Introduction
In today's hyper-connected world, authentication isn't just a technical requirement-it's the gateway to trust. Whether you're selling directly to consumers or collaborating with external business partners, understanding authentication and how users authenticate can significantly shape their experience, security posture, and operational agility.
This is where the debate of B2B vs B2C authentication becomes crucial.
Imagine a digital commerce platform that allows millions of consumers to log in effortlessly using social logins, while simultaneously enabling partner agencies to access internal dashboards securely via their own corporate credentials. Two very different needs. One platform. Different authentication journeys.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll unpack the nuances between B2B and B2C authentication, dive into key differences, explore lessons businesses can borrow from each model, and share best practices. We'll also spotlight how LoginRadius helps businesses scale securely through purpose-built Partner IAM.
History of User Management
User authentication has evolved from simple username-password combinations to complex, federated identity systems. Historically, businesses adopted basic credentials for internal access and later added external consumer login layers as digital services exploded.
The early 2000s witnessed the rise of B2C authentication, which enabled self-registration, email login, and social sign-ins. Platforms like Facebook and Google Login changed the way consumers accessed apps.
![]()
Meanwhile, B2B authentication remained manual. Excel sheets, shared passwords, and siloed partner portals were common. With the surge of SaaS platforms and interconnected B2B ecosystems, the demand for scalable, secure B2B user and customer management soared. Today, systems like LoginRadius offer robust B2B IAM solutions, with federated logins, SCIM provisioning, and AI- powered branding.
What Is B2B Authentication?
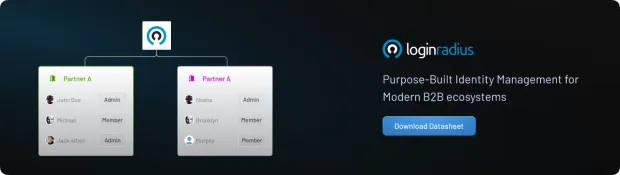
B2B authentication refers to the identity verification process for external organizations, partners, vendors, or resellers needing secure access to a business’s internal or shared resources. Instead of dealing with individual users, businesses manage entire organizations and their user hierarchies.
So, what is B2B authentication in practice? Think of a SaaS analytics provider giving marketing agencies access to campaign data via their own identity provider (IdP). Login is seamless, secure, and scoped to the agency’s assigned roles.
This is the essence of B2B API authentication: connecting partner systems through secure protocols like SAML, OIDC, or OAuth, and controlling access based on organizational roles.
Key Features:
-
Just-In-Time provisioning (JIT) : With Just-In-Time Provisioning, users are created dynamically upon their first login, eliminating the need for manual pre-provisioning of accounts and reducing administrative workload.
-
Admin-invited onboarding : Allows partner admins to invite their team securely, maintaining centralized control while supporting distributed user flows.
-
Granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) : Role-based access control ensures each user is mapped to specific roles and permissions based on their organizational affiliation, ensuring precise access control.
-
SCIM Integration : SCIM supports seamless user lifecycle management via SCIM for automatic provisioning, deactivation, and updates.
What Is B2C Authentication?
B2C authentication is designed for individual users or customers. These systems prioritize speed, simplicity, and scale. Whether it's signing into an online store or accessing a mobile banking app, B2C users expect fast and frictionless login experiences.
It typically involves self-registration, email/password, or social logins. The goal is user retention, reduced churn, and a seamless user experience.
Example: A food delivery app allows sign-in via Google or Apple accounts. The user doesn't think about authentication - they expect it to "just work."
Key Elements of B2C Login:
-
Multi-channel login options : Includes email/password, SMS OTP, or biometric logins to ensure accessibility across devices.
-
Social Identity Providers : Social login streamlines onboarding using platforms like Facebook, Google, and Apple.
-
Passwordless options : Introduces magic links and passkeys to remove login friction.
-
Adaptive MFA : Risk-based multi-factor authentication triggered during unusual behavior or new devices.
For organizations, ensuring B2B login is fast and secure is vital for customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
B2B vs B2C Authentication: Key Differences
Let’s break down the critical distinctions between B2B vs B2C authentication.
| Area | B2C Authentication | B2B Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| User Identity | Individual consumers with personal accounts | Organizational identities with multiple users per tenant |
| Onboarding | Self-service registration with social login or email | Invitation-based onboarding with JIT and SCIM for bulk provisioning |
| Authentication Protocols | Social logins, email/password, biometrics | SAML, OIDC, passwordless, org-specific MFA strategies |
| Access Control | Basic roles or preference-based access | Role hierarchies, policy-based access tied to organization and function |
| Branding | Consistent, universal experience across all users | Partner-specific themes, login flows, and branding per tenant |
| Provisioning Model | User-controlled, often manual | Automated and scalable via APIs and SCIM connectors |
| Data Isolation | Shared across a multi-user system | Strictly isolated environments for each partner organization |
B2C is optimized for mass-scale usability, while B2B emphasizes structure, security, and organizational segmentation.
What We Can Learn From B2B User Management
Despite the contrast, B2C solutions can adopt several winning principles from B2B:
-
Ease of use : Simplified sign-in, recovery options, and intuitive flows can reduce helpdesk load and improve onboarding satisfaction.
-
Personalization : Create login experiences that resonate with the brand of each partner using dynamic themes and localized interfaces.
