Introduction
In a world where cyber threats are evolving faster than ever, securing data isn’t just a best practice; it’s a fundamental requirement. From phishing attacks to database breaches and credential stuffing, today’s digital systems are constantly under siege. And if you’re building an application that handles user data, even something as simple as a login form, you are part of the security equation.
That’s where encryption, hashing, and salting come in. These aren’t just technical jargon tossed around in security whitepapers. They’re critical layers of defense that determine whether your system will survive an attack or become the next headline.
You’ve probably heard these terms before:
-
Encryption keeps data confidential as it moves across networks or sits in storage.
-
Hashing secures data like passwords in a one-way, tamper-proof format.
-
Salting adds a layer of randomness to make password hashes unbreakable by attackers using rainbow tables.
Yet despite their importance, they’re often misunderstood or worse, misused. So, what exactly are encryption, hashing, and salting? How do they work behind the scenes? What’s the real difference between encryption and hashing? And most importantly: how can developers like you use these techniques to keep users safe without adding unnecessary complexity?
This blog breaks it all down with practical insights and real-world examples. We'll explore: What is encryption?, What is hashing, and what is a hash?, What is salting? The difference between encryption and hashing, and how LoginRadius applies these principles to provide secure authentication for modern identity systems
Whether you're a backend engineer securing authentication flows, a DevSecOps pro designing defense-in-depth strategies, or a curious developer wanting to build more responsibly, this blog will give you the clarity and confidence to implement encryption, hashing, and salting the right way.
What is Encryption?
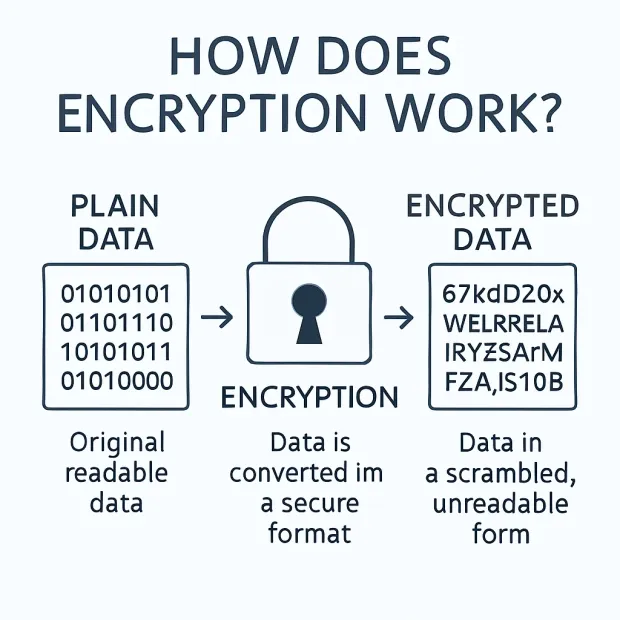
Encryption is the process of transforming readable data, known as plaintext, into an unreadable format called ciphertext, using a mathematical algorithm and an encryption key. This ensures that only authorized users can access the original content.
The primary goal of encryption is data confidentiality. Whether you're storing credit card numbers in a database, sending login credentials across a public network, or sharing documents via email, encryption helps prevent unauthorized access, even if the data is intercepted or stolen.
Think of it as placing your data in a vault with a lock. Unless someone has the correct key, they can’t open the vault, and the contents remain safe. Encryption acts as a digital lock that protects sensitive information across its lifecycle at rest, in transit, or even during processing.
Today, encryption is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity. It’s built into everything from HTTPS and VPNs to disk storage and messaging apps like WhatsApp and Signal.

How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption works through a series of mathematical functions called encryption algorithms that scramble data using a secret key. To restore the original message, the same or a corresponding key is used for decryption.
Let’s break it down:
-
Plaintext Input: The data you want to protect, like "MySecretPassword".
-
Encryption Algorithm + Key: The algorithm (e.g., AES or RSA) takes this input and transforms it into ciphertext, using a key as input.
