don’t become stolen identities.
For consumers, it’s a shield. For businesses, it’s a baseline. For developers, it’s a must-have layer in the authentication stack. That’s why 2FA continues to be one of the most effective, scalable, and impactful security controls of the modern era.
Common 2FA Attacks and How to Prevent Them
Two-factor authentication is powerful, but like any security method, it isn’t invincible. Attackers have evolved their techniques, targeting not just passwords but the second factor itself. Understanding these attack patterns is important for both everyday users and security professionals who design or maintain authentication systems.
Let’s break down the most common 2FA attacks and how to defend against each one.
1. SIM-Swap & SS7 Attacks (Targeting SMS 2FA)
What it is: A SIM-swap attack happens when an attacker tricks or bribes a mobile carrier into transferring your phone number to their SIM card. Once that’s done, they receive all your SMS OTPs.
Why it works: SMS relies on the telecom network, which wasn’t built for cybersecurity. Attackers exploit:
-
Carrier social engineering
-
Weak identity verification at call centers
-
Structural flaws in the SS7 telecom protocol
How to prevent it:
-
Avoid SMS as your primary 2FA method
-
Use TOTP or authenticator apps
-
Lock your mobile number with a carrier PIN
-
Prefer device-bound methods like FIDO2 or passkeys
Who’s at risk?
Everyone, but especially users with high-value accounts (crypto, banking, admin portals).
2. MFA Fatigue Attacks (Push Notification Abuse)
What it is: Attackers bombard a user with multiple push authentication prompts until the user accidentally taps “Approve” just to stop the notifications.
Why it works: Humans get tired. Push fatigue is psychological exploitation, not technical.
How to prevent it:
-
Enable “number matching” or “contextual push”
-
Rate-limit push attempts
-
Flag multiple denied attempts as suspicious
-
Avoid push notifications as the only method for high-risk access
Bonus tip for architects: Push + location + device context = drastically reduced fatigue success rates.
3. Phishing via Reverse Proxy (Most Dangerous Today)
What it is: Attackers use reverse-proxy toolkits (like EvilProxy or Modlishka) that clone real login pages and capture:
-
Password
-
OTP
-
Session cookies
Why it works: The proxy sits between you and the real website, relaying information in real time and stealing your authentication tokens.
How to prevent it:
-
Use phishing-resistant factors (FIDO2, WebAuthn, hardware keys)
-
Implement domain-bound passkeys
-
Educate users about URL spoofing
Why it matters: This is the biggest modern challenge to traditional 2FA flows.
4. OTP Malware & Clipboard Hijacking
What it is: Malware on a device can read incoming OTPs, grab authenticator app codes, or intercept clipboard values when a user copies/pastes login data.
Why it works: Compromised devices remove the “something you have” guarantee — the attacker has it too.
How to prevent it:
-
Encourage users to secure devices with OS-level protections
-
Use biometric-bound passkeys or hardware tokens
-
Avoid clipboard-based flows for sensitive apps
5. Social Engineering Attacks (Tricking Users Directly)
What it is: Attackers don’t hack systems, they hack people.
Why it works: Fear and urgency override caution.
How to prevent it:
-
Clear in-app messaging about never sharing codes
-
Out-of-band verification for sensitive actions
-
Behavior-based adaptive MFA triggers
6. Account Recovery Abuse (The Overlooked 2FA Weak Point)
What it is: Even if your login is secure, your recovery process might not be. Attackers request password resets through weak recovery flows.
Why it works: Many apps allow recovery via insecure:
-
Email-only verification
-
Outdated security questions
-
Easily guessable identity checks
How to prevent it:
-
Enforce multi-step identity verification
-
Tie recovery to device fingerprints
-
Use backup codes or secondary verification
How Strong 2FA Methods Neutralize These Attacks
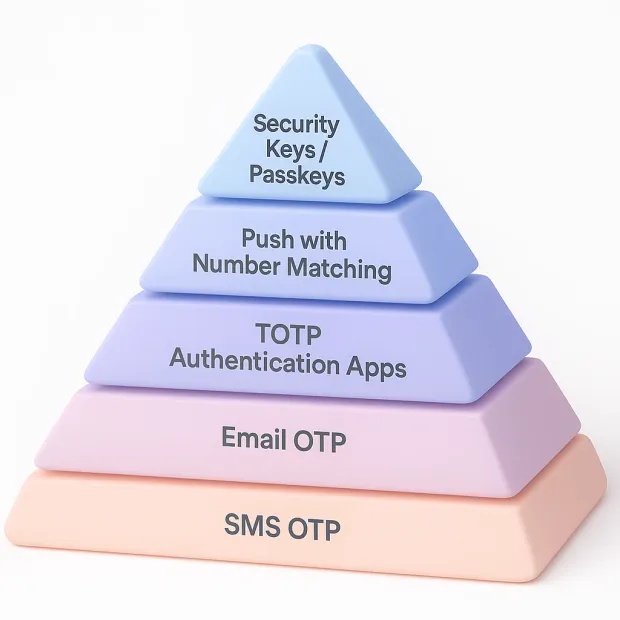
| Attack Type | Weak Methods Affected | Strong Methods That Resist |
|---|---|---|
| SIM-swap | SMS OTP | TOTP, Hardware Keys, Passkeys |
| Phishing | SMS, Email OTP | Security Keys, WebAuthn Passkeys |
| MFA Fatigue | Push | Number-matching Push, TOTP, Passkeys |
| OTP Malware | SMS, Email | Hardware Keys, Passkeys |
| Social Engineering | SMS, Email | Device-bound cryptographic methods |
The reality is simple: The stronger the factor, the lower the risk. Modern identity systems increasingly lean toward phishing-resistant, device-bound authentication especially for customer-facing apps and high-privilege accounts.