-
Frictionless security : Utilize behavioral insights and risk scoring to apply MFA only when necessary, ensuring security doesn’t compromise usability.
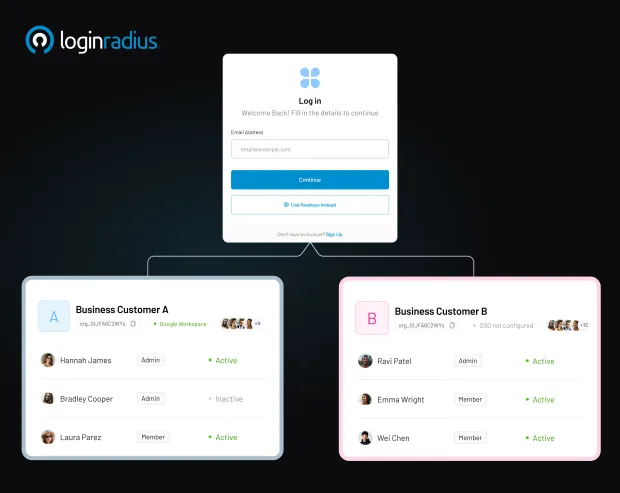
LoginRadius Partner/B2B IAM supports self-service portals with branded URLs. A partner logs in through a personalized page with their company logo and gets prompted for MFA only when risk is high. Download this insightful datasheet to know more about LoginRadius B2B IAM:
By blending B2C UX best practices into B2B user and customer management, companies improve partner satisfaction and reduce support overhead.
Differences in B2B and B2C Authentication Methods
Authentication methods diverge significantly in B2B vs B2C contexts.
B2B Authentication Methods:
-
Federated identity : Authenticate users using corporate IdPs through SAML or OIDC, enabling centralized partner login management.
-
Provisioning automation : JIT and SCIM ensure dynamic account creation and lifecycle updates.
-
RBAC and policy enforcement : Ensures users only access resources they’re entitled to, based on their org role.
-
B2B API authentication : B2B API authentication is used to connect third-party applications or integrations with minimal risk.
B2C Authentication Flow:
-
Standard login credentials : Email and password, or mobile OTPs.
-
Biometric authentication : FaceID or fingerprint for passwordless convenience.
-
Passkey adoption : Passkeys strengthens security while simplifying the user journey.
For example, a healthcare SaaS vendor utilizes LoginRadius to onboard labs and hospitals using SAML SSO and assign patient-data access roles. In contrast, patients log in via OTPs or passkeys.
Knowing your audience helps craft the right saas authentication experience.
Integrations and Customization in B2B Authentication
Customization and integration flexibility are non-negotiable in B2B IAM.
B2B platforms must integrate with:
-
Enterprise IdPs : Support Azure AD, Okta, Ping, and more to federate user identities.
-
Workforce tools : Seamless identity provisioning with HR platforms like Workday.
-
Operational platforms : Link identities to CRM, ERP, and ticketing systems to control access dynamically.
With LoginRadius, businesses use RESTful APIs and SDKs to:
-
Manage invitations at scale : Automate invites using APIs and pre-define user roles.
-
Provision users with SCIM : Create, modify, and delete partner user accounts via SCIM workflows.
-
Customize login UI : Match partner themes with branded portals, personalized domains, and multilingual support.
Example: A logistics platform uses LoginRadius to create separate login portals for suppliers and carriers. Each group sees a custom UI and has access only to role-specific modules. Learn how to implement B2B partner IAM with LoginRadius.
Best Practices for Effective User Management
For robust B2B security, follow these authentication best practices:
-
Use Just-In-Time Provisioning : Avoid idle accounts by provisioning only when needed. This improves security hygiene and resource efficiency.
-
Enable Federation + MFA : Integrate partner IdPs using SAML/OIDC and enforce MFA based on behavior or role sensitivity.
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) : Assign roles that reflect real-world access needs and avoid over-provisioning.
-
Self-Service Options : Empower partners to manage their own users, reducing dependence on internal IT.
-
Lifecycle Management : Implement automated deactivation, access recertification, and activity audits for compliance and control.
For instance, a global consulting firm onboards dozens of analysts via SAML SSO and JIT provisioning. LoginRadius tracks login activity, ensures MFA compliance, and offboards inactive users.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the B2B vs B2C authentication landscape is no longer optional—it's essential to delivering secure, scalable, and personalized digital experiences.
B2B demands organization-level access control, delegated admin, and federation. B2C requires smooth logins, strong UX, and adaptive security.
Choosing the right IAM solution determines how well your platform scales, secures data, and serves users across geographies.
Ready to transform how you authenticate your users and partners? Explore LoginRadius Partner IAM or dive into our developer docs to start building secure, branded, and governed authentication workflows today.
FAQs
Can a single IAM platform manage both B2B and B2C?
Yes. LoginRadius is a unified platform supporting both models with flexible architecture, allowing organizations to create tailored login flows per audience.
How does SSO differ in B2B vs B2C environments?
In B2C, SSO usually means social or cross-app login. In B2B , it involves federated SAML/OIDC logins with external IdPs, enabling organization-level access.
What’s the role of data residency in user management?
Data residency ensures compliance with local regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). LoginRadius offers geo-based hosting and tenant-based data boundaries.