-
Ciphertext Output: The result is unintelligible gibberish to anyone who doesn’t have the key. To decrypt the data and return it to plaintext, you need the corresponding decryption key.
Also, it's important to understand the key management implications between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric systems require secure key sharing between both parties, which can be challenging at scale. Asymmetric encryption avoids this by separating the encryption and decryption keys, making it better suited for open communication channels like HTTPS.
Both encryption and hashing have critical roles in cryptography. One key difference is that encryption is reversible; authorized users can decrypt data with a key, while hashing is irreversible and designed for verification. Encryption ensures only intended recipients can access the data (e.g., confidential file transfers), while hashing helps validate data or user identity without revealing the original input.
Real-World Analogy:
Imagine writing a note and placing it in a box locked with a special key. You give the box to someone, but not the key. No matter who intercepts the box, it’s useless to them unless they also have the key. That’s exactly how encryption keeps data secure.
In programming terms, encryption libraries (like OpenSSL or libsodium) take care of the math. As a developer, your job is to choose the right type of encryption, manage the keys safely, and apply best practices.
Types of Encryption
Encryption isn’t one-size-fits-all. It’s generally divided into two main categories, based on how keys are used: symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
1. Symmetric Encryption
In symmetric encryption, the same secret key is used for both encrypting and decrypting the data. This makes the process fast and efficient, especially useful when encrypting large amounts of data, such as entire files or databases.
However, the challenge lies in securely sharing the key between parties. If an attacker gets access to the key, they can decrypt everything.
Key Management Note: When using symmetric encryption, managing the encryption key securely is critical. Always use secure key vaults (e.g., AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault) and rotate keys periodically to reduce risk exposure from a compromised key.
Pro tip: Store keys in cloud KMS or HSM, not in app code or configuration files. Use secrets managers (like AWS Secrets Manager or Vault) for runtime access.
Examples of Symmetric Encryption Algorithms:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): The most widely used standard today. AES-256, in particular, offers very strong encryption and is used by governments and financial institutions. While AES is not a hashing algorithm, developers often refer to terms like
AES hashingorAES hashwhen using it alongside hashing techniques for layered encryption workflows. It's important to differentiate these contexts from true one-way hash functions.
While AES is trusted globally (even for classified U.S. government data), it relies heavily on secure key management. Its block size is fixed at 128 bits, and it supports key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits, making brute-force attacks practically infeasible with current computing capabilities.
-
DES (Data Encryption Standard): An early block cipher using a 56-bit key to encrypt 64-bit blocks of data. Once widely used, DES is now considered insecure due to its vulnerability to brute-force attacks.
-
3DES (Triple DES): A successor to DES, this algorithm applies DES three times to each data block with either two or three keys. While more secure than DES, it is slower and vulnerable to meet-in-the-middle attacks.
DES is now considered insecure due to its short key length and susceptibility to brute-force attacks. 3DES improved security by running DES three times with different keys, but it remains vulnerable to meet-in-the-middle attacks and has been deprecated by most modern systems.
Block Ciphers Are Used with Symmetric Key Encryption:
Stream vs Block Ciphers
-
Stream Cipher: Encrypts data one bit or byte at a time and is generally faster, suitable for lightweight environments (e.g., RC4).
-
Block Cipher: Encrypts data in fixed-size blocks (e.g., 128 bits). Examples include AES and DES. More common in modern cryptography due to structure and flexibility.
Common Encryption Algorithms:
-
ChaCha20: Alternative to AES in resource-constrained environments
-
Blowfish: A fast, symmetric block cipher with variable-length keys (32 to 448 bits). Though secure, its 64-bit block size makes it susceptible to birthday attacks in modern applications.
-
Twofish: A modern symmetric key block cipher and a finalist in the AES competition. It operates on 128-bit blocks and supports key sizes up to 256 bits. It is free to use and remains unbroken.