Best Practices for Deploying 2FA in Customer Apps
Implementing 2FA isn’t just about enabling a second step in the login flow. For customer-facing applications, especially those with large user bases, global audiences, and diverse devices the way you design, roll out, and maintain 2FA determines whether it strengthens security or frustrates users.
Below are the best practices that align with modern CIAM standards, developer expectations, and enterprise security guidelines.
1. Offer Multiple 2FA Options, Not Just One
Every user has different comfort levels and device capabilities. Some prefer app-based codes, others prefer biometrics, and some rely on hardware keys.
Recommended factor combinations:
-
TOTP (Google/Microsoft Authenticator)
-
Push notifications with context
-
Email or SMS OTP (as fallback only)
-
WebAuthn/FIDO2 security keys
-
Passkeys for passwordless sign-ins
Why it matters: Giving users flexibility reduces friction, increases adoption, and ensures inclusivity across devices and geographies.
2. Prioritize Stronger, Phishing-Resistant Factors
While SMS OTP is still common, it should never be the default for high-risk or business-critical applications.
Most secure options today:
-
WebAuthn + FIDO2 (security keys, biometrics, passkeys)
-
Device-bound passkeys
-
Cryptographic push notifications with number matching
These methods neutralize the biggest modern threats (phishing proxies, SIM-swap attacks, token theft).
3. Make 2FA Enrollment Effortless
A secure system that users can’t set up easily will never reach adoption.
Reduce friction by:
-
Displaying a simple onboarding modal after login
-
Using QR codes for instant TOTP setup
-
Offering “use this device as a passkey” prompts
-
Auto-detecting platform authenticator support (Android, iOS, Windows Hello)
Pro Tip: Apps that make onboarding easy see up to 30–40% higher 2FA adoption within the first week.
4. Design a Safe, User-Friendly Recovery Flow
This is one of the most overlooked parts of 2FA implementation.
If users lose their phone or reset their device, a poor recovery process can:
-
Lock them out
-
Trigger support tickets
-
Lead to angry churn
-
Introduce new vulnerabilities
Best practices:
-
Provide backup codes
-
Allow secondary email or trusted device verification
-
Use risk-based checks to re-verify sensitive actions
-
Require “step-up authentication” for recovery approvals
Architecture Tip for Developers: Never allow account recovery to bypass the strength of your primary 2FA factors.
5. Use Adaptive MFA, Not Static Rules
Static 2FA (“always ask for OTP”) frustrates users over time.
Adaptive MFA evaluates context like:
-
Device fingerprint
-
IP reputation
-
Geo-velocity (impossible travel)
-
Time-of-day patterns
-
User behavior anomalies
If everything looks normal, no need to challenge again. If something looks off, trigger step-up 2FA instantly.
This approach balances friction and security perfectly.
6. Secure the Entire 2FA Lifecycle
Implementing 2FA is just the start. Maintaining its security is an ongoing commitment.
Protect your 2FA flows by:
-
Limiting OTP attempts
-
Adding cooldown periods for failures
-
Logging suspicious access requests
-
Alerting users of unusual login patterns
-
Using encrypted storage for secrets (e.g., HSMs)
Developer Tip: Follow standards: RFC 4226, RFC 6238, WebAuthn API, and FIDO2 specs.
7. Educate Users, but Don’t Overwhelm Them
The best 2FA experiences feel natural, not instructional.
Avoid long tutorials or heavy text. Instead:
-
Use small, digestible tooltips
-
Include one-sentence explanations (“Why we ask for this”)
-
Offer visual cues for setup steps
-
Highlight secure behavior in-app
8. Ensure Global Scalability and High Availability
2FA is part of your login pipeline; when it’s down, your entire product is down.
Your CIAM provider must offer:
-
High-availability clusters (99.99% uptime)
-
Low-latency API responses worldwide
-
Edge delivery for OTP and push services
-
Scalability for traffic spikes (e.g., Black Friday, seasonal events)
This is where a production-grade CIAM platform like LoginRadius shines.
9. Keep Compliance Top-of-Mind
Make sure your 2FA flow aligns with:
-
GDPR
-
SOC 2 Type II
-
ISO 27001
-
PCI DSS
-
HIPAA (for healthcare apps)
-
NIST 800-63B digital identity guidelines
Strong authentication isn’t just a feature — it’s a regulatory requirement for many industries.
10. Monitor & Improve Continuously
Security isn’t a one-time setup.