-
Skipjack: Developed by the NSA, Skipjack is a symmetric key algorithm using 64-bit blocks and an 80-bit key. It was originally designed for voice encryption but is rarely used today due to limited key size.
Use Cases:
- Disk encryption: Full-disk encryption tools like BitLocker and FileVault use AES.
Internal application communication: Encrypting traffic between microservices or internal APIs.
- Database encryption: Protecting data at rest, especially in compliance-heavy industries like finance and healthcare.
Note: AES is sometimes paired with secure hashing functions for advanced cryptographic protocols, such as in authenticated encryption where encryption and hashing work in tandem.
2. Asymmetric Encryption
Also known as public-key encryption, asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys: a public key to encrypt data and a private key to decrypt it. The keys are mathematically linked, but it’s computationally infeasible to derive the private key from the public one.
This model solves the key-sharing problem because you can safely share your public key with anyone while keeping your private key secure.
Examples of Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms:
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): A widely used algorithm that underpins much of today’s secure communication.
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): A more efficient alternative to RSA, offering equivalent security with smaller key sizes—great for mobile and IoT environments.
Use Cases:
SSL/TLS for HTTPS: Your browser encrypts data using the website's public key, and only the site can decrypt it with its private key.
Email encryption: Tools like PGP and S/MIME use public/private key pairs to secure messages.
Digital signatures: Asymmetric encryption ensures message authenticity and integrity.
LoginRadius implements encryption in two key ways:
- Encryption in Transit:
-
All data is transported using HTTPS with TLS 1.2
-
Uses industry-standard ciphers, including TLS_ECDHE_RSA and TLS_RSA variants
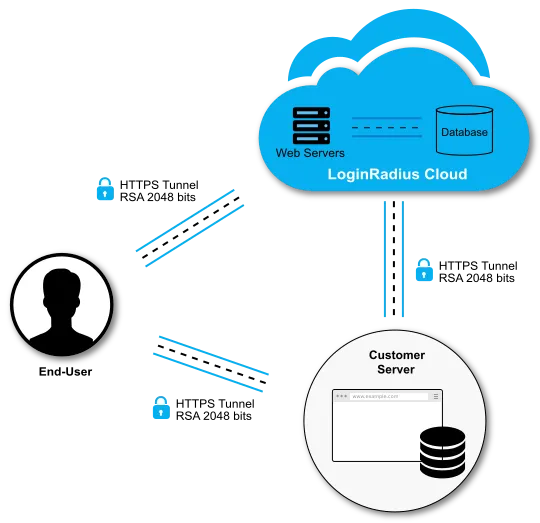
- Encryption at Rest:
-
Data stored by LoginRadius is encrypted using AES encryption
-
Requires a secret key for both encryption and decryption
-
Customer third-party provider credentials are encrypted via Azure Key Vault
It's important to note that while encryption is reversible (can be decrypted), this differs from hashing, which is used for passwords and cannot be reversed.
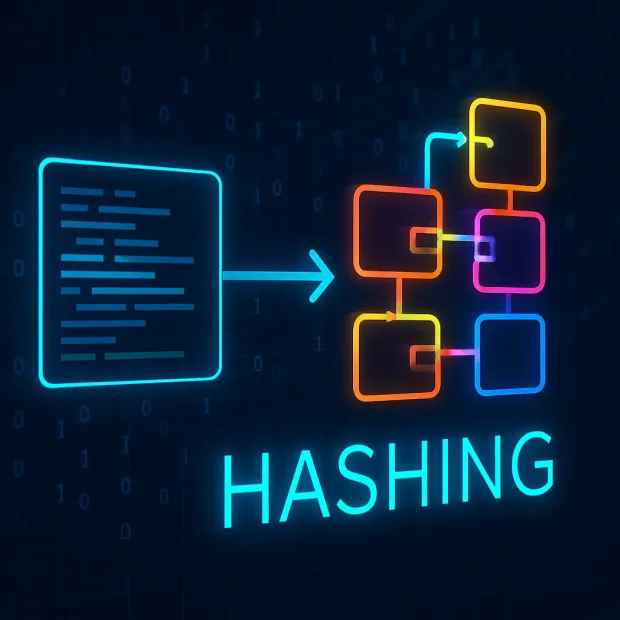
What is Hashing?
Hashing is a process that takes an input of any size text, file, or binary and transforms it into a fixed-length string, usually represented in hexadecimal. This transformation is done using a hashing algorithm, which applies a deterministic, one-way mathematical function. That means the same input will always result in the same hash, but you can’t reverse the hash to get the original input.
Unlike encryption, which is reversible (given the right key), hashing is designed to be irreversible. This property makes hashing ideal for verifying data integrity or securely storing sensitive values like passwords without needing to retrieve the original data.
If encryption is like locking something in a box, hashing is like shredding it beyond reconstruction—but in a reproducible way.
In cybersecurity, hashing is used to:
-
Verify data hasn’t been changed (e.g., file or message integrity)
-
Store sensitive values securely, especially passwords
-
Speed up lookups and comparisons, like in caching systems or database indexing
What is a Hash?
A hash is the fixed-length output generated by a hashing algorithm when applied to input data. Think of it as the digital fingerprint of your data. Just like no two people have the same fingerprint, no two distinct inputs should ideally have the same hash output—a property called collision resistance.
Here’s a quick hash encryption example:
Input: LoginRadius
Output (SHA-256):
f769c9d2b1f83b9ebc5fa57f67ffb85a5407299e9fc1d62d154af273b8db43c2
(output truncated for readability)
Now, try changing just one character:
Input: loginRadius
Output (SHA-256):
4aa8fa738302f8ad3f56c8c0e3648d6ea3b16bc46f7957a2a4278b7ac82de4c6
Completely different output.
This is known as the avalanche effect, a small change in input causes a dramatic and unpredictable change in the hash. It’s a vital security feature that helps ensure hashes can't be reverse-engineered or guessed.
This concept of irreversibility makes hashing ideal for authentication, where you don’t need the original data—just confirmation that two hashes match. For example, during login, the system doesn’t decrypt your password—it simply hashes your input and compares it with the stored hash.
What is Hash Encryption Decryption
The term "hash encryption and decryption" is actually a misconception because hashing and encryption are fundamentally different processes in cryptography. Let’s clarify:
Hashing
-
One-way function: You take an input (like a password) and generate a fixed-length output called a hash.
-
Irreversible: You cannot decrypt or reverse a hash to get the original input.
-
Use case: Secure password storage, data integrity verification, digital signatures.
-
Examples: SHA-256, bcrypt, Argon2
Note - So, there is no such thing as "hash decryption". Once something is hashed, it can't be undone.
Encryption
-
Two-way process: You encrypt data using a key to make it unreadable (ciphertext), and later decrypt it using a key to recover the original data.
-
Reversible: Provided you have the correct key.
-
Use case: Protecting data in transit or at rest (e.g., emails, files, API traffic).
-
Examples: AES (symmetric), RSA (asymmetric)
Some tools or APIs might label functions as hash encrypt, hash code encryption, or encrypted hash, which can create confusion. Always refer to the documentation to confirm whether they mean a reversible encryption process or one-way hashing.
What People Often Mean by “Hash Encryption and Decryption”
People sometimes use “hash encryption” when they actually mean:
-
Hashing a password (e.g., using bcrypt)
-
Encrypting a value (e.g., using AES)
-
Mistakenly thinking hashes can be reversed like encrypted data
If you're dealing with passwords: hash + salt (not encrypt).
If you're dealing with sensitive readable data: encrypt + decrypt (not hash).