Track:
-
2FA adoption rate
-
Drop-off points in setup
-
Authentication failure trends
-
Push fatigue events
-
Device loss patterns
These insights help you optimize UX while strengthening fraud prevention.
2FA vs MFA vs Passkeys: Where Authentication Is Heading
As digital security evolves, two-factor authentication isn’t the only method in the conversation anymore. Modern identity systems now blend several layers of 2FA and MFA with emerging passwordless technologies like passkeys. Each serves a different purpose, and understanding how they relate helps you choose the right authentication strategy for your business or application.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA is the starting point. It requires exactly two independent verification steps, typically a password plus a second factor such as a TOTP code, a push notification, or a hardware key. It dramatically improves security compared to password-only logins and remains the most widely adopted method across consumer apps.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA goes a step further. Instead of limiting authentication to two factors, it requires two or more. That could mean a password, a TOTP code, and a biometric scan all in one flow. MFA is used in higher-security environments, especially where privileged access or compliance requirements demand stronger assurance levels.
In practice, MFA gives organizations more flexibility: they can combine factors based on risk, behavior, or user role.
Passkeys (Passwordless Authentication)
Passkeys represent the future of authentication a world where passwords disappear entirely. They rely on public-key cryptography, stored securely on the user’s device, and verified using biometric sensors like Face ID or Touch ID. Because passkeys are device-bound and phishing-resistant, they eliminate many of the vulnerabilities associated with traditional 2FA methods.
How They Fit Together
You can think of 2FA as the foundation, MFA as the stronger and more dynamic extension of that foundation, and passkeys as the next-generation evolution. Many modern systems use a combination of all three. For example, users may log in with passkeys daily but still fall back to TOTP or push verification during recovery or high-risk scenarios.
In a CIAM context, these layers work together to create seamless, secure identity journeys across devices, geographies, and authentication experiences.
Across the industry, the trend is clear: organizations are moving toward phishing-resistant, cryptographic, and passwordless methods that reduce user friction and strengthen security.
Passkeys are growing rapidly, but 2FA and MFA will continue to play crucial roles for fallback flows, onboarding, accessibility, and legacy systems.
How LoginRadius Helps You Implement 2FA the Right Way
LoginRadius makes it easy for businesses to deploy strong, user-friendly 2FA without taking on the complexity of building it themselves. The platform supports all major authentication methods from TOTP and email OTP to advanced, phishing-resistant options like WebAuthn, security keys, and passkeys, so you can offer users the right balance of security and convenience.
What sets LoginRadius apart is how seamlessly it handles the entire lifecycle of 2FA. Users can enroll, switch devices, and recover their accounts without friction, while adaptive authentication quietly strengthens security in the background by stepping up verification only when something looks risky. This keeps genuine users moving smoothly while blocking suspicious behavior.
For developers, integration is straightforward. With clean SDKs, standards-based APIs, and pre-built workflows, you don’t have to worry about storing secrets, handling OTP time drift, or scaling authentication during peak traffic. LoginRadius is built to handle billions of API calls, ensuring fast and reliable 2FA performance globally.
And because the platform is backed by SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, and GDPR-compliant infrastructure, you get enterprise-grade security and regulatory confidence without additional overhead. In short, LoginRadius delivers secure, scalable, future-ready 2FA so you can focus on building great user experiences while knowing your authentication flows are protected.
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication has become one of the most important layers of modern digital security. It protects users from password theft, helps businesses reduce account takeovers, and strengthens zero-trust frameworks across industries. Whether you're securing a small consumer app or a global enterprise platform, 2FA adds resilience where it’s needed most at the login.
But as identity threats evolve, security needs to evolve too. Stronger methods like TOTP, push with context, WebAuthn, security keys, and passkeys are reshaping how authentication works. They provide the balance users expect today: frictionless experiences backed by cryptographic proof instead of fragile passwords.
Implementing this correctly, at scale, and without introducing user frustration is where many businesses struggle, and where LoginRadius makes the difference. With modern 2FA methods, adaptive authentication, global reliability, and developer-friendly API integration, LoginRadius helps organizations deliver secure, fast, and future-ready login experiences for millions of users.
If you’re ready to build a secure, seamless authentication experience for your customers, book a personalized LoginRadius demo today. Your users deserve safer access, and your business deserves the confidence that only proven, enterprise-grade CIAM can provide.
FAQs
Q: Is SMS-based 2FA secure enough?
A: SMS 2FA is better than password-only logins, but it’s vulnerable to SIM-swaps, SS7 attacks, and phishing. Stronger methods like TOTP or security keys offer higher protection.
Q: Which 2FA method is the most secure?
A: Security keys and passkeys are the strongest because they use device-bound cryptographic verification, making phishing and credential theft nearly impossible.
Q: Does 2FA increase login friction for users?
A: It can add a step, but modern methods like push notifications, biometrics, and passkeys keep the workflow seamless while drastically improving account security.
Q: Can attackers still bypass 2FA?
A: Weak factors (SMS, email OTP) can be bypassed through phishing or SIM-swaps. Strong factors like WebAuthn, passkeys, and hardware keys are extremely difficult to compromise.