Common Hashing Algorithms
There are many types of hash encryption algorithms, and while some like MD5 and SHA-1 are outdated, others like SHA-256, bcrypt, and Argon2 are widely used. Choosing the right hash encryptor can significantly improve security depending on the context of usage, such as login flows or secure file integrity checks.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common hashing algorithms and how they’re typically used:
1. SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit)
-
Part of the SHA-2 family, standardized by NIST
-
Outputs a 256-bit (64-character) hash
-
Extremely secure and widely used in digital certificates, blockchain, and HTTPS
-
Fast and efficient, but not ideal for password storage on its own due to speed
2. bcrypt
-
Built specifically for password hashing
-
Includes built-in salting and a configurable cost factor (work factor) that slows down hashing, making brute-force attacks harder
-
Automatically handles password salt and hash format storage
-
Used in LoginRadius for secure password hashing
3. scrypt
-
Like bcrypt, but adds memory-hard functions to make it resistant to GPU and ASIC attacks.
-
Ideal when attackers might use high-performance hardware
-
Slightly more resource-intensive than bcrypt
4. Argon2
-
The winner of the Password Hashing Competition (PHC)
-
Designed to resist both GPU-based and side-channel attacks
-
Offers configurable memory usage, time cost, and parallelism
-
Ideal for modern systems that demand scalable, memory-hard password hashing
-
While not yet as widely adopted as bcrypt, it is recommended for new applications by OWASP
Argon2 Configuration Tips:
Argon2’s strength lies in its tunable parameters. OWASP recommends:
-
memory_cost: 64MB or more
-
time_cost: 2 iterations or more
-
parallelism: based on number of threads/CPUs
These help balance security and performance for modern applications.
5. MD5 and SHA-1
-
Once popular, now considered cryptographically broken due to proven collisions.
-
Should never be used in password storage or secure applications
-
Only suitable for non-security use cases like basic checksum verification
LoginRadius Best Practices
-
Using bcrypt with a strong cost factor to hash passwords
-
Avoiding raw SHA-2, MD5, or SHA-1 for password storage
-
Combining hashing with salting and secure password policies for layered defense
We also support newer and more robust algorithms such as Argon2i and Argon2id, ideal for modern systems that need scalable, memory-hard password hashing. This ensures even better protection against brute-force attacks, especially in cloud-based identity environments.
In password security, hashing refers to converting plaintext passwords into a fixed-length string of characters using a cryptographic hash function. Hashing has two critical properties:
-
Irreversibility: Once a password is hashed, it cannot be reverted to its original form, even if the hashing algorithm is known.
-
Collision Resistance: No two different inputs should produce the same hashed output. This ensures uniqueness and protects against duplication attacks.
LoginRadius supports multiple hashing algorithms, including:
-
Argon2i
-
Argon2id
-
PBKDF2
-
SHA-1
-
SHA-256
-
SHA-512
-
MD5
-
And several others
The platform uses these cryptographic hash algorithms to store sensitive data such as passwords and security questions in the cloud database, providing the highest level of security for critical data points.
When implementing hashing, LoginRadius allows for different configurations:
-
Different salt types (Universal or User per password)
-
Various salt attachment methods (None, Append, or Prepend)
-
Configurable number of iterations for certain algorithms
This ensures that stored information can only be matched and cannot be decrypted. Explore LoginRadius Password Hashing Guide to learn more about hashing and its implementation.
Other Secure Hashing Techniques
- HMAC-SHA1 & HMAC-SHA256: Hash-based Message Authentication Codes use a combination of a cryptographic hash (like SHA-1 or SHA-256) and a secret key to verify message integrity and authenticity.
HMAC-SHA1 and HMAC-SHA256 offer message integrity and authenticity checks using a shared secret key and hashing algorithm. However, both are theoretically vulnerable to length extension attacks, and the shared key must be securely managed to avoid brute-force discovery.
-
PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2): A key derivation algorithm used for securely hashing passwords. It introduces multiple iterations and uses a salt to protect against brute-force and rainbow table attacks. Slower by design, it increases the computational effort needed to crack a password.
-
Argon2 Encryption: While Argon2 is technically not an encryption algorithm but a password hashing algorithm, it's worth noting due to its memory-hardness and strong resistance against side-channel and GPU attacks. Argon2 offers multiple variants like Argon2d, Argon2i, and Argon2id, suitable for password storage and key derivation.
Use Cases for Hashing
Hashing isn’t just a cryptographic curiosity—it’s used every day across software, networking, and cybersecurity applications.
Here are some of the most common use cases:
- Password Storage- When a user creates a password, the system doesn’t store the actual password. Instead, it stores a hash of it. When the user logs in again, the password they enter is hashed and compared to the stored hash. This means even if your database is compromised, the original passwords are not directly exposed, especially when combined with salting.
With LoginRadius, all passwords are hashed using bcrypt and salted individually before being stored.
- Data Integrity - Hashing is often used to ensure that a file, message, or block of data hasn’t been altered in transit. By comparing the original hash to a newly generated hash, you can quickly detect tampering.
Use cases include:
-
Software downloads (e.g., file checksums)
-
Blockchain transactions
-
API message verification
- Caching and Indexing- In applications where performance matters, hashing provides a quick way to compare or look up data.
Examples:
-
Storing hashed cache keys
-
Hash-based database indexes
-
Deduplicating data
Hashing enables fast comparisons without revealing or storing the original data.
When It Comes to Passwords: Hashing Alone Isn’t Enough
Hashing by itself is not sufficient to secure passwords. Why? Because if two users choose the same password, they will have the same hash, making it easy for attackers to identify and target common passwords using precomputed rainbow tables.
That’s why we don’t just hash passwords—we salt them. Let’s explore how salting solves this problem in the next section.
What is Salting?
Salting is the process of appending a random, unique string—called a salt—to a password before hashing it. This adds a layer of variability and uniqueness to every password hash, even if multiple users choose the same password.
Let’s say two users both choose the password mypassword. Without salting, both would produce the same hash, which becomes a serious vulnerability. However, with salting, each user’s password is hashed differently because the added salt changes the hash output.
The salt doesn’t need to be secret, but it must be unique per user and randomly generated. This ensures that even if two passwords are the same, their resulting hashes are entirely different.
In essence, salting disarms attackers who rely on large precomputed databases of common passwords and their corresponding hashes, known as rainbow tables.

Why is Password Salting Important?
Without salting, attackers can take a list of commonly used passwords, hash them once, and store them in massive rainbow tables. When they gain access to a password database, they simply compare the stored hashes with their table and recover the passwords in seconds.
This becomes especially dangerous when users use weak or common passwords like 123456, password, or qwerty. If two users have the same password, and hashing is applied without a salt, their stored hashes will match, revealing patterns and making brute-force attacks more efficient.
By introducing a unique salt per user, every password hash becomes unpredictable. Even if two users choose the same password:
-
Their salts are different
-
The input to the hash function is different
-
The resulting hash is completely different
This means attackers would need to generate rainbow tables for every possible salt—an impractical and computationally expensive task.
For even stronger security, developers can consider using peppering—an additional static, secret value (stored separately from the database) added to the password before hashing. Combined with salting, peppering adds another hurdle for attackers trying to reverse-engineer passwords, even if they compromise the database.
Example of Peppering:
A pepper is a secret key stored in application code or a secure environment variable (never in the database).
For example:
1pepper = os.environ.get("PEPPER_KEY")
2hash_input = user_password + user_salt + pepperHow Password Salting Works?
Let’s break down the process of how salting strengthens password security in a practical, step-by-step way:
-
User sets password: mypassword
-
Generate a random salt: 9f38a8 (the salt can be longer and is usually securely generated using a cryptographic random number generator)
-
Combine password and salt: mypassword9f38a8
-
Hash the salted password: Apply a secure hashing algorithm like bcrypt, scrypt, or Argon2
Result: bcrypt(mypassword9f38a8) → $2b$12$9f38a8$2f23...
- Store the hash (and sometimes the salt) in the database: Many algorithms like bcrypt store the salt within the resulting hash string. Others store the salt in a separate database field.
At LoginRadius, this entire workflow is abstracted and securely handled for you, ensuring passwords are both salted and hashed before being stored, following OWASP and NIST best practices.
Salting + Hashing = Safe Password Storage
It’s important to understand that salting alone doesn’t secure a password, and hashing alone doesn’t prevent duplicate hashes.
But when you combine them:
-
Hashing obfuscates the original password
-
Salting ensures uniqueness and resists precomputed attacks
This makes brute-force attacks, dictionary attacks, and rainbow table lookups significantly harder to execute, even for powerful adversaries.
At LoginRadius:
-
We never store plain-text passwords
-
Every password is hashed using bcrypt with a unique, per-user salt
-
Hashing is done at registration, password change, and login verification time
-
We comply with modern password security standards, as outlined in our cryptographic hashing documentation
This system helps our customers maintain security and compliance while reducing the risk of data breaches.
LoginRadius supports two types of salting:
-
System-wide salt: A fixed string applied uniformly to all passwords before hashing. This provides a consistent method for securing stored credentials.
-
Per-password salt (Recommended): A unique salt is generated for each password and stored alongside the hash. This is the recommended industry standard since even if two users choose the same password, their hashed values will differ.
LoginRadius provides various password hashing options and allows customers to set a random salt for each password to increase security.
The salt can be:
-
Universal (system-wide)
-
User per password (unique per user)
-
Attached in different ways (append, prepend, or none)
Encrypt vs Hash: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the encryption and hashing differences is critical when designing a secure application. While they may seem similar on the surface (they both transform data), their goals, mechanisms, and use cases are quite different.
| Feature | Encryption | Hashing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Confidentiality (keep data secret) | Data integrity and verification |
| Direction | Reversible (can decrypt) | One-way (irreversible) |
| Key Required? | Yes (private/public or shared key) | No |
| Use Case Examples | HTTPS, file encryption, secure messaging | Password storage, file integrity, digital signatures |
| Output Consistency | Varies with the key used | Always the same for the same input (unless salted) |
| Security Focus | Prevent unauthorized reading of data | Prevent unauthorized tampering or forgery |
Use encryption when you need to protect data confidentiality. Use hashing when you need a tamper-proof digital fingerprint for data verification.
Encryption vs Hashing in Real Life
Let’s look at some real-world use cases to understand when to choose encryption vs hashing.
Use Encryption When:
-
You need to retrieve the original data later
-
Data is sensitive in transit or at rest
-
You want to secure things like:
- Emails
- Payment card numbers
- Personal user data
- Database fields that need to be decrypted later (e.g., address or SSNs)
Use Hashing When:
-
You only need to verify the integrity or authenticity of data
-
You want to compare values without knowing the original input
-
You are storing user passwords
-
You are checking the file or message integrity
For example, a website stores the hash of your password, not the password itself. When you log in, your input is hashed again and matched to the stored hash, so there is no need to decrypt anything.
Hashing protects the system, even if the database is breached.
Hashing vs Encryption vs Salting: When to Use Each
Here’s a quick-reference table to help you understand when and why to use each technique:
| Technique | Used when |
|---|---|
| Encryption | You need to secure readable data in storage or during transmission |
| Hashing | You need to verify, compare, or obfuscate data irreversibly |
| Salting | You’re storing user-generated passwords and want to prevent reuse or attacks |
In most secure systems, you’ll use a combination of these:
-
HTTPS uses encryption (TLS) to secure data in transit
-
Passwords are hashed (using bcrypt) and salted to ensure security at rest
-
Tokens, such as JWTs, are often hashed or encrypted depending on the sensitivity of their claims
-
File uploads may be hashed (e.g., with SHA-256) to ensure no tampering occurred in transit
In LoginRadius, this layered security model is baked into the platform, so developers can focus on building while we handle the heavy lifting of identity and data protection.
How LoginRadius Implements Secure Password Management
At LoginRadius, user trust is non-negotiable, and that starts with protecting user credentials. Our password management system is built on modern, battle-tested cryptographic techniques that defend against today's most common and sophisticated attacks.
We don't just hash passwords—we architect an entire security lifecycle that protects them from end to end.
Here’s how LoginRadius ensures enterprise-grade password security:
1. Unique Salt for Every Password
Each time a user creates or updates a password, our system generates a unique cryptographic salt. This salt is appended to the password before hashing, ensuring that even identical passwords yield completely different hashes.
-
Prevents rainbow tables and precomputed attacks
-
Obfuscates patterns in user behavior (e.g., reused passwords)
2. Bcrypt for Hashing with Built-In Work Factor
We use bcrypt, a proven hashing algorithm that includes salting and a configurable cost factor to control computational time. Unlike SHA-2 (which is fast by design), bcrypt is intentionally slow, making brute-force attacks prohibitively expensive for attackers.
-
Automatic salting
-
Adaptive cost factor (can be increased as computing power improves)
-
Defends against GPU-accelerated brute-force attacks
3. Compliance with OWASP Best Practices
Our entire password management flow adheres to the OWASP Password Storage Cheat Sheet. This includes:
-
Rejecting weak and commonly used passwords
-
Enforcing strong entropy requirements
-
Supporting secure password reset flows
-
Protecting against timing attacks and injection vectors
4. NIST-Approved Cryptographic Standards
All hashing encryption mechanisms in LoginRadius align with recommendations from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). We follow guidelines such as:
-
Using only FIPS 140-2 validated algorithms
-
Storing only hashed, salted passwords—never plaintext
-
Ensuring secure key management practices, where applicable
5. Transparent Documentation and Developer Control
Our platform is designed to be developer-first, meaning:
-
You can configure hashing policies via the LoginRadius dashboard
-
Access comprehensive documentation for hashing, password strength policies, and reset workflows
-
Integrate seamlessly with your existing app stack using our SDKs and APIs
In short, LoginRadius provides not just tools, but a framework for secure password storage that scales with your application and your user base.
While often confused, encoding and encryption serve different purposes. Encoding transforms data into a new format (like Base64) so it can be safely transmitted and interpreted by systems. It is not secure, as anyone can decode it with a known algorithm. Encryption, on the other hand, transforms data into an unreadable format using a key and is meant to protect confidentiality—only users with the right key can decrypt it.
Final Thought
Security isn’t just about picking the right algorithm; it’s about knowing how and when to use encryption, hashing, and salting together to build layered defenses. Whether you're building a high-scale consumer app, a SaaS platform, or an enterprise portal, understanding these concepts will help you make smarter architectural decisions—and protect your users from real-world threats.
At LoginRadius, we’ve done the hard work for you. Our platform comes with secure-by-default configurations, pre-implemented hashing + salting, support for Argon2 and bcrypt, and developer tools that make implementation easy without compromising security. Whether you're working with traditional username-password authentication or advanced identity flows, LoginRadius helps you adopt best-in-class password management practices out of the box.
Want to learn more or explore how LoginRadius can simplify identity and password security for your app? Contact our team.
FAQs
What is password salting?
Password salting adds a unique, random string to passwords before hashing. It ensures even identical passwords generate different hashes, protecting against attacks.
What is the difference between hashing and encryption?
Hashing is irreversible and used for verification, while encryption is reversible and used for confidentiality. Both serve distinct roles in data security.
Is encryption more secure than hashing?
Not necessarily, each serves a different purpose. Encryption protects data privacy, while hashing ensures integrity and secure password storage.
Can encryption be made irreversible?
Technically, you can choose to discard the decryption key, making encrypted data unrecoverable. In that scenario irreversible encryption is practical, but It's not due to the algorithm, it's because you made it so by design (e.g., data destruction or one-way encryption)
What is a hash cipher?
A hash cipher isn’t a formal cryptographic term, but people often use it to describe hash functions or one-way ciphers used for securing passwords or data integrity. Unlike traditional ciphers, hashes are not reversible.


